Market Overview
The Israel Military Transport Aircraft market is valued based on its comprehensive fleet size and procurement cycles, with the Israeli Air Force (IAF) being one of the key drivers of demand. This market is propelled by strategic mobility needs, with heavy reliance on both fixed-wing and rotary-wing transport solutions for operational readiness, humanitarian aid, and rapid troop deployment. Notable contributions to market size stem from a combination of domestic production and international collaborations, underpinned by ongoing defense budgets aimed at enhancing fleet capabilities. According to the latest reports, Israel’s defense sector is expected to allocate around USD ~ billion in 2024 for various procurement programs, including military transport solutions.
Key dominant regions in the market include Israel, which remains the central hub of military transport aircraft development, particularly through state-owned Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI). Other notable contributors to the market’s dominance are international defense contractors like Boeing and Lockheed Martin, who provide solutions through FMS (Foreign Military Sales) and offset agreements. Israel’s market dominance is driven by the integration of cutting-edge technology in its fleet, local manufacturing capabilities, and high demand for rapid mobility solutions across the Middle East region.
Market Segmentation
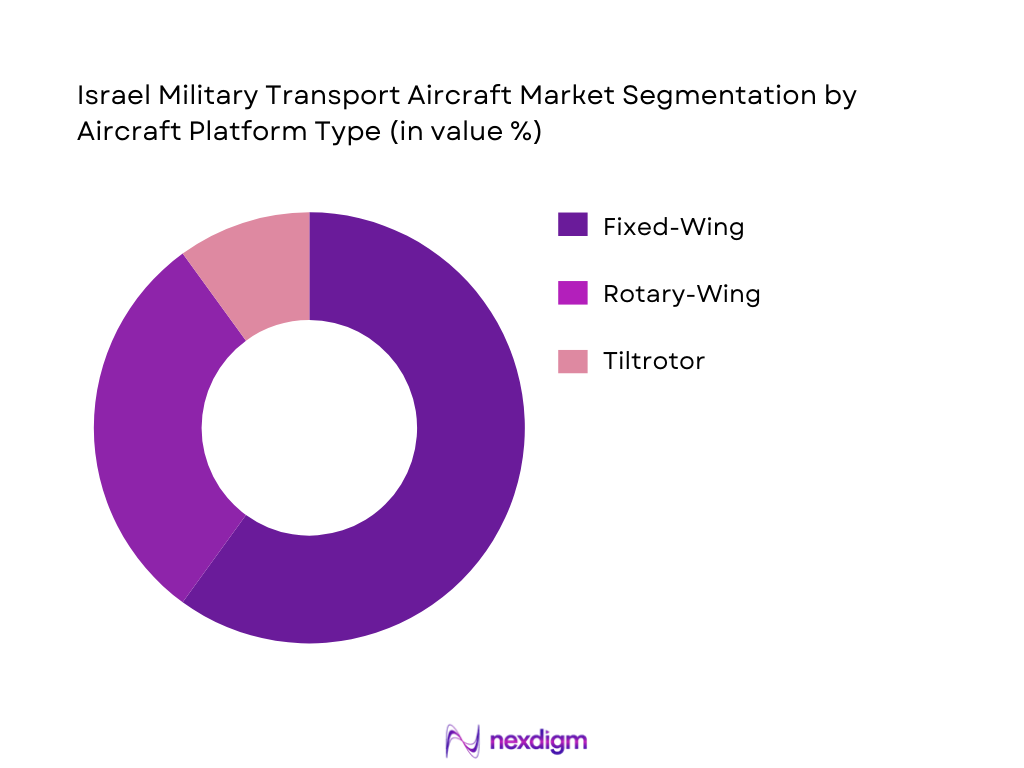
By Aircraft Platform Type
Israel’s military transport aircraft market is primarily segmented into fixed-wing, rotary-wing, and tiltrotor platforms. Fixed-wing platforms, such as the C-130 Hercules, dominate the market due to their capacity for strategic airlift and troop movement, which aligns with Israel’s defense strategy. Rotary-wing aircraft are also crucial for tactical transport, primarily for operations in challenging terrains like mountainous regions. Tiltrotor platforms, although emerging, are expected to gain traction in the future due to their hybrid nature, combining both rotary and fixed-wing advantages for rapid deployment and mobility.
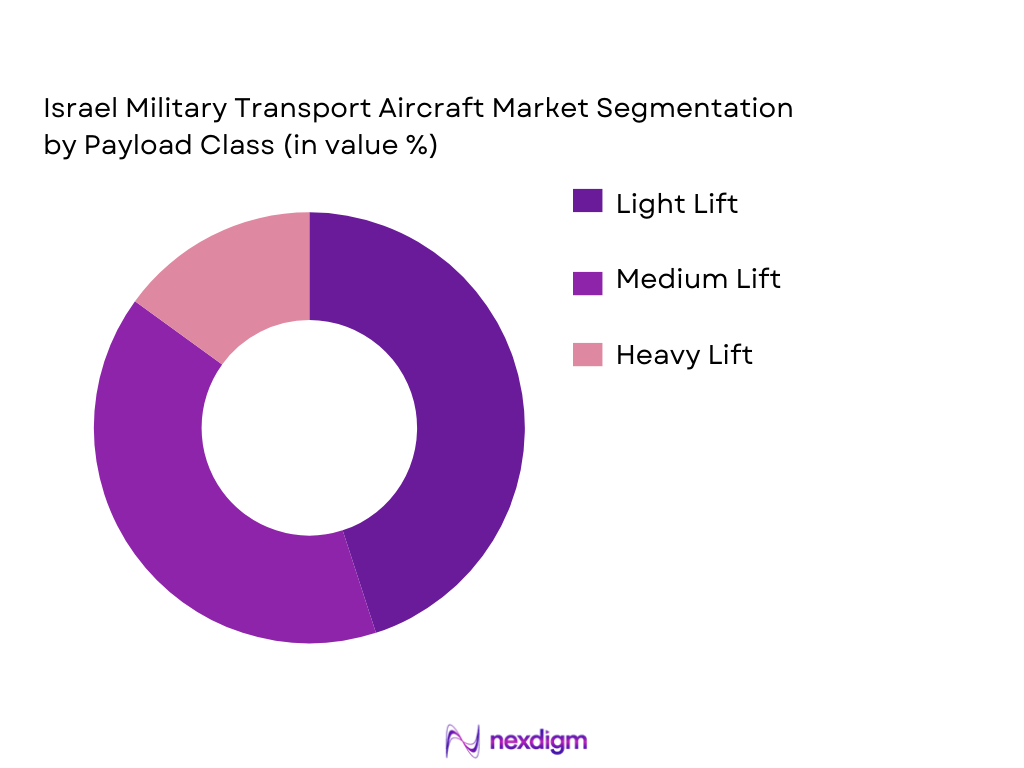
By Payload Class
The market is segmented based on payload class into light, medium, and heavy lift categories. Light lift platforms dominate the Israeli market as they offer flexible solutions for personnel transport and equipment resupply, especially in urban and confined spaces. Medium lift aircraft, such as the Boeing CH-47 Chinook, remain essential for troop movement and larger logistical support, while heavy lift platforms cater to the most critical operations, including strategic airlift. Israel’s defense strategy prioritizes medium lift aircraft due to their operational versatility and deployment speed.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the Israel Military Transport Aircraft market is characterized by a few dominant global players. These include both domestic manufacturers and major international defense contractors. Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) remains a leader in developing and producing transport aircraft. However, Boeing and Lockheed Martin also hold substantial shares due to their strong presence in the market, particularly through FMS contracts with Israel. The market is highly competitive, with frequent collaborations between local and global players to meet Israel’s defense needs.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Aircraft Type Expertise | Manufacturing Capability | Export Orientation | After-Sales Support | Technology Innovation |
| Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing Defense | 1916 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus Defence & Space | 2000 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Sikorsky Aircraft (Lockheed Subsidiary) | 1923 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Military Transport Aircraft Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Force Projection Metrics
Force projection is a key growth driver in the Israel Military Transport Aircraft market, playing a crucial role in enhancing Israel’s ability to quickly deploy military assets across different regions. The need for swift, flexible transportation solutions has driven demand for advanced military transport aircraft. These aircraft, including both fixed-wing and rotary-wing platforms, allow for the rapid movement of troops, equipment, and supplies, ensuring the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) are always prepared for potential conflicts. Israel’s military strategies are heavily reliant on maintaining a high level of operational readiness and flexibility. Transport aircraft are pivotal for strategic airlift operations, enabling quick deployment of forces in response to regional tensions. Moreover, these aircraft are vital for providing logistical support in emergency and humanitarian missions. The ability to project military power efficiently through air transport is integral to Israel’s defense strategy, ensuring both defense and deterrence capabilities. As global security dynamics evolve, Israel’s demand for advanced military transport solutions continues to rise, reinforcing the market’s growth.
Strategic Mobility Requirements
Strategic mobility is a critical component of Israel’s defense strategy, serving as a growth driver for the Israel Military Transport Aircraft market. The need for rapid and efficient movement of military personnel, equipment, and supplies is essential to maintain operational flexibility and responsiveness, particularly in a region marked by geopolitical instability. Strategic mobility refers to the ability to deploy forces quickly over long distances and sustain them in forward-operating environments. For Israel, which faces constant security threats from neighboring countries and non-state actors, the capability to swiftly project military power is vital for both defense and deterrence.Israel’s military doctrine emphasizes the ability to mobilize forces at short notice, and transport aircraft are the backbone of this capability. Fixed-wing platforms such as the C-130 Hercules are crucial for long-range airlift missions, allowing the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) to deploy troops, heavy equipment, and supplies rapidly across the Middle East. In addition to traditional military operations, strategic mobility supports humanitarian aid efforts, peacekeeping missions, and disaster relief, enhancing Israel’s ability to project influence and fulfill international commitments.
Market Challenges
Funding Volatility
Funding volatility is a critical challenge in the Israel Military Transport Aircraft market. Defense procurement budgets in Israel are susceptible to fluctuations based on economic conditions, political priorities, and changes in military strategy. These budgetary shifts can impact the timely procurement or upgrading of aircraft. Large transport platforms such as the C-130 require substantial investments, and inconsistent funding can delay fleet modernization, leaving older aircraft in service for longer than optimal. These delays may result in a reliance on outdated platforms, which could affect mission efficiency and readiness. Funding volatility complicates long-term planning for the Israeli Ministry of Defense (MOD), as the defense budget is often allocated to various defense sectors, not just military transport. Moreover, the cyclical nature of military spending means there may be periods where budget cuts or reallocation to other defense areas hinder procurement, complicating procurement cycles for critical systems. This uncertainty can create instability within the market, affecting both suppliers and defense contractors involved in the supply chain.
Export Control Regimes
Export control regimes present a significant challenge for the Israel Military Transport Aircraft market. Israel’s defense sector, while highly advanced, is often reliant on international collaborations to source key components and technology for its aircraft. The export control regimes—both domestic and international—affect procurement processes and technological integration. For example, Israel frequently enters into Foreign Military Sales (FMS) agreements with the United States for acquiring defense technologies, but these are subject to U.S. regulations that govern the transfer of military hardware. These regulations may limit Israel’s access to certain advanced technologies, causing delays or limiting its ability to procure the latest systems for its fleet. In addition, Israel’s own defense export policies are stringent, with some technologies considered sensitive and restricted for export. This limits Israel’s ability to engage freely in the global supply chain and source components from a wider range of international suppliers. Export controls, therefore, create barriers that can delay or restrict the pace of technological advancements and integration of modern systems in Israel’s military transport fleet.
Opportunities
Fleet Upgrade Programs
Fleet upgrade programs present a significant opportunity in the Israel Military Transport Aircraft market. Many of Israel’s existing transport aircraft, including the C-130 Hercules and CH-47 Chinook, are nearing the end of their service life. To address this, the Israeli Ministry of Defense has prioritized fleet modernization through upgrades. These upgrades involve enhancing avionics, improving fuel efficiency, and integrating modern mission systems to keep older aircraft operational for an extended period. Fleet upgrades are a more cost-effective solution than purchasing entirely new aircraft, especially considering the high costs associated with acquiring large transport platforms. These modernization efforts also enable Israel to maintain the operational capabilities of its fleet, keeping them at the cutting edge without the financial burden of replacing the entire fleet. Additionally, upgrading existing platforms allows for the integration of new technologies, such as enhanced communication and navigation systems, to improve the overall performance of the fleet. Given the tight defense budgets globally, fleet upgrade programs are seen as a way to maximize the value of existing assets while ensuring they meet evolving military needs.
Autonomous & AI‑enabled Transport Systems
The integration of autonomous and AI-enabled transport systems offers a promising opportunity for growth in the Israel Military Transport Aircraft market. Israel has been a leader in defense technology, and the use of AI in military transport operations is a natural extension of its innovation-driven defense strategy. Autonomous aircraft, or those equipped with AI-driven systems, could perform missions such as cargo loading, mission planning, and route optimization with minimal human intervention. This reduces operational costs and the risk to human life, especially in hostile environments. Autonomous systems can also enhance efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, optimizing flight routes, and enabling better management of flight schedules. Moreover, AI could improve predictive maintenance, allowing for timely servicing and reducing downtime of aircraft. The Israeli Ministry of Defense is already exploring AI applications for logistics and transport, recognizing that automation could significantly improve operational efficiency and flexibility. As defense logistics continue to evolve, the integration of autonomous and AI technologies presents a significant opportunity to redefine the capabilities of military transport aircraft, making them more agile and cost-efficient.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the Israeli military transport aircraft market is poised to grow as Israel continues to modernize its airlift capabilities. This growth will be driven by the increasing need for rapid deployment, improved logistical support in defense operations, and advancements in both airlift technology and unmanned systems integration. Additionally, regional tensions and the ongoing need for humanitarian missions will further accelerate the demand for military transport aircraft in the region. Israel’s unique geopolitical and strategic position will continue to drive innovation, ensuring it remains a key player in the defense aerospace industry.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
- Boeing Defense
- Lockheed Martin
- Airbus Defence & Space
- Sikorsky Aircraft (Lockheed Subsidiary)
- Bell Helicopter
- Northrop Grumman
- General Dynamics
- Raytheon Technologies
- Textron Aviation
- Leonardo Helicopters
- Dassault Aviation
- Saab Group
- Thales Group
- Embraer
Key Target Audience
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Israeli Ministry of Defense)
- Military Procurement Units (IAF, MOD)
- Defense Contractors (Aerospace OEMs, Subcontractors)
- International Defense Alliances (NATO, UNSC)
- Military Transport and Logistics Companies
- Strategic Defense Consultants
- Aerospace and Defense Manufacturers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves mapping out key variables affecting Israel’s Military Transport Aircraft market. These include military procurement budgets, aircraft fleet size, technological integration, and geopolitical factors. The data is gathered through both secondary and primary research methodologies, including expert interviews and industry reports.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This step includes evaluating historical data such as fleet procurement patterns, operational needs, and military logistics. An analysis of demand drivers, including defense budget allocation and strategic mobility requirements, will also be conducted to build a comprehensive market model.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Expert consultations will be conducted with industry practitioners, including military officers, aerospace engineers, and OEM representatives, to validate market hypotheses. These interviews help refine the accuracy of our data and offer insights into the current trends affecting the market.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves synthesizing the collected data, verifying the market trends, and finalizing the report. This stage ensures that the findings are both comprehensive and reliable, with insights directly applicable to stakeholders within the Israeli defense and aerospace sectors.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions (Military Transport Aircraft Roles, Lift Categories, Operational Scope), Data Sources and Validation (Government Procurement Data, Defense Contracts, Flight Hour Logs), Abbreviations (ICAO, IAF, FMS, RFP/RFQ, COTS, MOD), Market Sizing Approach (Aircraft Fleet Valuation, Order Backlog Analysis, Payload Capacity Metrics), Primary Research Framework (Defense OEM & MOD Interviews, Procurement Officer Surveys), Limitations and Forecast Confidence)
- Definition and Scope (Strategic Airlift, Tactical Lift, Rotary and Fixed Wing)
- Market Genesis and Evolution (IDF Transport Fleet History)
- Defense Procurement Policy Context (MOD Budget Allocations, FMS Pathways)
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis (OEM, Tier‑1/2 Suppliers, MRO Ecosystem)
- Technology Architecture (Avionics, Payload Systems, Logistics Interfaces)
- Growth Drivers
Force Projection Metrics
Strategic Mobility Requirements
Regional Conflict Dynamics
Airlift Capability Optimization
Joint Operations with Allies - Market Challenges
Funding Volatility
Export Control Regimes
High Lifecycle Costs
Fluctuations in Fuel Prices - Opportunities
Fleet Upgrade Programs
Autonomous & AI-enabled Transport Systems
ISR-Transport Integration
Increased Demand for Humanitarian Missions - Emerging Trends
Green Propulsion R&D
Digital Logistics Platforms
Smart Aircraft Integration
Modular Payload Systems - Regulatory and Policy Environment
Export Licenses
Aerospace Standards Compliance
Government Procurement Frameworks
Aviation Safety Certifications
- Market Value, 2020-2025
- Volume Consumption Across Subsegments, 2020-2025
- Composite Adoption Intensity, 2020-2025
- By Aircraft Platform Type (In Value %)
Fixed Wing (Strategic Airlift)
Rotary Wing (Tactical Transport)
Tiltrotor (VTOL Platforms) - By Payload Class (In Value %)
Light Lift
Medium Lift
Heavy Lift - By Mission Profile (In Value %)
Troop Transport (Personnel Mobility)
Cargo Resupply
Aeromedical Evacuation
Humanitarian Aid Response
Strategic Deployment - By Procurement Source (In Value %)
Domestic OEM
Foreign OEM (FMS/Direct Purchase)
Co‑Production/Offset Agreements - By Component Type (In Value %)
Airframe
Propulsion
Avionics & Systems
Integrated Logistics Support
- Market Share Analysis (Value and Units by OEM and Integrator)
- Cross‑Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Defense Contract Wins, Strengths, Weaknesses, Manufacturing Footprint, Global Support Network, R&D Intensity, Fleet Field Performance Metrics, Pricing Benchmarks, MOD Supplier Ratings, Number of Service Agreements, after‑Sales Support Coverage, Offset & Local Partnership Footprint, Certification Status)
- Competitor SWOT Summaries
- Pricing & Contract Structure Analysis (Fixed Price, Cost Plus, Performance Milestones)
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
Elbit Systems – Transport Systems Integration, Avionics & Mission Tech
Boeing Defense – FMS Transport Offerings, CH‑47/Other Systems
Lockheed Martin – C‑130 Variants and Support Packages
Airbus Defence & Space – A400M and Logistics Support
Sikorsky (Lockheed Subsidiary) – Heavy Lift Rotorcraft (CH‑53K)
Kawasaki Heavy Industries – Fixed Wing Support Components
Antonov – Heavy Strategic Lift Platforms (Partnerships/FMS)
Embraer – Medium Lift Aircraft and Regional Tactical Transports
Rheinmetall – Logistics Integration Systems
Ilyushin (Part of United Aircraft Corporation) – Strategic Transport Platforms
HAL (Hindustan Aeronautics Limited) – Transport Component Collaborations
Textron (Cessna/Beechcraft) – Light Transport Platforms
Leonardo – Rotary Lift Platforms
Rolls‑Royce – Engine Systems and Aftermarket Support
- Israeli Air Force Fleet Requirements (Lift Demand Modeling, Mission Readiness Indicators)
- MOD Budget Allocation Impacts (Operational, Capital Procurement)
- Procurement Decision Framework
- Forecast by Value & Growth Scenarios, 2026-2035
- Forecast by Volume & Composite Penetration, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Aircraft Segment, 2026-2035


