Market Overview
The Israel space propulsion systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by consistent investments across defense and commercial space programs. Activity levels in 2024 and 2025 reflected steady mission deployment volumes, increased subsystem qualification programs, and sustained satellite manufacturing throughput. Demand remained concentrated around propulsion modules, control subsystems, and mission-critical components supporting orbital insertion and maneuvering. Technology development cycles were influenced by defense requirements, miniaturization priorities, and platform reliability standards across space missions.
The market is primarily concentrated around established aerospace and defense clusters, with activity centered in regions hosting satellite manufacturing, propulsion testing, and defense research infrastructure. Strong collaboration between government agencies, defense contractors, and private technology firms supports ecosystem maturity. Policy alignment with national space programs, defense modernization initiatives, and export compliance frameworks continues to shape deployment patterns, supplier participation, and technology commercialization pathways.
Market Segmentation
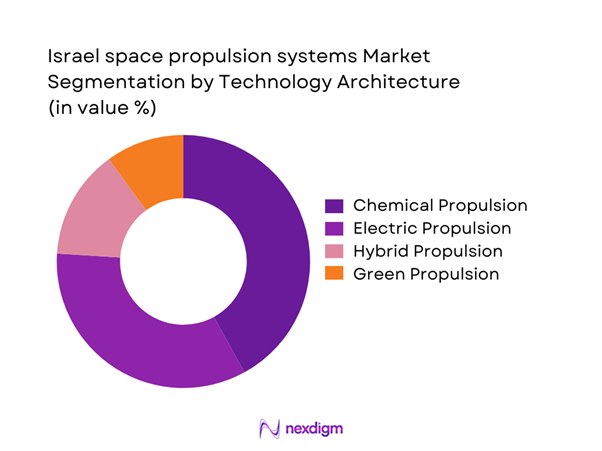
By Technology Architecture
The market is dominated by chemical and electric propulsion technologies, with electric systems gaining traction due to efficiency and long-duration mission suitability. Chemical propulsion continues to hold importance for launch and rapid maneuvering applications. Hybrid and green propulsion systems are gradually entering operational use, supported by sustainability initiatives and regulatory preferences. Technology selection is closely linked to mission profile, satellite mass class, and endurance requirements. Israeli programs increasingly prioritize modular architectures that enable flexibility across defense and commercial missions while maintaining high reliability under extreme operating conditions.
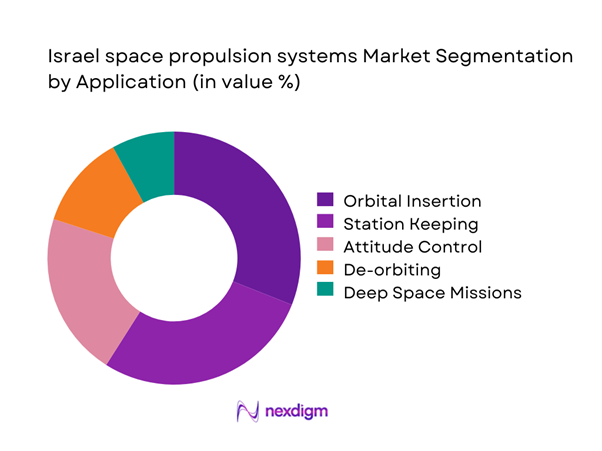
By Application
Application-based segmentation is driven by orbital insertion, station keeping, and attitude control requirements. Defense and reconnaissance missions dominate propulsion utilization due to higher maneuverability and reliability demands. Commercial satellite operations increasingly adopt propulsion systems optimized for life extension and fuel efficiency. Deep space and exploration missions remain limited but show growing adoption of advanced propulsion technologies. Application diversity continues to expand as satellite constellations increase and mission profiles become more complex.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established aerospace companies and specialized propulsion developers. Market participants focus on technological differentiation, system reliability, and compliance with defense-grade standards. Competitive intensity is shaped by long development cycles, high entry barriers, and strong government involvement in procurement decisions.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus Defence and Space | 2014 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel space propulsion systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising defense satellite deployment
Rising defense satellite deployment continues to drive propulsion demand across surveillance, reconnaissance, and secure communication missions. Defense agencies increased satellite launches during 2024 to enhance real-time intelligence and monitoring capabilities. Propulsion systems remain critical for orbital positioning and maneuverability across these defense platforms. Increased geopolitical tensions have reinforced investment priorities toward space-based defense assets. Domestic manufacturing capabilities are expanding to support rapid deployment schedules. Mission reliability requirements further elevate propulsion system performance expectations. Defense programs emphasize long operational life and precise orbital adjustments. Propulsion technology upgrades remain essential to sustain extended mission durations. Continuous innovation supports enhanced thrust efficiency and fuel optimization. These factors collectively reinforce sustained propulsion demand across defense applications.
Expansion of small satellite missions
Expansion of small satellite missions has accelerated propulsion adoption across commercial and governmental space programs. Small satellites increasingly require compact and efficient propulsion for orbit maintenance. In 2024, deployment volumes for small satellites continued rising across multiple mission categories. Cost-efficient propulsion architectures are becoming essential for constellation-based operations. Manufacturers focus on miniaturization without compromising performance or reliability. Modular propulsion units enable faster satellite integration and deployment cycles. Growing launch frequency supports recurring propulsion system demand. Increased payload diversity also drives specialized propulsion configurations. Technological advances support improved thrust-to-weight ratios for small platforms. These developments collectively strengthen propulsion system utilization in small satellite missions.
Challenges
High development and qualification costs
High development and qualification costs remain a significant barrier for propulsion system advancement. Extensive testing requirements increase development timelines and capital intensity. Qualification procedures demand compliance with stringent aerospace and defense standards. Engineering iterations often require multiple validation cycles before deployment approval. Specialized testing facilities further elevate operational expenditure. Smaller manufacturers face financial constraints during prolonged development phases. Cost pressures can limit experimentation with emerging propulsion technologies. Certification requirements vary across mission profiles and agencies. These factors collectively restrict rapid commercialization of innovative propulsion systems. Managing cost efficiency remains a critical challenge for industry participants.
Export control and ITAR restrictions
Export control and ITAR restrictions significantly affect international collaboration and technology transfer. Compliance requirements limit component sourcing and cross-border partnerships. Licensing procedures often extend project timelines and increase administrative complexity. Restricted technology sharing impacts joint development initiatives with foreign entities. Manufacturers must implement strict documentation and compliance systems. These controls influence supplier selection and market access strategies. Export limitations also affect scalability for commercially viable propulsion products. Regulatory uncertainty can delay procurement and deployment schedules. Navigating compliance frameworks requires specialized legal and operational expertise. Overall, export controls remain a persistent operational constraint.
Opportunities
Miniaturized propulsion for smallsats
Miniaturized propulsion for smallsats presents significant growth potential across commercial and defense missions. Increasing small satellite deployments create demand for compact propulsion solutions. Advances in materials and micro-thruster design enable improved performance efficiency. Reduced mass requirements enhance payload capacity and mission flexibility. Developers are focusing on scalable designs suitable for constellation deployment. Integration simplicity improves manufacturing and assembly timelines. Market interest is growing for propulsion systems compatible with standardized satellite platforms. Performance optimization supports longer mission lifecycles. These factors collectively position miniaturized propulsion as a key opportunity area. Continued innovation will accelerate adoption across mission profiles.
Electric propulsion adoption growth
Electric propulsion adoption growth is driven by efficiency advantages and extended operational life. Operators increasingly prefer electric systems for station keeping and orbit adjustments. Lower propellant mass enables higher payload utilization. Technological maturity has improved reliability and thrust performance. Electric propulsion supports cost-effective long-duration missions. Integration with power-efficient satellite platforms enhances overall mission economics. Development activity increased during 2024 and 2025 across multiple programs. Government-backed initiatives further encourage adoption of electric propulsion. Market confidence continues to strengthen as in-orbit performance data accumulates. This trend supports sustained long-term growth opportunities.
Future Outlook
The market outlook remains positive as Israel continues strengthening its space and defense capabilities through sustained investment and technological advancement. Increased collaboration between government agencies and private firms is expected to accelerate innovation. Emphasis on small satellite platforms and electric propulsion will shape future development priorities. Regulatory stability and expanding mission requirements are likely to support consistent market expansion through 2035.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Northrop Grumman
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Thales Alenia Space
- OHB SE
- Safran
- Moog Inc.
- ArianeGroup
- Exotrail
- Accion Systems
- Phase Four
- L3Harris Technologies
- Rocket Lab
Key Target Audience
- Defense and space procurement agencies
- National space agencies
- Satellite manufacturers
- Launch service providers
- Aerospace system integrators
- Government and regulatory bodies including Israel Space Agency
- Investments and venture capital firms
- In-orbit service and satellite operators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables were identified through analysis of propulsion technologies, mission profiles, regulatory frameworks, and deployment trends across Israeli space programs.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was developed using application mapping, technology classification, and program-level assessment of propulsion utilization patterns.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through expert discussions with engineers, program managers, and industry specialists involved in propulsion development.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation, ensuring consistency across qualitative insights, deployment data, and technology trends.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and propulsion system scope mapping, Platform and mission-based segmentation framework, Bottom-up propulsion unit and subsystem market sizing, Revenue attribution by propulsion type and mission class, Primary validation with Israeli space agencies and propulsion OEMs, Data triangulation across launch, satellite, and defense programs, Assumptions and constraints related to classified defense programs)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution and strategic importance
- Mission and application landscape
- Ecosystem structure and value chain
- Supply chain and manufacturing footprint
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising defense satellite deployment
Expansion of small satellite missions
Government funding for indigenous space capabilities
Growing demand for high-efficiency propulsion
Increasing commercial launch activities
Strategic national security investments - Challenges
High development and qualification costs
Export control and ITAR restrictions
Limited economies of scale
Complex integration and testing cycles
Long certification timelines
Dependence on government budgets - Opportunities
Miniaturized propulsion for smallsats
Electric propulsion adoption growth
Dual-use defense and commercial platforms
International collaboration programs
In-orbit servicing and maneuvering demand - Trends
Shift toward electric and green propulsion
Increased use of modular propulsion units
Focus on long-duration mission capability
Adoption of additive manufacturing
Rising interest in autonomous propulsion control - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Launch vehicles
LEO satellites
MEO and GEO satellites
Deep space and exploration platforms
Defense and ISR spacecraft - By Application (in Value %)
Orbital insertion
Attitude and orbit control
Station keeping
De-orbiting and end-of-life maneuvering
Deep space propulsion - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Chemical propulsion
Electric propulsion
Hybrid propulsion
Cold gas propulsion
Green propulsion systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense and military
Commercial satellite operators
Government space agencies
Research institutions
Private launch service providers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Autonomous propulsion systems
Ground-controlled propulsion
Hybrid command and autonomous systems - By Region (in Value %)
Israel domestic programs
North America collaborations
Europe partnerships
Asia-Pacific cooperation
Rest of world missions
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology maturity, propulsion type portfolio, mission compatibility, production capacity, pricing strategy, government contracts exposure, export capability, R&D intensity)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
IMI Systems
Aerojet Rocketdyne (L3Harris)
Northrop Grumman
Safran
Airbus Defence and Space
Thales Alenia Space
OHB SE
Moog Inc.
Exotrail
Accion Systems
Phase Four
ArianeGroup
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


