Market Overview
The Israel military marine vessel engines market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady procurement cycles and platform modernization across naval fleets. Recent performance indicates annual spending levels fluctuating between USD ~ million and USD ~ million, driven by propulsion upgrades, lifecycle replacements, and integration of higher power-density systems. Demand remains anchored in defense allocations supporting surface combatants, patrol craft, and special operations vessels, with procurement volumes remaining stable despite long certification and integration timelines.
The market is geographically concentrated around major naval bases and defense industrial clusters along the Mediterranean coast and the southern maritime corridor. These areas benefit from dense ecosystems of shipyards, maintenance hubs, and defense electronics integrators that support propulsion system deployment. Demand concentration is further reinforced by operational readiness requirements, proximity to strategic waterways, and mature defense procurement frameworks that enable sustained engine replacement and upgrade programs across active and reserve fleets.
Market Segmentation
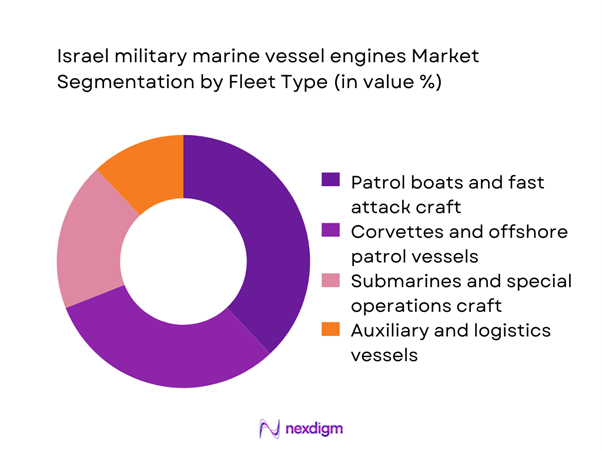
By Fleet Type
Patrol boats and fast attack craft dominate engine demand due to their high deployment frequency, rapid fleet turnover, and intensive operational cycles. These vessels require propulsion systems optimized for acceleration, endurance, and reliability under continuous coastal security missions. Corvettes and offshore patrol vessels follow closely, supported by long-term fleet modernization initiatives that prioritize power density and reduced acoustic signatures. Submarines and special operations craft represent niche but high-value segments, where engine performance is closely tied to stealth, redundancy, and survivability standards, reinforcing sustained investment in advanced propulsion architectures.
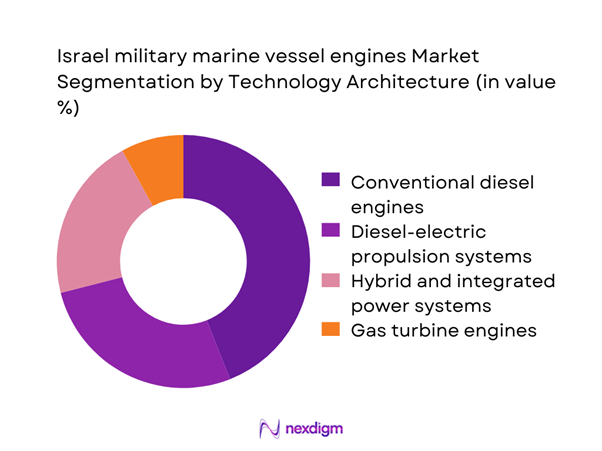
By Technology Architecture
Conventional diesel engines continue to anchor the market due to proven reliability, established maintenance infrastructure, and compatibility with existing fleets. However, diesel-electric and hybrid propulsion systems are gaining momentum as operational doctrines shift toward lower acoustic signatures and improved fuel efficiency. Integrated power systems are increasingly favored for next-generation vessels, enabling flexible power distribution across propulsion, onboard systems, and mission equipment. Gas turbine engines remain limited to select high-speed platforms, where acceleration and peak output outweigh lifecycle efficiency considerations, maintaining a specialized but strategic role.
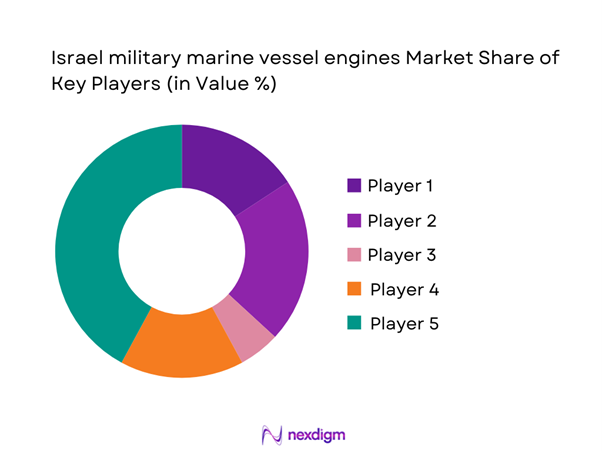
Competitive Landscape
The Israel military marine vessel engines market is moderately concentrated, with a small group of global propulsion specialists supplying most high-performance and mission-critical systems. Entry barriers remain high due to certification complexity, long procurement cycles, and stringent defense compliance requirements, favoring established players with proven naval track records.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Rolls-Royce Power Systems | 1915 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MAN Energy Solutions | 1758 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Wärtsilä | 1834 | Finland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Caterpillar Marine | 1925 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Cummins Marine | 1919 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel military marine vessel engines Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of Israel Navy surface combatant fleet
Ongoing modernization programs are driving sustained demand for new-generation propulsion systems across corvettes, patrol vessels, and multi-role platforms. Recent procurement cycles have supported engine upgrades valued at USD ~ million annually, reflecting priorities around higher power density, reduced fuel consumption, and improved reliability. Fleet renewal initiatives are aligned with operational requirements for extended patrol durations and rapid response missions, increasing engine utilization rates across ~ vessels. As legacy systems approach end-of-life thresholds, replacement volumes are projected to remain stable, supported by consistent defense allocations of USD ~ million toward propulsion and powertrain modernization.
Rising maritime security threats in Eastern Mediterranean and Red Sea
Escalating maritime security risks have increased operational tempo for naval and coastal defense fleets, resulting in higher engine utilization and accelerated maintenance cycles. Patrol deployments now average ~ missions annually per vessel class, driving greater demand for robust propulsion platforms capable of sustained high-speed operations. Defense planners have allocated USD ~ million toward readiness programs focused on engine reliability and redundancy, ensuring rapid deployment capabilities. The need to secure strategic shipping lanes and offshore assets has further expanded the active fleet footprint to ~ vessels, reinforcing long-term demand for high-performance marine engines.
Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle cost of military-grade engines
Military-spec marine engines carry acquisition costs that can exceed USD ~ million per unit, placing sustained pressure on procurement budgets. Beyond initial investment, lifecycle expenses linked to maintenance, spares, and overhauls account for cumulative outlays of USD ~ million across a typical service period. These financial demands complicate fleet expansion and slow replacement cycles, especially for auxiliary and secondary vessels. Budget planners must balance propulsion upgrades against competing priorities such as sensors and weapons systems, limiting the pace of engine modernization across ~ active platforms.
Dependence on foreign suppliers and export control restrictions
A significant share of high-performance propulsion systems is sourced from overseas manufacturers, exposing procurement schedules to export licensing timelines and geopolitical sensitivities. Delays affecting ~ engine deliveries annually have created operational bottlenecks, particularly for time-sensitive fleet upgrades. Compliance with international trade controls adds administrative layers that extend lead times and increase program management costs by USD ~ million. This dependency also constrains customization flexibility, as modifications often require additional approvals, affecting integration schedules across ~ vessels undergoing refit.
Opportunities
Fleet expansion programs for offshore patrol vessels and corvettes
Planned expansion of offshore patrol and corvette fleets presents a strong growth avenue for propulsion suppliers, with new-build programs projected to support engine demand worth USD ~ million over upcoming procurement cycles. These platforms require mid-to-high power output systems optimized for endurance missions, creating opportunities for standardized engine families across ~ vessels. Government allocations for maritime security have prioritized multi-role vessels, ensuring steady procurement volumes that can sustain long-term service and maintenance contracts valued at USD ~ million.
Adoption of hybrid propulsion for stealth and fuel efficiency
Hybrid propulsion systems are gaining traction as naval planners prioritize lower acoustic signatures and reduced fuel consumption. Pilot programs integrating hybrid drives across ~ vessels have demonstrated operational savings of USD ~ million in fuel and maintenance expenditures. These systems also support silent running modes critical for surveillance and special operations missions, increasing their strategic value. As performance benchmarks improve, broader fleet adoption is expected, opening pathways for suppliers specializing in integrated power management and energy storage solutions.
Future Outlook
The Israel military marine vessel engines market is expected to remain resilient through the next decade, supported by consistent naval modernization, heightened maritime security priorities, and gradual adoption of advanced propulsion technologies. Fleet expansion, combined with retrofit programs, will sustain demand across both conventional and hybrid engine platforms. As regulatory and operational requirements evolve, suppliers that align with integrated power systems and lifecycle support models will be best positioned to capture long-term value in this strategically critical defense segment.
Major Players
- Rolls-Royce Power Systems
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Wärtsilä
- Caterpillar Marine
- Cummins Marine
- GE Aerospace Marine Engines
- Volvo Penta
- Hyundai Heavy Industries Engine & Machinery
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- HD Hyundai Infracore
- Yanmar Marine
- Fairbanks Morse Defense
- Anglo Belgian Corporation
- STX Engine
Key Target Audience
- Israel Ministry of Defense procurement divisions
- Israel Navy logistics and fleet management units
- Government defense acquisition agencies
- Maritime security and coast guard authorities
- Shipyards and naval vessel integrators
- Engine maintenance, repair, and overhaul providers
- Investments and venture capital firms focused on defense technologies
- National regulatory bodies overseeing defense exports and compliance
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study defines critical variables such as fleet size, propulsion replacement cycles, and defense budget allocations influencing engine demand. Operational deployment frequency and maintenance intervals are mapped to assess utilization intensity. Regulatory and certification frameworks are reviewed to understand entry barriers. These variables establish the analytical foundation for market sizing and trend evaluation.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Demand is constructed by mapping vessel classes to propulsion requirements and service lifecycles. Procurement patterns are analyzed to determine baseline replacement and upgrade volumes. Defense spending flows are aligned with engine procurement categories to structure the market framework. This step ensures internal consistency across value and volume perspectives.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Initial market assumptions are tested through structured interactions with naval engineering specialists and defense procurement professionals. Feedback validates technology adoption rates and replacement timelines. Scenario checks are applied to stress-test demand assumptions under varying security and budget conditions. This process refines growth and risk outlooks.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All validated inputs are consolidated into a coherent market narrative covering structure, dynamics, and future direction. Quantitative insights are aligned with qualitative assessments of technology and policy trends. The final output integrates segmentation, competitive context, and strategic implications. This synthesis ensures decision-ready intelligence for stakeholders.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, military marine vessel engine taxonomy across diesel gas turbine and hybrid propulsion systems, market sizing logic by fleet size overhaul cycles and new build programs, revenue attribution across engine sales spares and MRO services, primary interview program with naval operators shipyards and engine OEMs, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational usage pathways across naval and security fleets
- Ecosystem structure and supplier tiers
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of Israel Navy surface combatant fleet
Rising maritime security threats in Eastern Mediterranean and Red Sea
Increased adoption of high-speed patrol and interceptor craft
Lifecycle replacement of aging propulsion systems
Shift toward higher power density and fuel-efficient engines
Expansion of unmanned and special operations vessels - Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle cost of military-grade engines
Dependence on foreign suppliers and export control restrictions
Long certification cycles for naval propulsion systems
Integration complexity with legacy platforms
Maintenance and spare parts availability constraints
Budget volatility in defense procurement - Opportunities
Fleet expansion programs for offshore patrol vessels and corvettes
Adoption of hybrid propulsion for stealth and fuel efficiency
Growth in mid-life upgrade and engine retrofit programs
Increased demand for condition-based maintenance solutions
Collaboration with allied navies for common engine platforms
Local MRO and assembly partnerships in Israel - Trends
Shift toward hybrid-electric and integrated power systems
Growing emphasis on low acoustic signature engines
Digital engine control and predictive maintenance adoption
Standardization of propulsion modules across vessel classes
Increased focus on emissions compliance even in defense fleets
Modularization for faster deployment and maintenance - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Unit Economics, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Patrol boats and fast attack craft
Corvettes and offshore patrol vessels
Submarines and special operations craft
Auxiliary and logistics vessels - By Application (in Value %)
Main propulsion
Auxiliary power generation
Hybrid-electric drive support
Emergency and redundancy systems - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Conventional diesel engines
Gas turbine engines
Diesel-electric propulsion systems
Hybrid and integrated power systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Naval defense forces
Coast guard and maritime security
Special operations units
Border and port security agencies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone engine control systems
Networked ship management systems
Integrated combat system connectivity
Remote diagnostics and condition monitoring - By Region (in Value %)
Northern naval bases
Central Mediterranean operational zones
Southern Red Sea and Eilat sector
Overseas deployment and allied operations
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (engine power output range, fuel efficiency, lifecycle cost, maintenance interval, acoustic signature, compliance certifications, delivery lead time, aftersales support footprint)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Rolls-Royce Power Systems (MTU)
MAN Energy Solutions
Wärtsilä
Caterpillar Marine
Cummins Marine
GE Aerospace Marine Engines
Volvo Penta
Hyundai Heavy Industries Engine & Machinery
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
HD Hyundai Infracore (Doosan Engines)
Yanmar Marine
Fairbanks Morse Defense
Anglo Belgian Corporation (ABC Engines)
STX Engine
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics within defense agencies
- Buying criteria and vendor selection processes
- Budget allocation and long-term maintenance planning
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service and lifecycle support expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Unit Economics, 2026–2035


