Market Overview
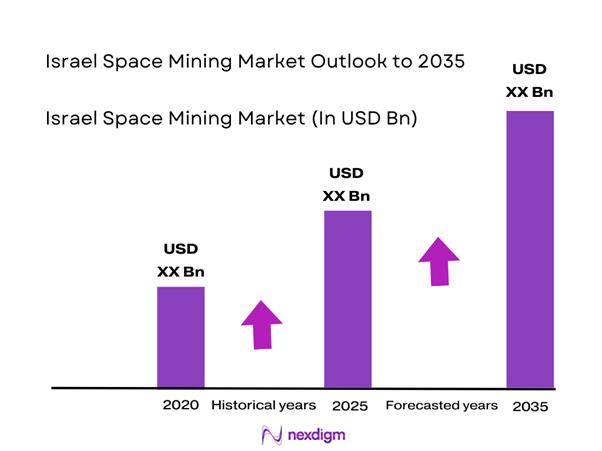
The Israel Space Mining market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting early-stage commercialization supported by advanced aerospace capabilities and targeted government initiatives. Activity levels in the most recent period showed approximately ~ missions under development and ~ technology validation programs. Investment intensity remains moderate, with pilot projects dominating operational focus. The market demonstrates strong alignment with national innovation priorities, supported by expanding private participation and growing interest in extraterrestrial resource utilization technologies.
Israel’s space mining ecosystem is concentrated around technology clusters in central and southern regions, supported by mature aerospace infrastructure and defense-linked research institutions. Demand concentration is driven by advanced robotics development, propulsion testing facilities, and satellite systems integration capabilities. The ecosystem benefits from close collaboration between government agencies, startups, and defense contractors. Regulatory support, streamlined testing approvals, and access to launch partnerships further reinforce market maturity and operational readiness.
Market Segmentation
By Application
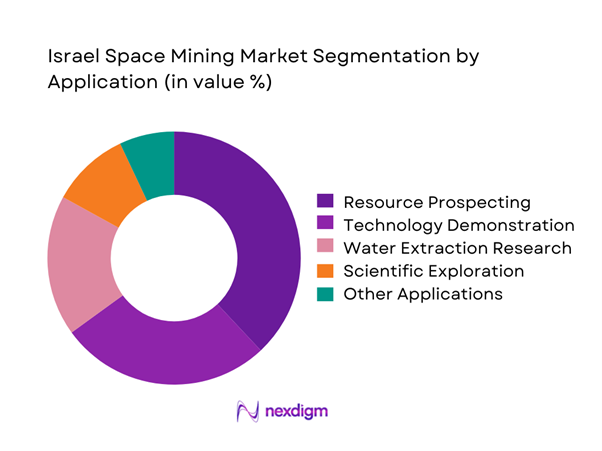
The application landscape is dominated by resource prospecting and technology demonstration missions, which account for the majority of ongoing development activities. Water extraction research and in-space resource validation programs receive substantial attention due to their long-term role in orbital refueling and mission sustainability. Scientific payload deployment remains a critical secondary application, supporting mineral identification and surface analysis. The dominance of exploratory missions reflects Israel’s strategic focus on capability validation before commercial-scale extraction. Growing alignment with international lunar initiatives is strengthening application diversity, while increasing emphasis on autonomous operations is shaping future deployment models across mission categories.
By Technology Architecture
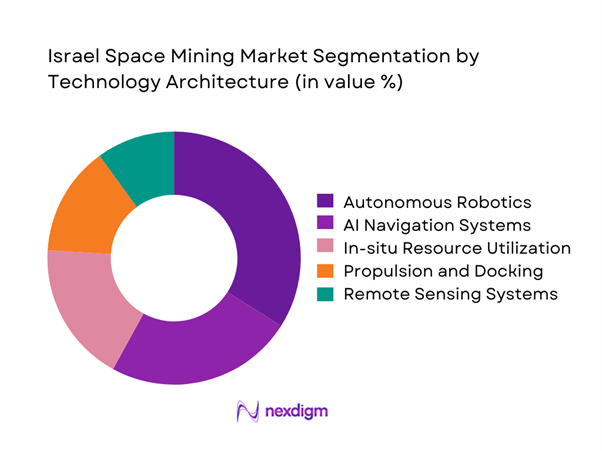
Technology architecture segmentation is led by autonomous robotic systems due to their critical role in hostile space environments. AI-enabled navigation and sensing platforms follow closely, enabling precision operations and real-time decision-making. In-situ resource utilization systems are gaining momentum as mission designs shift toward sustainability. Propulsion and docking technologies remain essential for mission execution, while remote sensing platforms support data-driven exploration strategies. Continuous innovation in robotics and software integration is strengthening system reliability, enabling Israel to maintain competitiveness in advanced space mining architectures.
Competitive Landscape
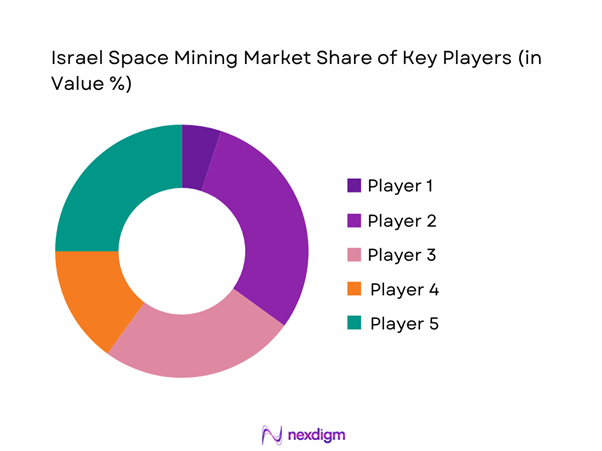
The competitive landscape of the Israel space mining market is characterized by a mix of defense-origin enterprises, space-focused startups, and technology integrators. Market competition centers on system reliability, autonomous capabilities, and mission-readiness rather than scale. Collaboration with government agencies and international partners plays a crucial role in project execution. Intellectual property development and systems engineering depth serve as key differentiators across participants.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SpaceIL | 2011 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Helios Space Corporation | 2018 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Space Mining Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Government-backed space innovation programs
Government-backed space innovation programs significantly influence Israel’s space mining development through sustained policy alignment and strategic funding frameworks. These initiatives support technology validation, prototype testing, and collaborative research with national aerospace entities. Public programs encourage participation from startups and established defense firms, accelerating technological maturity. Regulatory clarity offered through these programs reduces operational uncertainty and investment hesitation. Structured grant mechanisms enable continuous experimentation across propulsion, robotics, and sensing technologies. National space agendas prioritize long-term exploration capabilities, reinforcing sector stability. Government-backed missions create demand for indigenous technologies and system integration expertise. Institutional support strengthens international partnerships and data-sharing opportunities. These programs also foster talent development through specialized research initiatives. Overall, government involvement provides foundational stability for sustained market progression.
Rising demand for in-space resources and fuel
Rising demand for in-space resources and fuel is reshaping mission economics and strategic planning priorities. Increased satellite deployments have intensified interest in orbital refueling solutions and resource independence. Water-derived fuel concepts are gaining traction as viable enablers of extended missions. Demand is reinforced by growing ambitions for lunar and deep-space exploration programs. Mission planners increasingly prioritize in-space resource utilization to reduce launch dependency. Technological feasibility demonstrated in recent trials has accelerated industry confidence. This demand encourages investment in extraction, storage, and processing systems. Commercial entities view in-space resources as essential for long-duration missions. Strategic autonomy considerations further amplify demand growth. Collectively, these factors position resource utilization as a central market driver.
Challenges
High capital investment requirements
High capital investment requirements remain a significant barrier for Israel’s space mining initiatives. Development of space-grade systems requires extended research cycles and specialized engineering expertise. Infrastructure costs related to testing, validation, and launch integration are substantial. Limited access to large-scale funding restricts rapid commercialization efforts. Private investors often perceive long development timelines as financial risk. Capital intensity also limits participation of smaller technology firms. Dependence on government grants can constrain operational flexibility. Cost overruns during development phases further increase financial exposure. Scaling from prototype to mission-ready systems remains capital intensive. These factors collectively slow market expansion and deployment timelines.
Technological uncertainties and mission risk
Technological uncertainties and mission risk present ongoing challenges for space mining operations. Limited operational history creates uncertainty around system reliability in extraterrestrial environments. Harsh space conditions impose significant engineering constraints on equipment performance. Autonomous system failures can result in complete mission loss. Testing limitations on Earth restrict accurate simulation of space conditions. Integration of multiple complex subsystems increases operational risk. Data transmission delays complicate real-time decision-making processes. Limited redundancy options elevate mission vulnerability. Risk mitigation strategies often increase development complexity and cost. These uncertainties continue to challenge investor confidence and project scalability.
Opportunities
Lunar water extraction for refueling
Lunar water extraction for refueling represents a transformative opportunity for Israel’s space mining sector. Availability of water resources enables production of hydrogen-based propellants in space. This capability significantly reduces dependency on Earth-launched fuel. Refueling infrastructure supports longer mission durations and expanded exploration scope. Growing international lunar missions increase demand for localized fuel supply. Technological advancements are improving extraction and processing feasibility. Strategic positioning in lunar initiatives enhances collaboration potential. Israel’s expertise in robotics supports efficient extraction system development. Long-term cost efficiencies strengthen commercial viability. This opportunity aligns with global exploration roadmaps and sustainability goals.
Public-private partnerships in space exploration
Public-private partnerships in space exploration offer significant growth potential for the Israeli space mining ecosystem. Collaborative frameworks reduce financial risk through shared investment models. Government participation enhances credibility and regulatory access for private entities. Private sector innovation accelerates technology development cycles. Partnerships enable access to testing facilities and mission platforms. Joint ventures facilitate knowledge transfer and workforce development. Such collaborations attract international interest and co-investment opportunities. Risk-sharing mechanisms improve project feasibility and scalability. Coordinated missions strengthen national space capabilities. These partnerships are essential for long-term market expansion.
Future Outlook
The Israel space mining market is expected to advance steadily through increased mission activity and technology maturation. Continued government backing and international collaborations will enhance operational readiness. Advancements in autonomous systems and resource utilization technologies will shape future deployments. The market is likely to witness gradual transition from experimental missions to structured commercial programs over the forecast period.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- SpaceIL
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Helios Space Corporation
- Astroscale
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Blue Origin
- Astrobotic Technology
- ispace Inc.
- Moon Express
- Planetary Resources
- Deep Space Industries
- Airbus Defence and Space
Key Target Audience
- Space technology investment firms
- Venture capital and private equity funds
- Israel Space Agency
- Ministry of Innovation, Science and Technology
- Defense procurement authorities
- Satellite and launch service providers
- Aerospace component manufacturers
- Space mission integrators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables related to technology readiness, mission type, and regulatory environment were identified. Industry-specific parameters were mapped to understand operational dependencies. Key performance indicators were selected to reflect market dynamics accurately.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was structured around application areas, technology platforms, and deployment models. Qualitative and quantitative inputs were aligned to establish coherent market structure. Scenario analysis supported evaluation of development trajectories.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through expert consultations across aerospace engineering, policy, and mission design domains. Assumptions were refined based on operational feasibility and technology readiness assessments.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated insights were consolidated into structured analysis formats. Cross-verification ensured consistency across sections. Final outputs were aligned with industry terminology and strategic relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope for Space Resource Utilization, Space Mining Value Chain Mapping and Segmentation Logic, Bottom-Up Market Sizing Based on Mission Programs and Investments, Revenue Attribution by Technology and Mission Phase, Primary Interviews with Space Agencies and Commercial Operators, Data Triangulation Using Satellite Launch and Payload Databases, Assumptions and Limitations Related to Mission Timelines and Regulatory Uncertainty)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission development pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and value chain framework
- Regulatory and policy environment
- Growth Drivers
Government-backed space innovation programs
Rising demand for in-space resources and fuel
Advancements in autonomous robotics and AI
Strategic focus on space sovereignty
Growing private sector participation
Declining launch and mission costs - Challenges
High capital investment requirements
Technological uncertainties and mission risk
Limited commercial-scale mining precedents
Regulatory ambiguity in space resource ownership
Long development and ROI cycles
Reliance on international launch capabilities - Opportunities
Lunar water extraction for refueling
Public-private partnerships in space exploration
Export of space mining technologies
Integration with satellite servicing missions
Development of in-orbit manufacturing ecosystems
Strategic collaborations with global space agencies - Trends
Miniaturization of mining payloads
Use of AI-driven autonomous mining systems
Rise of dual-use space technologies
Increased venture funding in space startups
Focus on sustainable space operations
Growth of lunar exploration missions - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Revenue per Mission, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Robotic mining spacecraft
Prospecting and exploration probes
Orbital processing platforms
Lunar surface mining units
Asteroid capture vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Water extraction and fuel production
Rare earth and metal extraction
In-space manufacturing feedstock
Scientific exploration
Technology demonstration missions - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Autonomous robotic systems
AI-enabled navigation and extraction
In-situ resource utilization systems
Propulsion and docking systems
Remote sensing and analytics platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Space agencies and government programs
Commercial space mining companies
Satellite operators
Defense and aerospace contractors
Research institutions - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Deep space communication networks
Satellite relay systems
Ground station integration
Inter-satellite communication links - By Region (in Value %)
Israel
North America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
Rest of the World
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology readiness level, mission success rate, payload capability, investment scale, partnership network, IP portfolio, launch access, geographic presence)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
SpaceIL
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Helios Space Corporation
Astroscale
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
Blue Origin
Astrobotic Technology
ispace Inc.
Moon Express
Planetary Resources
Deep Space Industries
Airbus Defence and Space
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Revenue per Mission, 2026–2035


