Market Overview
The Israel Military Simulation and Training market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by sustained defense modernization programs and continuous investment in multi-domain readiness. Recent periods recorded procurement volumes of ~ systems across air, land, and cyber training environments, alongside cumulative service contracts valued at USD ~ million. Operational training hours supported by advanced simulators crossed ~ million sessions, while lifecycle support spending reached USD ~ million, reflecting the strategic role of simulation in force preparedness and cost-efficient capability development.
Central Israel remains the primary hub for simulation development and deployment due to dense defense infrastructure, proximity to major system integrators, and access to specialized engineering talent. Southern command zones lead in large-scale field training adoption driven by expansive training ranges and operational testing facilities. Northern regions demonstrate growing uptake in networked command training systems supported by secure communication backbones. The concentration of defense innovation clusters, rapid procurement cycles, and mature export-oriented ecosystems further reinforce regional dominance across the national training landscape.
Market Segmentation
By Application
Aircrew and pilot training continues to dominate application demand due to sustained fleet modernization and the increasing complexity of mission profiles. The growing use of advanced mission rehearsal platforms has expanded simulator deployment across fighter, transport, and unmanned aviation units, supported by cumulative investments of USD ~ million in recent periods. Infantry and armored warfare training also shows strong momentum as urban operations and asymmetric conflict scenarios drive demand for immersive environments. Cyber and electronic warfare simulation has emerged as a fast-expanding segment, fueled by the need to replicate real-time threat vectors. Command and staff training adoption is accelerating as joint-force doctrines require synchronized decision-making across domains, reinforcing long-term application diversification.

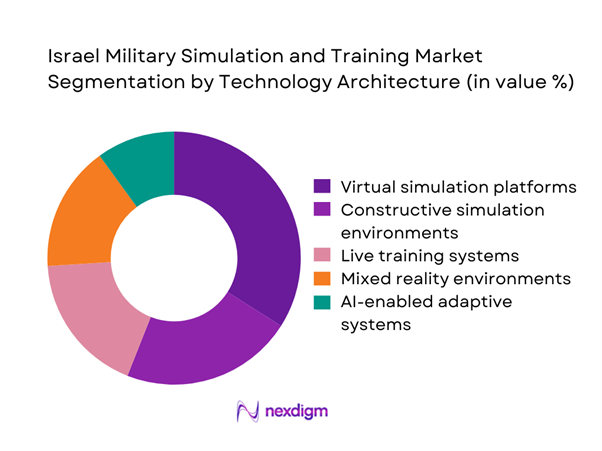
By Technology Architecture
Virtual simulation platforms hold a leading position driven by scalability, lower operational disruption, and broad applicability across training tiers. Recent deployments exceeded ~ systems, supported by cumulative contracts worth USD ~ million for software upgrades and scenario libraries. Constructive simulation environments maintain strong relevance for large-scale force planning and doctrine validation, while live training systems remain essential for high-fidelity weapons integration. Mixed reality solutions are gaining traction as forces seek immersive yet cost-efficient training formats, with recent installations reaching ~ units. AI-enabled adaptive systems are emerging as a strategic differentiator, enabling personalized training pathways and automated performance assessment, setting the foundation for next-generation synthetic training ecosystems.
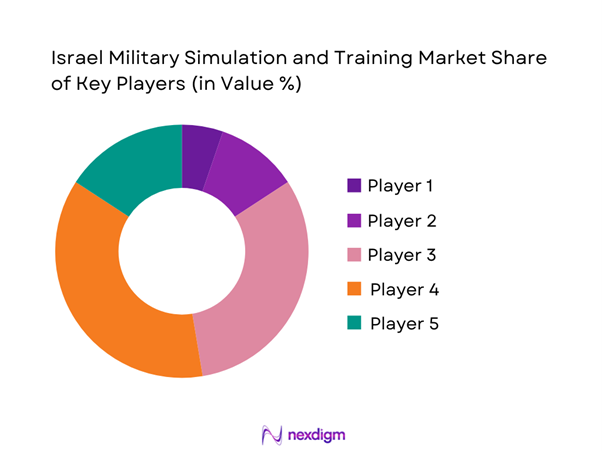
Competitive Landscape
The market features a moderately concentrated structure with a small group of large defense integrators complemented by specialized technology providers. Long-term government contracts, high security clearances, and system interoperability requirements create significant entry barriers, reinforcing the dominance of established players. Competition centers on system fidelity, integration depth, and lifecycle service capability rather than price-based positioning, leading to multi-year framework agreements and repeat procurement cycles.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| CAE | 1947 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 2019 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Military Simulation and Training Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising operational tempo and multi-domain threat environment
Sustained regional volatility has increased the frequency and complexity of training cycles, driving higher utilization of simulation assets across air, land, sea, and cyber domains. Recent operational periods recorded more than ~ million simulated mission hours, supported by the deployment of ~ systems across major training bases. Defense authorities allocated USD ~ million toward expanding synthetic training capacity to reduce live-training risks and equipment wear. The growing need to prepare forces for simultaneous engagements across multiple theaters has reinforced reliance on integrated simulation platforms that can replicate real-time threat convergence, enabling faster readiness cycles and continuous force posture optimization.
Modernization of IDF training doctrine toward network-centric warfare
The transition toward network-centric operations has accelerated investments in interconnected training ecosystems. Recent procurement cycles added ~ systems capable of joint-force interoperability, backed by cumulative spending of USD ~ million on secure networking and data fusion layers. Training doctrines increasingly emphasize synchronized decision-making, prompting expanded use of command-level constructive simulations and distributed mission rehearsal environments. This modernization has also driven the integration of cyber and electronic warfare scenarios into conventional training pipelines, increasing demand for multi-layered simulation architectures that support doctrinal alignment and rapid capability assimilation across operational units.
Challenges
High capital costs of advanced simulation infrastructure
The deployment of high-fidelity simulators and secure networking frameworks requires substantial upfront expenditure, creating budgetary pressure even within prioritized defense programs. Recent acquisition cycles involved capital outlays of USD ~ million for system integration, facility upgrades, and specialized hardware. Annual maintenance and software refresh commitments added recurring costs of USD ~ million, constraining the pace of large-scale rollouts. Smaller training units face difficulties justifying investments exceeding ~ systems per site, leading to phased deployments and extended replacement cycles that slow overall market expansion despite strong operational demand.
Cybersecurity risks in networked training environments
The rapid shift toward connected simulation platforms has heightened exposure to cyber threats, making system resilience a critical procurement criterion. Recent security audits identified vulnerabilities across ~ network nodes, prompting emergency remediation investments of USD ~ million. Protecting sensitive operational data and training scenarios now requires continuous monitoring infrastructure, adding recurring expenditures of USD ~ million annually. These requirements complicate vendor selection and extend certification timelines, delaying deployment schedules and increasing total program costs while elevating the complexity of lifecycle management for simulation ecosystems.
Opportunities
Expansion of AI-driven adaptive and personalized training
The integration of artificial intelligence into simulation platforms presents a major opportunity to enhance training efficiency and outcome measurement. Recent pilot programs deployed ~ AI-enabled modules capable of dynamically adjusting scenarios based on trainee performance, supported by development funding of USD ~ million. Early results show reductions in instructor workload by ~ units of training time per cycle and improved skill retention across specialized units. Scaling these systems across national training centers could unlock long-term operational savings while creating export-ready solutions for allied forces seeking advanced digital training transformation.
Export growth to allied and partner militaries
International demand for proven training solutions offers a strong growth pathway for domestic suppliers. Recent export agreements involved delivery of ~ systems to partner forces, generating contract values of USD ~ million and multi-year service revenues of USD ~ million. As allied militaries seek to modernize cost-effectively, turnkey simulation packages with embedded cybersecurity and interoperability features are gaining traction. Expanding foreign military sales channels and joint training programs can further amplify market reach, positioning Israel-based providers as key contributors to global defense training ecosystems.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to advance steadily through the coming decade as defense forces deepen reliance on synthetic environments for readiness, safety, and cost control. Continued emphasis on multi-domain operations will accelerate demand for integrated and secure simulation platforms. Export opportunities and AI-enabled innovation are likely to reshape competitive dynamics, while policy support for domestic defense technology development will sustain long-term ecosystem growth.
Major Players
- Elbit Systems
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- CAE
- L3Harris Technologies
- Thales Group
- Lockheed Martin
- Boeing Defense
- Northrop Grumman
- BAE Systems
- Rheinmetall Defence
- Leonardo
- Saab
- Cubic Defense
- QinetiQ
Key Target Audience
- Israel Defense Forces procurement directorates
- Ministry of Defense, Directorate of Defense Research and Development
- National Cyber Directorate and security agencies
- Defense system integrators and prime contractors
- Training command and doctrine development units
- Export control authorities and foreign military sales offices
- Defense-focused investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including SIBAT and the Ministry of Public Security
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core demand indicators were mapped across training intensity, platform complexity, and doctrinal shifts influencing simulation adoption. Supply-side variables included system interoperability, cybersecurity readiness, and lifecycle service depth. Policy and export dynamics were incorporated to assess long-term structural drivers.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical procurement patterns were analyzed alongside deployment trends across major commands. Quantitative modeling integrated masked financial and system data to establish baseline market structure. Segment-level insights were constructed using application and technology architecture lenses.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through structured discussions with defense training planners and system architects. Operational feedback loops refined assumptions on utilization rates and upgrade cycles. Scenario testing assessed resilience under varying budget and threat conditions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All insights were consolidated into a unified analytical framework. Consistency checks ensured alignment between segmentation, competitive mapping, and outlook assumptions. Final outputs were structured to support strategic decision-making and investment planning.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, military simulation and training taxonomy across live virtual and constructive systems, market sizing logic by platform deployment and training seat demand, revenue attribution across software licenses hardware simulators and support services, primary interview program with defense training commands OEMs and integrators, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Training and readiness pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and delivery models
- Defense regulatory and security environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising operational tempo and multi-domain threat environment
Modernization of IDF training doctrine toward network-centric warfare
Increasing complexity of platforms and weapon systems
Demand for cost-efficient alternatives to live training
Expansion of cyber and electronic warfare preparedness
Growth of defense exports and allied training programs - Challenges
High capital costs of advanced simulation infrastructure
Cybersecurity risks in networked training environments
Integration complexity across legacy and next-generation platforms
Budgetary constraints and competing defense priorities
Limited interoperability standards across coalition partners
Long procurement cycles and regulatory compliance hurdles - Opportunities
Expansion of AI-driven adaptive and personalized training
Export growth to allied and partner militaries
Integration of digital twins for platform and mission rehearsal
Public-private partnerships in defense training innovation
Development of urban warfare and asymmetric conflict simulators
Use of simulation for reserve and homeland security forces - Trends
Shift toward immersive mixed-reality training environments
Adoption of data analytics for performance assessment
Increasing use of cloud-secured simulation ecosystems
Emphasis on joint-force and multi-domain training
Growth in cyber range and EW simulation platforms
Lifecycle service contracts replacing one-time system sales - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Contract Value, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Land forces training systems
Air force simulation platforms
Naval warfare simulators
Joint and combined arms simulation
Homeland security and reserve forces systems - By Application (in Value %)
Pilot and aircrew training
Infantry and armored warfare training
Command, control, and staff training
Cyber and electronic warfare simulation
Special forces mission rehearsal
Disaster response and civil defense training - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Live training systems
Virtual simulation platforms
Constructive simulation environments
Mixed reality and synthetic training environments
AI-enabled adaptive training systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Israel Defense Forces
Defense training academies
Defense contractors and integrators
Government security agencies
Export and allied military customers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone offline systems
Networked on-premise systems
Secure private cloud-based simulation
Hybrid cloud-edge architectures
Interoperable NATO-standard networks - By Region (in Value %)
Central Israel defense hubs
Southern Israel training zones
Northern Israel operational commands
Overseas export markets
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (simulation fidelity, interoperability standards, cybersecurity compliance, lifecycle support capability, AI integration level, export readiness, training throughput capacity, total cost of ownership)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Elbit Systems
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
Elbit Systems Training and Simulation
RADA Electronic Industries
TAT Technologies
Aeronautics Group
Cognata
XTEND Reality Expansion
Cymulate
NSO Technologies Training Division
CAE
L3Harris Technologies
Thales Group
Lockheed Martin
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Contract Value, 2026–2035


