Market Overview
The Israel Space Based Solar Power market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by expanding satellite research programs and early-stage orbital power initiatives. Activity levels increased across 2024 and 2025 as national agencies prioritized energy resilience and space-based infrastructure development. Investments focused on demonstrator platforms, microwave transmission testing, and launch integration planning. Growing alignment between defense and civil energy objectives supported funding continuity. Technology validation programs accelerated through collaborative aerospace projects. Policy backing strengthened long-term confidence in space-enabled renewable power generation.
The market is concentrated around central Israel and southern technology corridors where aerospace infrastructure, defense installations, and research centers are established. Strong linkages between satellite manufacturers, launch service providers, and energy authorities shape demand concentration. Government-backed innovation clusters support testing facilities and component manufacturing. Urban energy demand and strategic defense requirements drive deployment priorities. Regulatory alignment between space and energy ministries enables coordinated development. Mature digital and satellite communication ecosystems further reinforce regional dominance.
Market Segmentation
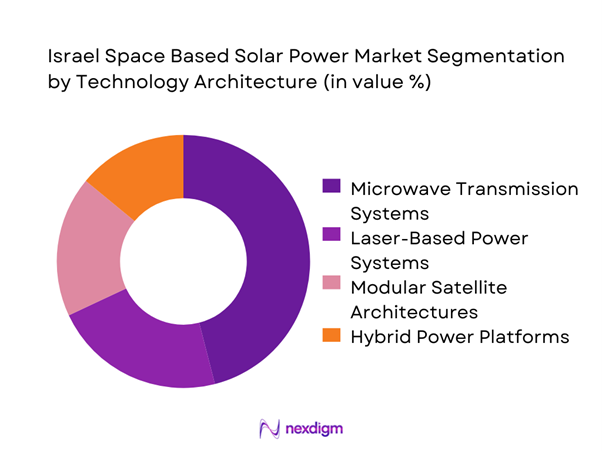
By Technology Architecture
Microwave-based power transmission dominates due to proven efficiency, mature component availability, and compatibility with existing satellite platforms. Laser-based systems remain in experimental phases, primarily supported by research institutions and defense agencies. Modular architectures are gaining traction as they allow scalable deployment and in-orbit assembly flexibility. Hybrid designs combining photovoltaic arrays with advanced beam control systems are increasingly prioritized. Technology selection is strongly influenced by transmission stability, safety standards, and orbital deployment feasibility.
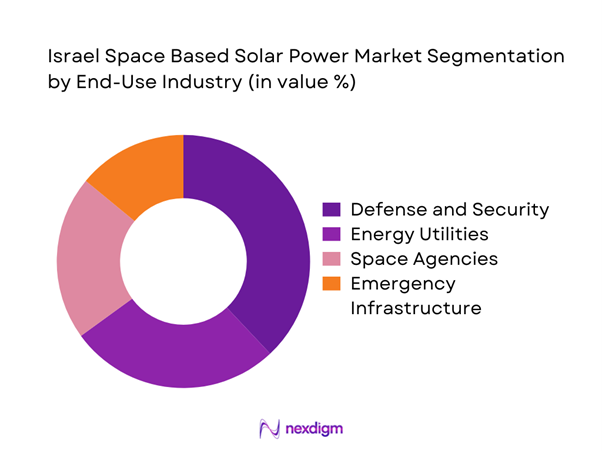
By End-Use Industry
Defense and national security applications account for the largest adoption due to continuous power requirements and strategic autonomy goals. Civil energy utilities follow, driven by long-term clean energy diversification plans. Space agencies utilize SBSP platforms for technology validation and orbital power experiments. Emergency and disaster management agencies increasingly evaluate SBSP for resilient backup power. Commercial infrastructure adoption remains limited but is gradually expanding through pilot projects.
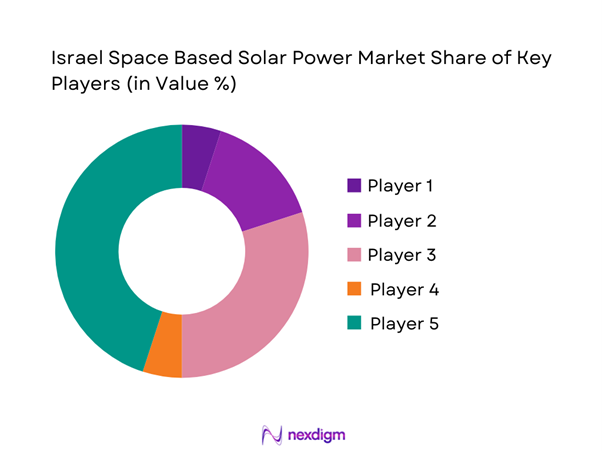
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by strong participation from aerospace manufacturers, defense contractors, and space technology developers. Market positioning depends on orbital engineering capability, system integration expertise, and regulatory alignment. Collaboration with government agencies remains essential for project execution and funding access.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus Defence and Space | 2014 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Space Based Solar Power Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising national energy security and resilience requirements
Israel increasingly prioritizes energy independence due to geopolitical sensitivities and infrastructure vulnerability concerns. Space based solar power offers uninterrupted generation independent of terrestrial constraints or climate variability. National defense strategies increasingly emphasize resilient off-grid energy availability. Satellite-based power supports critical installations during emergencies and grid disruptions. Government policy frameworks increasingly recognize space energy as strategic infrastructure. Research funding allocations reflect long-term energy security planning objectives. Energy diversification initiatives strengthen interest in orbital power alternatives. Defense agencies support pilot deployments for operational reliability validation. Cross-ministry coordination enhances program execution efficiency. These factors collectively accelerate institutional adoption of space-based solar technologies.
Limited land availability for terrestrial renewables
Israel faces geographical limitations restricting large-scale solar farm expansion within national boundaries. Urban density and environmental protection limit terrestrial renewable deployment options. Space-based systems provide scalable alternatives without land usage conflicts. Coastal and desert constraints further increase interest in orbital energy solutions. Infrastructure congestion encourages exploration of non-terrestrial generation models. Policy planners view space solar as complementary to rooftop installations. Limited grid expansion capability increases reliance on external generation sources. Energy planners increasingly evaluate orbital platforms for baseload stability. Strategic land conservation objectives reinforce interest in space-based power. These constraints collectively strengthen market momentum.
Challenges
High upfront capital expenditure and long development cycles
Space-based solar projects require extensive upfront investment before operational returns materialize. Long technology validation cycles delay commercial scalability and investor confidence. Capital intensity limits participation to government-backed or large industrial entities. Development timelines extend across multiple planning and testing phases. Budget approvals depend on long-term strategic alignment rather than short-term returns. Cost recovery remains uncertain during early deployment stages. Infrastructure buildout demands sustained financial commitment. Project delays can significantly impact overall feasibility assessments. Financing models remain under development across stakeholders. These factors collectively restrain rapid market expansion.
Technical risks in wireless power transmission efficiency
Power transmission losses remain a critical concern for commercial viability. Atmospheric interference can impact microwave or laser transmission stability. Precision alignment requirements increase system complexity and operational risk. Safety standards impose strict limits on transmission power density. Technology reliability under continuous operation remains under evaluation. System redundancy increases design complexity and costs. Transmission efficiency improvements require ongoing research investment. Regulatory scrutiny further slows large-scale deployment approval. Integration challenges with ground infrastructure persist. These technical risks constrain immediate commercialization potential.
Opportunities
Dual-use military and civilian power applications
Space-based solar systems offer strong alignment with both defense and civilian energy needs. Military installations benefit from autonomous and resilient power availability. Civilian infrastructure gains access to stable renewable energy sources. Dual-use frameworks improve investment justification and funding continuity. Shared infrastructure reduces overall system deployment costs. Defense validation accelerates technology maturity for civilian adoption. Policy alignment enables coordinated program development. Export potential increases through proven dual-use applications. Cross-sector collaboration strengthens innovation outcomes. These factors significantly enhance market attractiveness.
Export of SBSP technologies and subsystems
Israel’s advanced aerospace capabilities position it well for international SBSP component exports. Specialized subsystems can integrate into global space energy programs. Export opportunities extend to power transmission modules and control systems. Strategic partnerships enhance international market access. Global interest in clean energy supports technology demand growth. Defense-linked credibility strengthens export competitiveness. Regulatory harmonization supports cross-border collaboration. Innovation-driven exports diversify national technology portfolios. Long-term service agreements increase recurring revenue potential. Export expansion represents a major growth avenue.
Future Outlook
The Israel Space Based Solar Power market is expected to transition from pilot projects to structured deployment phases over the coming decade. Continued government backing and defense collaboration will remain critical enablers. Technological maturation and international partnerships are likely to improve commercial feasibility. Integration with national energy strategies will further strengthen adoption momentum. Long-term prospects remain favorable as space-based energy gains strategic importance.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Lockheed Martin
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Northrop Grumman
- Thales Alenia Space
- Boeing Defense
- Mitsubishi Electric
- OHB SE
- Maxar Technologies
- Redwire Space
- Raytheon Technologies
- Space Solar
- Solaren Corporation
Key Target Audience
- Government and regulatory bodies including Ministry of Energy and Israel Space Agency
- Defense and national security organizations
- Electric utility companies
- Aerospace and satellite manufacturers
- Infrastructure development agencies
- Renewable energy project developers
- Strategic investors and venture capital firms
- Technology integrators and system engineers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope was defined by analyzing space energy programs, national energy strategies, and orbital power initiatives. Key demand and supply variables were identified through sector mapping. Technology readiness and regulatory influences were assessed.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Qualitative and quantitative data were structured around application areas and technology segments. Trend analysis incorporated policy developments and infrastructure readiness. Market behavior patterns were evaluated across 2024 and 2025.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through discussions with aerospace engineers, energy planners, and policy stakeholders. Technical feasibility and adoption timelines were reviewed. Feedback loops refined assumptions and scenario modeling.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All findings were consolidated through triangulation of technical, regulatory, and industry perspectives. Insights were normalized to ensure consistency. Final outputs were structured to support strategic decision-making.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Orbital SBSP Scope Delimitation, Space-Based Solar Power System Taxonomy and Segmentation Logic, Bottom-Up Capacity and Revenue Estimation from Demonstration to Commercial Phases, Revenue Attribution across Space Segment and Ground Receiving Infrastructure)
- Definition and scope of space based solar power in the Israeli energy and space context
- Market evolution from research programs to pilot orbital platforms
- Power generation transmission and terrestrial reception pathways
- Ecosystem structure involving aerospace primes utilities and defense agencies
- Supply chain spanning launch services space hardware and rectenna infrastructure
- Regulatory and policy environment covering space activities spectrum allocation and energy regulation
- Growth Drivers
Rising national energy security and resilience requirements
Limited land availability for terrestrial renewables
Advancements in small satellite and reusable launch technologies
Government support for space and dual-use defense technologies
Long-term decarbonization and clean baseload power objectives - Challenges
High upfront capital expenditure and long development cycles
Technical risks in wireless power transmission efficiency
Regulatory complexity in spectrum and orbital slot allocation
Dependence on launch cost reductions and space logistics
Public acceptance and environmental safety concerns - Opportunities
Dual-use military and civilian power applications
Export of SBSP technologies and subsystems
Integration with national smart grid and storage systems
International collaboration on space energy missions
Spin-off innovations in wireless power and space robotics - Trends
Shift from concept studies to orbital demonstration missions
Increasing role of defense agencies in early adoption
Modular and scalable satellite power architectures
Public-private partnerships in space energy projects
Convergence of space technology and renewable energy ecosystems - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Unit Economics, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Low Earth Orbit SBSP Demonstration Satellites
Medium Earth Orbit Power Platforms
Geostationary Orbit Commercial Power Satellites
Hybrid Constellation-Based SBSP Fleets - By Application (in Value %)
Grid-Scale Baseload Power Supply
Defense and Strategic Energy Security
Remote and Off-Grid Power Supply
Emergency and Disaster Resilient Power - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Microwave Power Transmission Systems
Laser-Based Power Beaming Systems
Modular Sandwich Panel Architectures
In-Space Assembly and Robotics Enabled Platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
National Electric Utilities
Defense and Security Establishments
Space and Aerospace Agencies
Critical Infrastructure Operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Microwave Beaming Links
Laser Optical Links
Hybrid Microwave-Laser Links
Ground Rectenna Network Integration - By Region (in Value %)
Central Israel
Northern Israel
Southern Israel
Offshore and Strategic Remote Zones
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Orbital capability, Power transmission efficiency, Launch integration strategy, Technology readiness level, Cost per delivered kilowatt, Defense sector alignment, Partnership ecosystem strength, R&D investment intensity)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
Boeing
Airbus Defence and Space
Thales Alenia Space
Mitsubishi Electric
OHB SE
Maxar Technologies
Redwire Space
Solaren Corporation
Space Solar
Raytheon Technologies
- Demand and utilization drivers across civilian and defense sectors
- Procurement and tender dynamics led by government agencies
- Buying criteria including reliability lifecycle cost and security
- Budget allocation models and long-term financing preferences
- Implementation barriers technical regulatory and operational
- Post-purchase service monitoring and upgrade expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Unit Economics, 2026–2035


