Market Overview
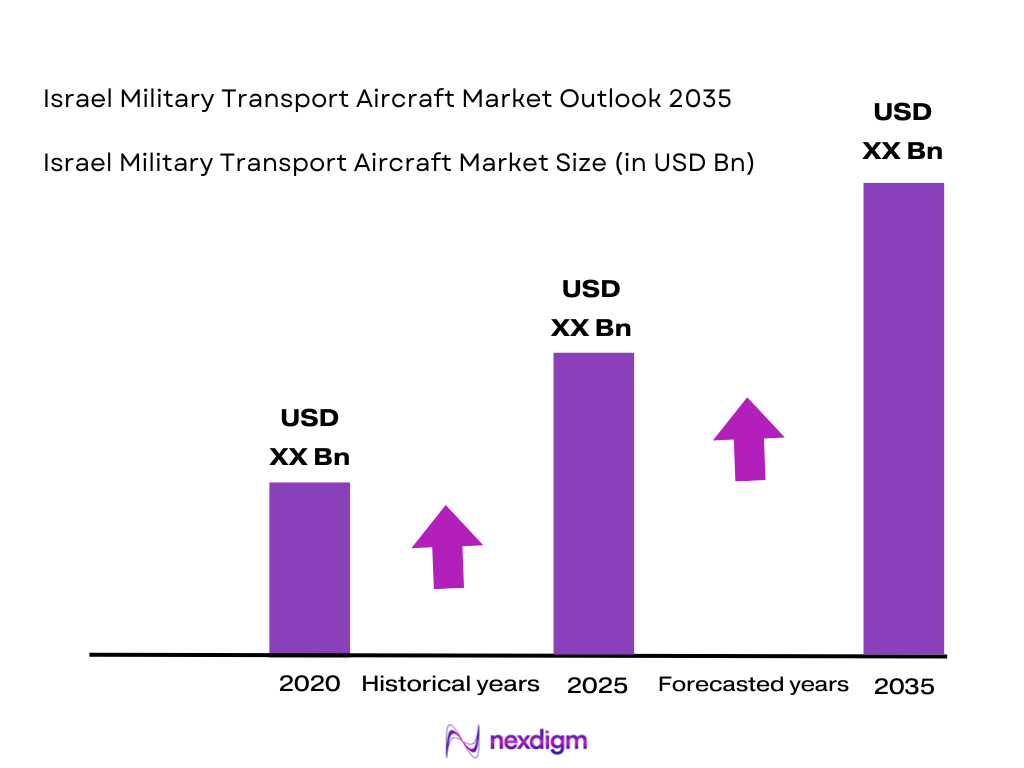
The Israel Military Training Aircraft market, as part of the global military trainer aircraft sector, was valued at approximately USD ~ billion in 2024 according to industry estimates, demonstrating sustained defense investment tied to pilot training modernization and fleet replacement programs. The preceding year saw this market at around USD ~ billion in 2024, underpinned by procurement of turboprop and jet-based trainers aligned with expanding pilot throughput requirements and the need to support advanced combat aircraft readiness in air forces worldwide.
Key markets driving the Israel Military Training Aircraft sector include North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific due to established defense industrial bases, high defense budgets, and ongoing modernization programs that necessitate advanced training platforms with integrated simulation capabilities. Dominance in these regions stems from procurement funding, technology leadership, and strategic partnerships that accelerate trainer aircraft deliveries and sustainment. Israel’s own market benefits from domestic defense production capabilities and integration with Western platforms.
Market Segmentation
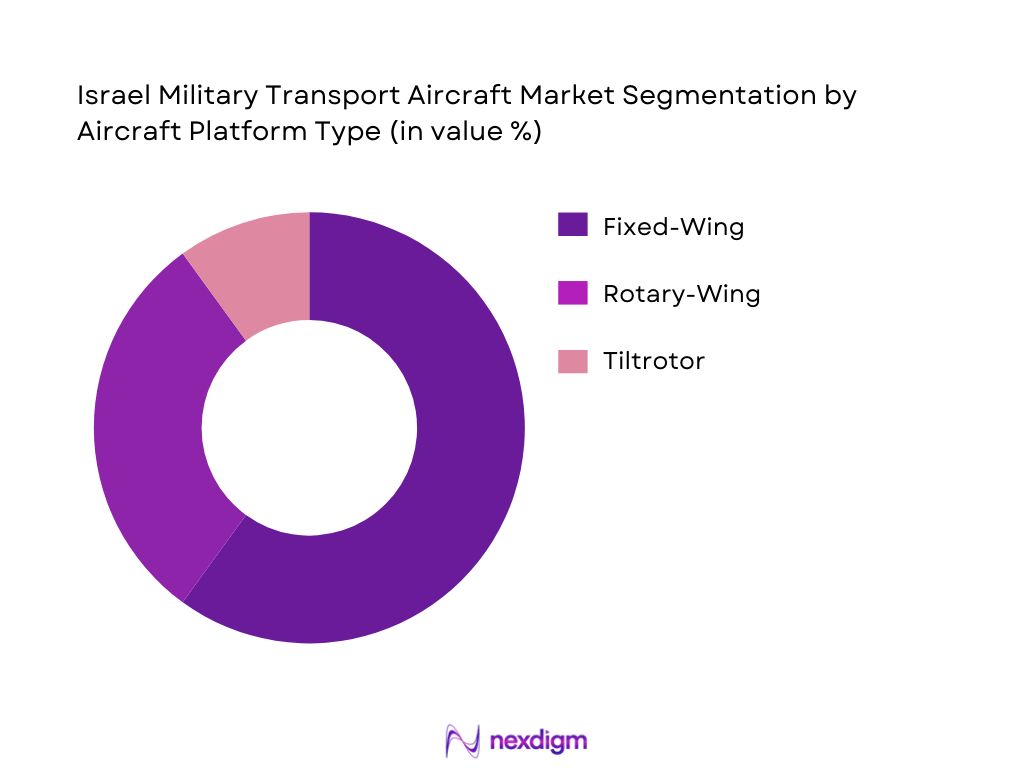
By Training Aircraft Type
Under this segmentation, Advanced Jet Trainer Aircraft dominate due to their relevance in preparing pilots for 4th- and 5th-generation combat aircraft. These platforms offer high-fidelity flight characteristics, advanced avionics suites, and embedded tactical systems that align with modern pilot training syllabi. This demand is reinforced by air forces transitioning from legacy turboprop trainers to jet trainers that bridge intermediate and advanced phases, enabling efficient progression into frontline fighter roles.
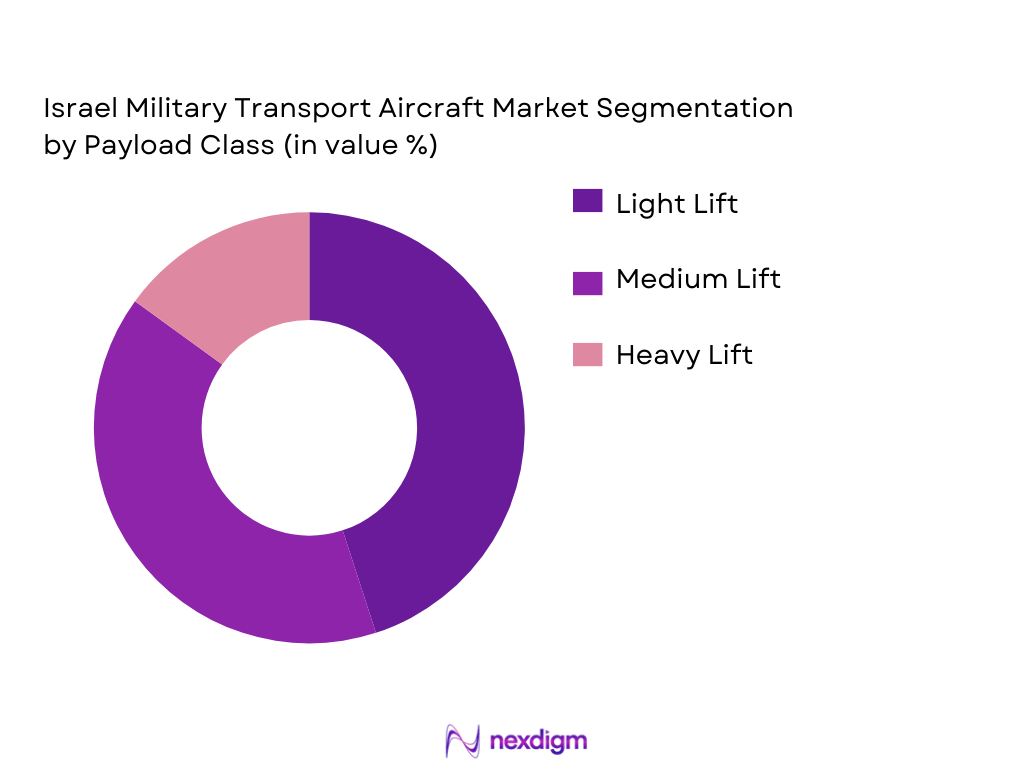
By Propulsion Type
Propulsion demand favors turboprop engines for basic and intermediate training due to lower lifecycle costs and fuel efficiency, while turbofan and turbojet configurations are increasingly prioritized for advanced and lead-in fighter trainers because they replicate performance envelopes closer to combat aircraft and support advanced syllabus requirements.
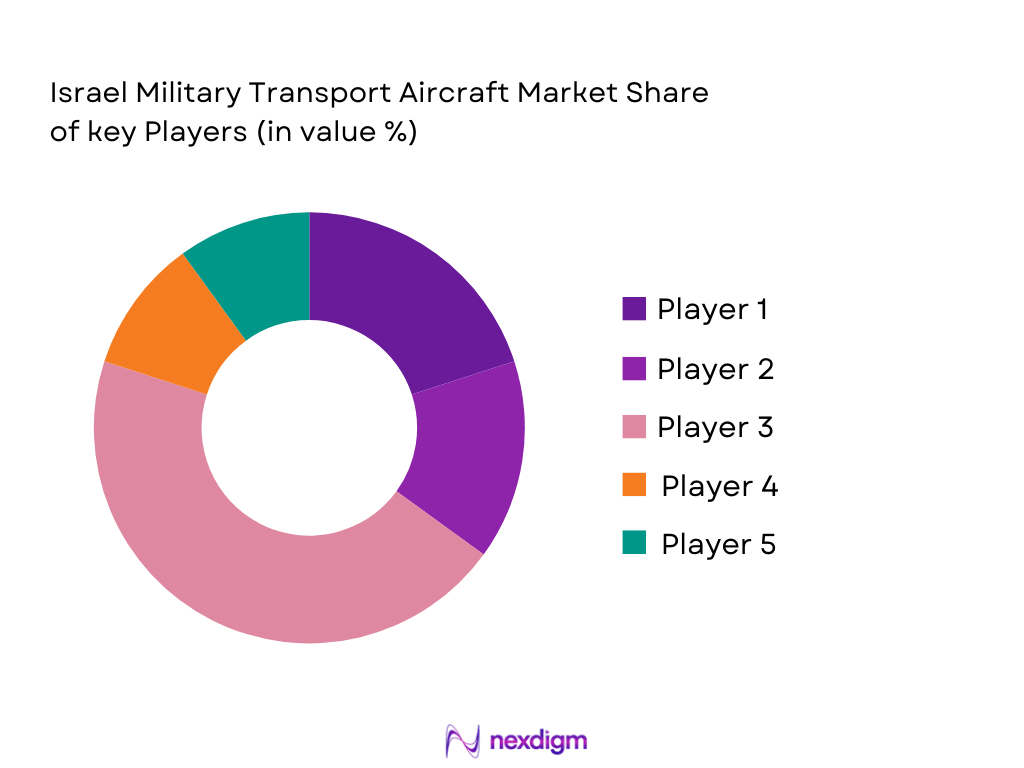
Competitive Landscape
The military training aircraft market features a mix of established OEMs and niche aerospace suppliers, with competition centered on platform capability, training system integration, cost of ownership, and aftermarket support. Consolidation among key global players underscores the importance of technological differentiation and strategic alliances to secure long-term defense contracts.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Platform Portfolio (Trainer Types) | Propulsion Focus | Training Systems Integration | Global Footprint | Aftermarket Support | R&D Investment |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pilatus Aircraft | 1939 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Military Training Aircraft Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Pilot Throughput Requirements
The Israel Military Training Aircraft market is strongly driven by increasing pilot throughput requirements linked to operational readiness and force sustainability. The Israeli Air Force operates one of the most intensive pilot training pipelines globally due to high sortie rates, continuous operational deployments, and a focus on maintaining qualitative military superiority. Rising retirement rates of experienced pilots, combined with expanding mission profiles such as air defense, precision strike, and ISR, have increased demand for accelerated yet high-quality pilot training. Training aircraft allow air forces to scale flight hours without overburdening frontline fighters, which are expensive to operate and maintain. Advanced trainers equipped with embedded simulation and digital debriefing tools enable higher student-to-instructor ratios and faster skill progression. This throughput-driven demand directly supports sustained procurement, upgrades, and long-term contracts for training aircraft platforms and associated systems.
Induction of Advanced Combat Aircraft
The induction of advanced combat aircraft into Israel’s air force structure is a critical driver shaping the military training aircraft market. Fifth-generation and advanced fourth-generation fighters incorporate complex avionics, sensor fusion, electronic warfare, and network-centric combat capabilities that cannot be effectively introduced using legacy training platforms. As a result, training aircraft must increasingly replicate frontline aircraft cockpit layouts, flight control logic, mission systems, and data-link environments. Lead-in fighter trainers and advanced jet trainers reduce the performance and capability gap between training and operational aircraft, lowering transition risk and improving combat readiness. This shift increases demand for high-fidelity trainers with advanced flight envelopes, modern propulsion systems, and integrated tactical simulation, reinforcing sustained investment in sophisticated training aircraft platforms.
Market Challenges
Airworthiness and Certification Constraints
Airworthiness and certification constraints present a significant challenge in the Israel Military Training Aircraft market. Military training aircraft must comply with stringent national and international airworthiness standards, particularly when platforms incorporate advanced avionics, software-defined systems, and embedded simulation capabilities. Certification processes for flight control software, mission computers, and safety-critical subsystems are time-consuming and costly, often extending program timelines. Israel’s close operational alignment with Western defense partners also requires compatibility with NATO and allied certification frameworks, further increasing compliance complexity. Any modification or upgrade to training aircraft systems typically necessitates re-certification, impacting fleet availability and cost efficiency. These constraints can slow platform induction, limit rapid modernization, and create barriers for new entrants or indigenous solutions.
High Acquisition and Lifecycle Costs
High acquisition and lifecycle costs remain a persistent challenge in the market. Advanced training aircraft increasingly resemble frontline combat platforms in terms of avionics, propulsion, and system complexity, driving up procurement costs. Beyond acquisition, lifecycle expenses related to maintenance, spares, software upgrades, simulator synchronization, and sustainment contracts place long-term pressure on defense budgets. Training aircraft fleets operate at high utilization rates, accelerating wear and increasing maintenance demands. Cost sensitivity is further amplified by the need to balance training investments against competing priorities such as combat aircraft upgrades, air defense systems, and intelligence platforms. Managing total cost of ownership while maintaining training quality is therefore a critical constraint influencing procurement strategies.
Opportunities
Advanced Trainer Modernization
Advanced trainer modernization represents a major opportunity within the Israel Military Training Aircraft market. Existing trainer fleets can be upgraded with modern avionics, digital cockpits, embedded mission simulation, and improved propulsion systems to extend service life and enhance training relevance. Modernization programs offer cost-effective alternatives to full fleet replacement while allowing alignment with evolving combat aircraft technologies. Upgraded trainers can support advanced syllabus elements such as beyond-visual-range tactics, electronic warfare training, and network-centric operations. These modernization efforts also create opportunities for domestic industry participation in avionics integration, software development, and sustainment, strengthening the local defense aerospace ecosystem.
Indigenous Avionics Integration
Indigenous avionics integration presents a strategic growth opportunity for the market. Israel’s strong domestic defense electronics and aerospace capabilities enable the development and integration of locally produced avionics, mission computers, data links, and training management systems into military training aircraft. Indigenous integration reduces reliance on foreign suppliers, mitigates export control risks, and allows greater customization to national operational doctrines. Locally developed systems can be rapidly updated to reflect evolving threat environments and operational lessons. This capability also enhances export competitiveness by offering modular, adaptable training solutions. As training aircraft become more software-centric, indigenous avionics and digital systems will play an increasingly central role in shaping future training platforms.
Future Outlook
Over the forecast period, the Israel Military Training Aircraft market is positioned for continued growth driven by increasing defense allocations, the retirement of aging trainer fleets, and the integration of simulation-linked training systems that reduce costs and increase pilot proficiency. Advances in digital avionics, synthetic training, and network-centric training integration will shape procurement decisions, while geopolitical needs for readiness support sustained demand. Emphasis on indigenous and collaborative programs may further expand domestic and export opportunities, fostering innovation across training aircraft types.
Major Players in the Market
- Elbit Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Lockheed Martin
- Leonardo
- Pilatus Aircraft
- Boeing Defense
- BAE Systems
- Dassault Aviation
- Northrop Grumman
- Embraer Defense
- Korea Aerospace Industries
- Textron Aviation Defense
- Sierra Nevada Corporation
- HAL
- Saab
Key Target Audience
- Air Force Training Program Directors
- Defense Procurement Authorities (e.g., Israel Ministry of Defense, U.S. Defense Security Cooperation Agency)
- Platform OEM Strategic Planners
- Military Budget Allocators
- Aircrew Training Systems Integrators
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms (Defense & Aerospace)
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Defense Export Control, Airworthiness)
- Defense Logistics and Sustainment Directors
Research Methodology
Step 1 – Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involved mapping major stakeholders and defining trainer aircraft categories, propulsion types, training roles, avionics architectures, and integration levels using secondary defense databases and industry sources to delineate critical market variables.
Step 2 – Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data on order books, deliveries, platform selections, and defense budget allocations were compiled and analyzed to assess market penetration across segments and regions, ensuring alignment with fiscal defense cycles and training modernization drivers.
Step 3 – Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on growth drivers and market challenges were validated via consultations with defense procurement leads, aircrew training commanders, and OEM specialists to refine demand assumptions and confirm procurement trends shaping the market landscape.
Step 4 – Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insight synthesis involved cross-referencing bottom-up demand indicators with top-down defense spending forecasts and platform replacement schedules to validate market size estimates and derive actionable insights for business professionals operating in the military training aircraft domain.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Platform Classification Logic, Training Aircraft Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Primary Interviews with Air Force Trainers and OEMs, Defense Procurement Validation, Limitations and Analytical Boundaries)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Role in Air Force Readiness
- Evolution of Pilot Training Doctrine
- Role of Training Aircraft in Combat Aircraft Induction
- Integration with Simulator-Based Training Ecosystems
- Market Structure and Ecosystem Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Pilot Throughput Requirements
Induction of Advanced Combat Aircraft
Emphasis on Network-Centric Warfare Training
Reduction of Frontline Aircraft Training Burden
- Market Challenges
Airworthiness and Certification Constraints
High Acquisition and Lifecycle Costs
Export Control and ITAR Dependencies
- Opportunities
Advanced Trainer Modernization
Indigenous Avionics Integration
AI-Enabled Training Analytics
- Technology Trends
Digital Flight Control Systems
Embedded Threat Simulation
Data-Driven Training Performance Monitoring
- Regulatory and Compliance Framework
Military Airworthiness Standards
NATO Compatibility
Export Licensing
SWOT Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Stakeholder and Procurement Ecosystem
- Market Value, 2020-2025
- Volume Consumption Across Subsegments, 2020-2025
- Composite Adoption Intensity, 2020-2025
- By Training Aircraft Type (In Value %)
Basic Trainer Aircraft
Intermediate Trainer Aircraft
Advanced Jet Trainer Aircraft
Lead-In Fighter Trainer Aircraft
Multi-Role Training Platforms
- By Propulsion Type (In Value %)
Turboprop Engines
Turbojet Engines
Turbofan Engines
- By Training Role (In Value %)
Ab-Initio Flight Training
Instrument Flight Training
Weapons Training
Tactical Maneuver Training
Fighter Lead-In Training
- By Cockpit and Avionics Architecture (In Value %)
Analog Cockpit
Glass Cockpit
Embedded Tactical Avionics
Sensor and EW Emulation Suites
Helmet-Mounted Cueing Compatibility
- By Integration Level with Ground Training Systems (In Value %)
Standalone Aircraft Training
Simulator-Integrated Training
Live-Virtual-Constructive Training Integration
Network-Centric Training
- Market Share Landscape by Platform Value
- Platform Penetration across Training Phases
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Training Phase Coverage, Aircraft Flight Hour Cost, Avionics Fidelity vs Frontline Fighters, Simulator Interoperability, Weapons and Sensor Emulation Capability, MRO Localization Potential, Upgrade and Growth Margin, Export Clearance Flexibility)
- Company Benchmarking and Strategic Positioning
- Detailed Company Profiles
Elbit Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
Lockheed Martin
Leonardo
Korea Aerospace Industries
Pilatus Aircraft
Boeing Defense
BAE Systems
Dassault Aviation
Textron Aviation Defense
Aermacchi
HAL
Sierra Nevada Corporation
Northrop Grumman
Embraer Defense
- Air Force Training Command Requirements
- Annual Training Hours per Pilot
- Budget Allocation Logic
- Evaluation and Selection Criteria
- Offset and Industrial Participation Expectations
- Forecast by Value & Growth Scenarios, 2026-2035
- Forecast by Volume & Composite Penetration, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Aircraft Segment, 2026-2035


