Market Overview
The Israel Space Batteries market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady expansion supported by satellite manufacturing activity and defense-led space programs. Recent output volumes and system deployments indicate consistent demand across civil and military missions, with production levels aligned to mission-specific energy density requirements. Technology adoption remains concentrated around lithium-based architectures, while integration depth has increased across platforms. Continuous testing cycles and qualification standards contribute to stable development momentum and predictable procurement behavior across space-grade battery applications.
The market is primarily concentrated in central and southern Israel, where aerospace infrastructure, defense clusters, and satellite integration facilities are located. Strong collaboration between government agencies, defense contractors, and private space companies drives localized demand. The presence of testing laboratories, cleanroom manufacturing, and launch coordination capabilities supports ecosystem maturity. Policy backing for national space programs and technology exports further strengthens regional dominance and long-term industry sustainability.
Market Segmentation
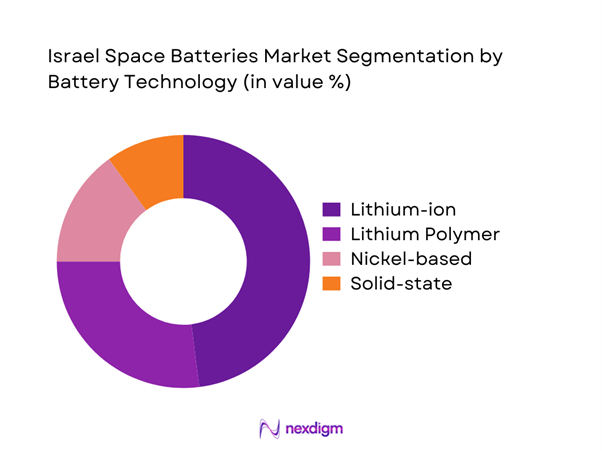
By Battery Technology
The lithium-ion segment dominates due to high energy density, flight heritage, and compatibility with small satellite platforms. Lithium polymer systems follow closely, driven by form factor flexibility and thermal stability advantages. Nickel-based chemistries maintain limited adoption in legacy platforms due to reliability in extreme environments. Emerging solid-state batteries are gaining interest for long-duration missions, supported by research initiatives. Technology choice is largely influenced by mission life, radiation tolerance, and integration complexity rather than cost alone.
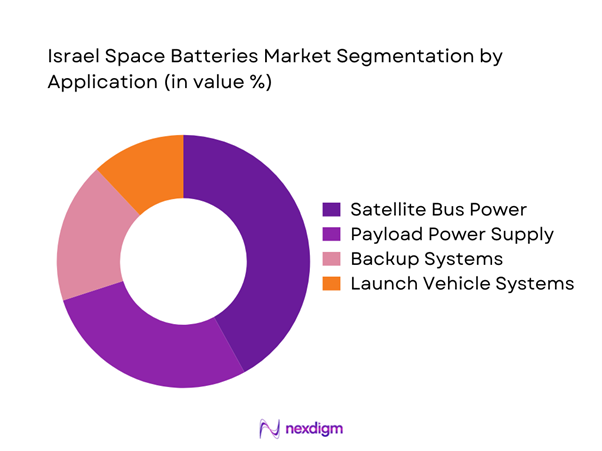
By Application
Satellite bus power systems represent the largest application segment due to continuous onboard energy requirements. Payload power supply follows closely, driven by high-performance imaging and communication loads. Backup and redundancy systems maintain consistent demand across missions. Launch vehicle power applications remain niche but stable. Growth is influenced by increasing satellite miniaturization and mission duration requirements rather than launch frequency alone.
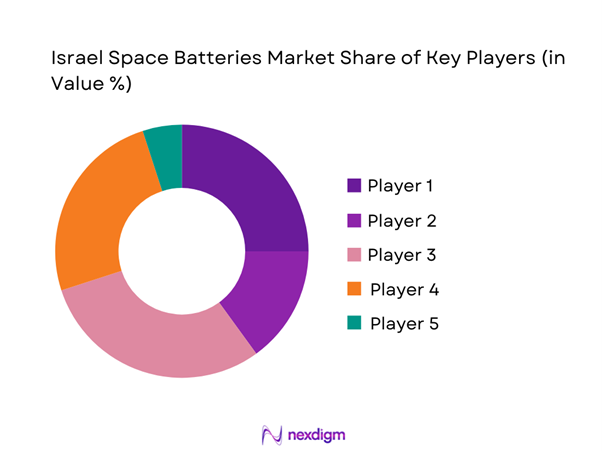
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of defense-aligned manufacturers and specialized space technology providers. Companies focus on qualification depth, reliability, and long-term mission support rather than price competition. Strategic partnerships with satellite integrators and government agencies shape positioning. Entry barriers remain high due to certification complexity and mission-critical performance expectations.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Epsilor Electric Fuel | 2000 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SpacePharma | 2012 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Space Batteries Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising domestic satellite manufacturing programs
Israel’s expanding satellite production ecosystem has accelerated demand for reliable onboard power storage solutions. Government-backed missions increased satellite output volumes across defense and commercial categories. Local manufacturing capabilities encouraged tighter integration between battery suppliers and system integrators. Engineering collaboration improved power system customization for varying orbital requirements. Standardization across satellite platforms increased repeat procurement cycles. Battery qualification pipelines expanded in response to increased payload diversity. Production scheduling alignment reduced lead times for energy subsystem deliveries. Demand stability improved due to multi-mission planning approaches. Indigenous manufacturing reduced reliance on external suppliers significantly. These factors collectively strengthened sustained demand growth across recent operational cycles.
Increased defense and intelligence satellite deployments
Defense-led satellite deployments significantly increased demand for high-reliability battery systems. Intelligence missions require uninterrupted power across extended operational lifetimes. Battery redundancy standards increased to meet mission-critical reliability benchmarks. Deployment frequency rose with enhanced surveillance and communication needs. Power system specifications became more stringent due to sensitive payload requirements. Secure supply chain requirements favored domestic battery developers. Defense procurement cycles supported predictable ordering patterns. Testing protocols expanded to simulate harsh orbital conditions. Energy density optimization became a primary design consideration. These developments reinforced consistent procurement momentum within defense programs.
Challenges
High qualification and testing costs
Space-grade battery qualification involves extensive thermal, vacuum, and radiation testing cycles. These procedures significantly increase development timelines and operational expenditures. Specialized facilities are required to meet space certification standards. Smaller manufacturers face financial constraints entering qualification phases. Iterative testing prolongs product commercialization timelines. Limited testing infrastructure creates scheduling bottlenecks. Requalification is often required for minor design modifications. These factors collectively restrict rapid innovation adoption. Cost pressures affect pricing flexibility across supply contracts. This challenge remains a structural constraint for market scalability.
Radiation and thermal stability constraints
Space radiation exposure significantly degrades battery performance over time. Thermal fluctuations require advanced material engineering solutions. Design complexity increases to manage orbital temperature variations. Shielding adds weight penalties affecting satellite payload efficiency. Material degradation impacts long-term mission reliability. Testing for radiation resilience requires extended validation cycles. Performance uncertainty limits adoption of newer chemistries. Engineering trade-offs affect energy density targets. Environmental resilience remains a persistent technical barrier. These limitations influence design conservatism across the industry.
Opportunities
Expansion of small satellite constellations
Growth in small satellite constellations is creating sustained demand for compact power systems. Shorter development cycles favor modular battery architectures. Constellation deployment increases volume requirements across standardized platforms. Manufacturers benefit from repeatable design frameworks. Cost optimization becomes feasible through scaled production runs. Demand for lightweight batteries continues to increase. Energy efficiency improvements support longer operational lifetimes. Integration simplicity becomes a competitive differentiator. Mission diversity expands application-specific battery customization. This trend creates long-term growth potential across the market.
Development of solid-state space batteries
Solid-state battery development offers significant performance and safety advantages. Higher energy density enables extended mission durations. Improved thermal stability reduces cooling system complexity. Lower degradation rates enhance lifecycle reliability. Research programs support accelerated prototype validation. Adoption potential increases for deep-space missions. Manufacturing scalability remains under development but promising. Reduced fire risk improves system safety compliance. Material innovation drives competitive differentiation. This opportunity positions next-generation technologies for future adoption.
Future Outlook
The Israel space batteries market is expected to evolve steadily through 2035, driven by expanding satellite programs and technology innovation. Increased focus on small satellite deployments and advanced battery chemistries will shape development priorities. Policy support and defense investments are likely to sustain demand. Long-term growth will depend on qualification efficiency and next-generation energy storage adoption.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Epsilor Electric Fuel
- SpacePharma
- SolarEdge Technologies
- Tadiran Batteries
- Arotech
- Gilat Satellite Networks
- Orbit Communication Systems
- Batim Advanced Power
- Brenmiller Energy
- StoreDot
- Addionics
- CellEra
Key Target Audience
- Satellite manufacturers and integrators
- Defense and aerospace procurement agencies
- Israeli Space Agency
- Ministry of Defense Israel
- Commercial satellite operators
- Launch service providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Space technology system integrators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key technical, operational, and application-level variables were identified through industry mapping and mission architecture assessment. Focus was placed on battery chemistries, deployment environments, and system integration requirements.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was developed using application segmentation, technology classification, and deployment patterns. Demand mapping incorporated production cycles and mission planning frameworks.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through expert discussions with engineers, integrators, and procurement specialists. Assumptions were refined based on operational constraints and technology readiness levels.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Data points were consolidated through triangulation and scenario analysis. Final outputs were structured to reflect market behavior, risks, and future growth pathways.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and satellite-grade battery classification, platform-based segmentation and orbit-specific taxonomy, bottom-up market sizing using satellite production and launch data, revenue attribution by battery chemistry and mission profile, primary validation with Israeli space integrators and power system suppliers, triangulation using launch manifests and defense procurement disclosures, assumptions on lifecycle replacement and in-orbit degradation)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission-critical power requirements
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and sourcing dynamics
- Regulatory and space qualification environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising domestic satellite manufacturing programs
Increased defense and intelligence satellite deployments
Growing small satellite and nano-satellite missions
Advancements in lithium-based space-grade batteries
Government-backed space R&D investments - Challenges
High qualification and testing costs
Radiation and thermal stability constraints
Limited domestic supply chain depth
Long development and validation cycles
Stringent space agency certification requirements - Opportunities
Expansion of small satellite constellations
Development of solid-state space batteries
Export opportunities for Israeli space subsystems
Public–private space collaboration programs
Dual-use battery technology commercialization - Trends
Shift toward high energy-density battery chemistries
Miniaturization of power storage systems
Increased adoption of modular battery architectures
Focus on longer mission life cycles
Integration of smart battery management systems - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
LEO satellites
MEO satellites
GEO satellites
Deep space and interplanetary missions
Defense and intelligence satellites - By Application (in Value %)
Power storage for satellite bus
Payload power supply
Launch vehicle subsystems
Backup and redundancy systems
Onboard energy management - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Lithium-ion batteries
Lithium polymer batteries
Nickel-hydrogen batteries
Solid-state batteries
Hybrid battery systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense and intelligence
Commercial satellite operators
Space research organizations
Telecommunications
Earth observation and remote sensing - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone satellite systems
Constellation-based systems
Inter-satellite linked platforms
Ground-synchronized systems - By Region (in Value %)
Central Israel
Southern Israel
Northern Israel
Rest of Israel
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology maturity, energy density, cycle life, radiation tolerance, pricing, production scalability, qualification standards, customer base)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
SpacePharma
SolarEdge Technologies
Epsilor Electric Fuel
Saft Groupe
GS Yuasa
EaglePicher Technologies
ABS Batteries
VARTA Space & Defense
AAC Clyde Space
Saft America
Exide Technologies
Enersys
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


