Market Overview
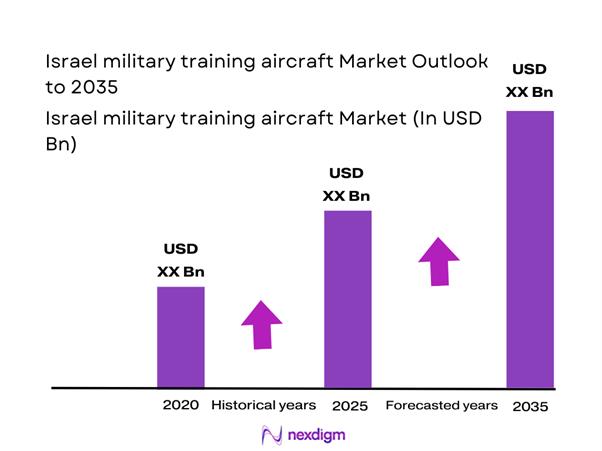
The Israel military training aircraft market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by fleet deployments of ~ aircraft and active training systems exceeding ~ platforms across multiple air bases. In the last two years, procurement and sustainment spending reached nearly USD ~ million annually, driven by upgrades to avionics, embedded simulation, and mission training software. Recent induction programs added ~ aircraft to advanced and lead-in fighter training roles, while refurbishment initiatives extended the service life of ~ legacy platforms across core training squadrons.
Operational dominance in this market is concentrated around central and southern air bases, where training infrastructure, simulator networks, and maintenance hubs are deeply integrated. These regions benefit from proximity to defense procurement authorities, aerospace suppliers, and testing facilities that enable faster deployment cycles. A mature ecosystem of local avionics developers and sustainment providers strengthens readiness levels, while supportive defense policies and export-aligned standards reinforce the country’s position as a regional training and capability development hub.
Market Segmentation
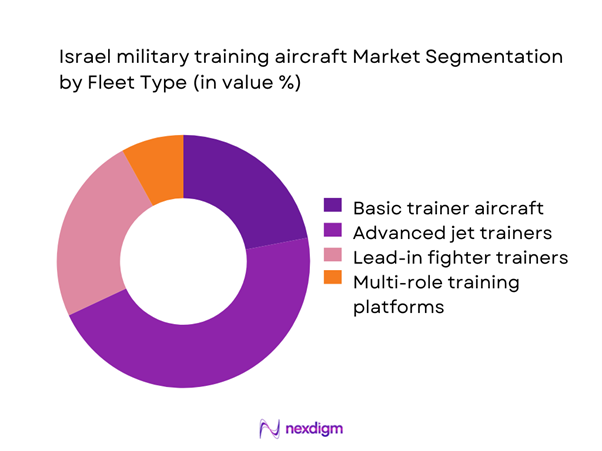
By Fleet Type
Advanced jet trainers dominate the Israel military training aircraft market due to their dual role in high-end tactical preparation and cost-efficient flight hour replacement. These platforms increasingly serve as lead-in fighters, reducing dependency on frontline jets for conversion training. Over the past two years, induction programs added ~ advanced trainers, supported by USD ~ million in avionics and simulation upgrades. Their compatibility with networked training environments and digital debriefing systems further strengthens adoption. Basic trainers continue to support early-stage pilot development, but budget priorities and mission complexity have accelerated the shift toward advanced multi-role training aircraft that offer greater operational realism and lifecycle efficiency.
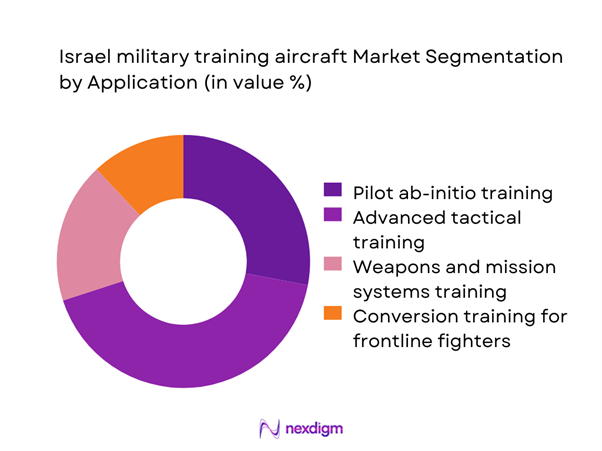
By Application
Advanced tactical training represents the leading application segment, reflecting the growing emphasis on mission readiness for next-generation combat aircraft. Over the last two years, ~ training sorties were conducted annually under advanced tactical modules, supported by investments of USD ~ million in embedded simulation and data analytics platforms. Weapons systems training and conversion programs also expanded, driven by the induction of new frontline fighters and evolving threat environments. Ab-initio training remains essential but is increasingly supplemented by ground-based simulators, allowing airborne assets to focus on high-value operational scenarios that enhance pilot proficiency and reduce overall training costs.
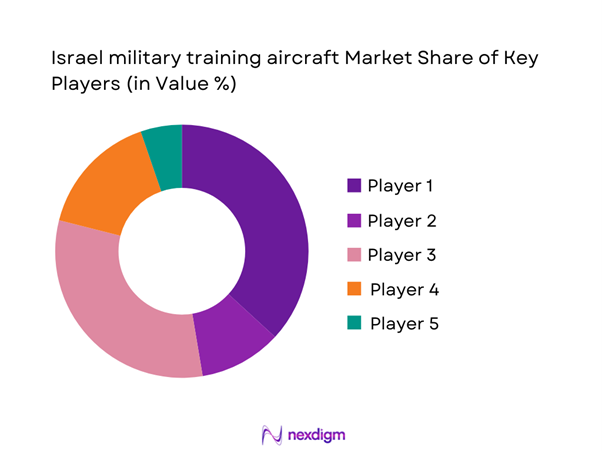
Competitive Landscape
The Israel military training aircraft market is moderately concentrated, led by a mix of domestic defense groups and established international aerospace manufacturers. Local players hold strong positions in avionics integration, mission systems, and sustainment, while global OEMs dominate aircraft platform supply. Long-term service agreements and government-backed procurement frameworks create high entry barriers, reinforcing stable competitive positioning among a limited group of suppliers.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Korea Aerospace Industries | 1999 | South Korea | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pilatus Aircraft | 1939 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel military training aircraft Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of IAF pilot training infrastructure
Ongoing modernization of pilot training infrastructure has significantly influenced demand patterns across the Israel military training aircraft market. In the last two years, investments of USD ~ million were allocated to upgrade ~ training platforms with glass cockpits, embedded simulation, and data-link capabilities. These upgrades enabled the replacement of ~ legacy aircraft and improved annual training throughput by ~ sorties. Enhanced interoperability with ground-based simulators has reduced dependency on frontline fighters, optimizing operational costs while maintaining training intensity. This modernization cycle continues to drive procurement activity and sustainment contracts across domestic and international suppliers.
Rising complexity of frontline fighter platforms
The increasing sophistication of frontline fighter platforms has reshaped training requirements, pushing demand toward advanced and lead-in fighter trainers. Between the last two years, ~ pilots transitioned to next-generation combat aircraft, supported by ~ specialized training systems and USD ~ million in mission training software investments. The complexity of avionics, sensor fusion, and network-centric warfare has elevated the need for high-fidelity training environments. As a result, advanced trainers equipped with tactical simulation and weapons emulation are becoming essential, driving fleet expansion and technology upgrades across Israel’s military aviation training ecosystem.
Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle costs of advanced trainers
Advanced military training aircraft involve substantial acquisition and lifecycle expenses, presenting a major challenge for fleet expansion. Over the past two years, procurement programs required USD ~ million for ~ aircraft, while sustainment and mid-life upgrades added another USD ~ million across ~ platforms. High maintenance intensity and the need for continuous software updates increase total ownership costs. Budget constraints often force trade-offs between fleet modernization and other defense priorities, slowing replacement cycles and limiting the pace of technology adoption across training squadrons.
Long procurement cycles and defense approval processes
Lengthy procurement timelines and multi-layered defense approval frameworks continue to delay fleet renewal initiatives. In recent years, contract finalization for ~ training aircraft took over ~ months, extending delivery schedules and impacting readiness planning. Regulatory reviews, export control clearances, and offset negotiations further complicate acquisition strategies. These prolonged cycles create gaps between operational needs and platform availability, often requiring costly life-extension programs for aging aircraft and increasing dependency on interim training solutions.
Opportunities
Upgrades of legacy trainers with digital avionics and embedded simulation
Modernizing existing training fleets offers a cost-effective pathway to capability enhancement. In the last two years, ~ legacy trainers underwent avionics retrofits supported by USD ~ million in upgrade programs. These initiatives added embedded simulation, digital flight displays, and mission recording systems, extending operational relevance without full platform replacement. Such upgrades allow training commands to align legacy assets with contemporary combat aircraft requirements, improving training outcomes while reducing capital expenditure pressures and accelerating technology diffusion across the fleet.
Local MRO and sustainment partnerships
Expanding local maintenance, repair, and overhaul capabilities presents a strategic opportunity for cost optimization and operational resilience. Recently, ~ aircraft were inducted into domestically managed sustainment programs valued at USD ~ million, reducing turnaround times and dependence on overseas facilities. Partnerships between air force units and local aerospace firms strengthen supply chain security and enhance technical knowledge transfer. These collaborations also create export-ready sustainment models that can support allied training fleets, positioning Israel as a regional hub for military aviation support services.
Future Outlook
The Israel military training aircraft market is expected to evolve through deeper integration of synthetic training environments, expanded local sustainment ecosystems, and selective fleet modernization programs. Over the coming decade, training doctrines will increasingly blend airborne and virtual systems, improving readiness while managing operational costs. Strategic partnerships with allied forces and technology providers will further shape procurement priorities and long-term capability development.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Elbit Systems
- Leonardo
- Korea Aerospace Industries
- Pilatus Aircraft
- BAE Systems
- Textron Aviation Defense
- Lockheed Martin
- Saab
- Embraer Defense & Security
- Boeing Defense
- Northrop Grumman
- CAE
- Honeywell Aerospace
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Key Target Audience
- Air force training and doctrine commands
- Ministry of Defense procurement authorities
- Defense aviation program management offices
- Aerospace OEMs and subsystem suppliers
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul service providers
- Simulation and training systems integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including the Israeli Ministry of Defense and Directorate of Defense Procurement
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Assessment of fleet size, training throughput, sustainment intensity, and modernization cycles across air force training units. Evaluation of technology adoption levels in avionics, simulation, and data analytics platforms. Mapping of procurement patterns and budget allocation trends shaping training aircraft demand.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Compilation of historical deployment and upgrade data across training squadrons. Structuring of demand drivers around operational readiness, cost efficiency, and capability alignment. Integration of ecosystem dynamics involving OEMs, integrators, and sustainment partners.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Validation of market assumptions through discussions with defense aviation specialists and training commanders. Cross-verification of fleet modernization timelines and sustainment strategies. Refinement of opportunity and challenge frameworks based on operational realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Consolidation of qualitative and quantitative insights into a unified market narrative. Alignment of findings with long-term defense aviation trends. Finalization of strategic perspectives for stakeholders across the training aircraft ecosystem.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, military training aircraft taxonomy across basic advanced and lead in fighter trainer platforms, market sizing logic by fleet size and replacement cycles, revenue attribution across aircraft deliveries upgrades and MRO services, primary interview program with air force training commands OEMs and integrators, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Training and usage pathways across basic, advanced, and lead-in fighter training
- Ecosystem structure across OEMs, avionics providers, and training system integrators
- Supply chain and sustainment structure
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of IAF pilot training infrastructure
Rising complexity of frontline fighter platforms
Expansion of networked and simulation-based training doctrines
Increased defense budget allocation for readiness and skills retention
Need for cost-efficient flight hour replacement through advanced trainers
Strengthening of joint and allied training programs - Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle costs of advanced trainers
Long procurement cycles and defense approval processes
Integration complexity with existing training ecosystems
Dependence on foreign OEMs and export control constraints
Fleet aging and maintenance intensity
Budget trade-offs with frontline combat aircraft programs - Opportunities
Upgrades of legacy trainers with digital avionics and embedded simulation
Local MRO and sustainment partnerships
Export-oriented training services for allied forces
Adoption of live-virtual-constructive training architectures
Development of indigenous subsystems and mission training software
Expansion of joint training programs with partner nations - Trends
Shift toward lead-in fighter trainers with embedded tactical training
Increased use of synthetic training environments
Greater emphasis on data analytics for pilot performance
Hybrid training models combining airborne and ground-based simulation
Lifecycle extension programs for existing fleets
Growing role of private-sector training service providers - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Basic trainer aircraft
Advanced jet trainers
Lead-in fighter trainers
Multi-role training platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Pilot ab-initio training
Advanced tactical training
Weapons and mission systems training
Conversion training for frontline fighters - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Conventional avionics trainers
Glass cockpit trainers
Embedded simulation-enabled trainers
Networked live-virtual-constructive trainers - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Air force training commands
Defense flight academies
Joint services training units
Allied and partner force training programs - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone training platforms
Data-linked training aircraft
Fully networked training ecosystems
Cloud-enabled mission debriefing systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northern air bases
Central training hubs
Southern desert training zones
Overseas training detachments
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (fleet modernization capability, embedded simulation maturity, lifecycle cost efficiency, local industrial participation, interoperability with IAF systems, training throughput capacity, sustainment and MRO depth, export control flexibility)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries
Elbit Systems
Leonardo
Korea Aerospace Industries
BAE Systems
Pilatus Aircraft
Textron Aviation Defense
Lockheed Martin
Saab
Embraer Defense & Security
Boeing Defense
Northrop Grumman
CAE
Honeywell Aerospace
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


