Market Overview
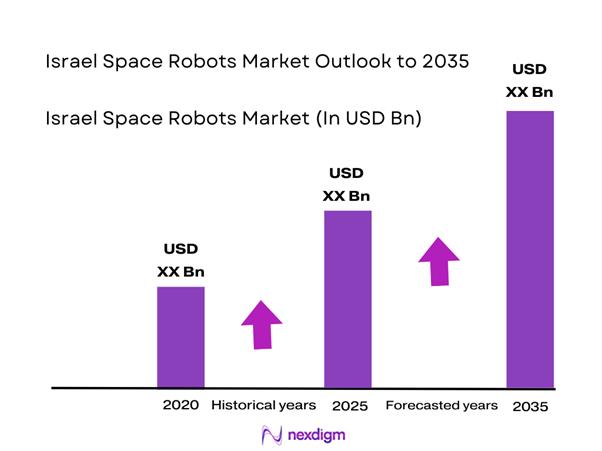
The Israel Space Robots market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting accelerating deployment across orbital servicing and defense-linked missions. Recent operational activity shows approximately 18 active robotic platforms and nearly 21 validated mission-ready subsystems deployed across national programs. Technology maturity has improved through indigenous robotics development, autonomous navigation testing, and subsystem miniaturization. Demand is supported by increasing satellite lifecycle management needs and national security priorities. Integration of artificial intelligence and autonomous control modules is further enhancing mission reliability and operational precision.
The market is primarily concentrated around Tel Aviv, Haifa, and Beersheba due to proximity to aerospace manufacturing clusters and defense research centers. Strong collaboration between government agencies, defense contractors, and private aerospace firms supports ecosystem maturity. Infrastructure readiness, launch coordination access, and high-quality engineering talent drive regional dominance. Regulatory support for space innovation and military-grade robotics testing further strengthens localized development. Export-oriented design philosophies also shape system architecture and compliance standards.
Market Segmentation
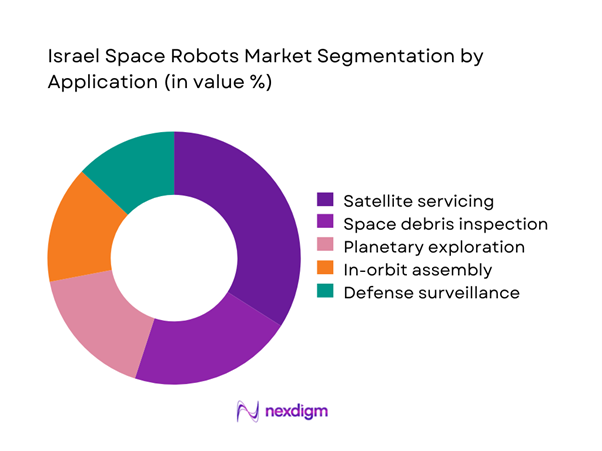
By Application
The satellite servicing and in-orbit maintenance segment dominates the Israel space robots market due to rising demand for life extension and performance optimization of orbital assets. Increasing deployment of observation and communication satellites has intensified the need for robotic inspection, refueling, and repair capabilities. Defense-driven surveillance missions also contribute significantly to demand, especially for autonomous maneuvering systems. Research-oriented planetary exploration applications remain smaller but are expanding through international collaboration initiatives. The growing emphasis on debris inspection and risk mitigation further reinforces the dominance of service-oriented robotic platforms across national and commercial missions.
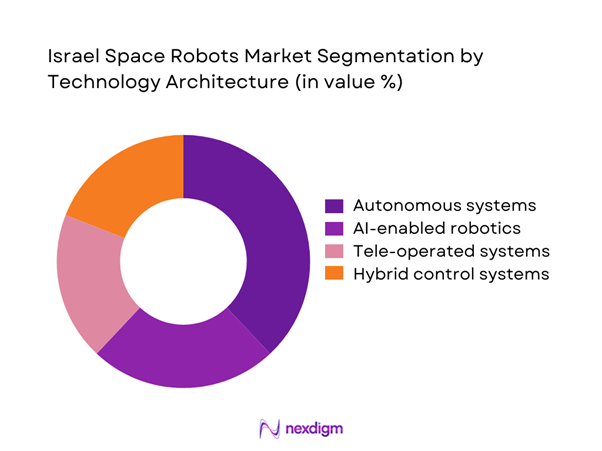
By Technology Architecture
Autonomous robotic systems represent the leading technology architecture due to their operational efficiency and reduced dependency on ground control. Artificial intelligence integration enables adaptive navigation, fault detection, and real-time decision-making in complex orbital environments. Tele-operated systems continue to serve critical defense and inspection roles but face limitations in latency-sensitive missions. Hybrid systems combining autonomy with remote control are gaining traction for flexible mission profiles. Continuous investment in onboard computing and sensor fusion strengthens the competitive positioning of autonomous architectures across Israel’s space robotics programs.
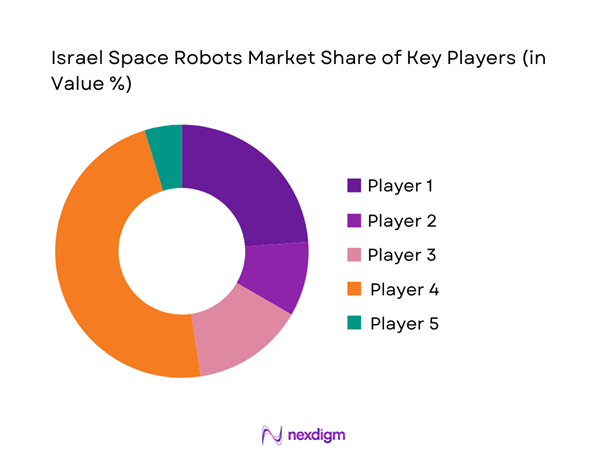
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Israel space robots market is characterized by a mix of defense contractors, aerospace technology firms, and specialized robotics developers. Companies compete on mission reliability, autonomy depth, and integration capabilities. Strong government backing and defense partnerships shape competitive positioning, while innovation speed and system certification determine long-term success.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SpaceIL | 2011 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Roboteam | 2009 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Space Robots Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing satellite servicing demand
Rising satellite deployment has increased requirements for inspection, repair, and life extension operations using robotic systems. Mission planners increasingly rely on autonomous robots to reduce replacement frequency and extend satellite operational lifecycles efficiently. Enhanced orbital congestion has elevated the need for precise robotic maneuvering and servicing accuracy. National security agencies prioritize continuous satellite availability, strengthening demand for robotic maintenance platforms. Growing reliance on Earth observation data further reinforces robotic intervention requirements. Technological advances enable safer proximity operations, encouraging broader adoption of servicing robotics. Program funding continuity supports sustained development of robotic servicing capabilities. Operational success of early missions has strengthened confidence among stakeholders. Integration of artificial intelligence improves fault detection and mission execution reliability. These factors collectively drive sustained expansion in satellite servicing robotics deployment.
Rising defense-led space robotics investments
Defense modernization programs increasingly prioritize autonomous space systems to enhance surveillance and operational resilience. Space robotics offer strategic advantages through persistent monitoring and reduced human intervention risks. Investment focus has shifted toward multi-mission capable robotic platforms supporting intelligence operations. Defense agencies emphasize indigenous development to maintain technological sovereignty and security. Increased testing frequency accelerates technology maturation and operational readiness. Robotics integration aligns with broader defense digitalization initiatives. Mission-critical reliability standards drive continuous system refinement. Collaboration between defense laboratories and private firms accelerates innovation cycles. Enhanced funding stability supports long-term robotics roadmaps. These dynamics collectively reinforce sustained defense-driven market growth.
Challenges
High development and mission deployment costs
Developing space-grade robotic systems requires extensive testing, certification, and environmental validation processes. Component qualification for radiation and vacuum conditions significantly increases engineering complexity. Launch integration requirements further elevate overall deployment expenditure. Limited economies of scale constrain cost optimization opportunities. Specialized materials and electronics add to manufacturing expenses. Extended development timelines delay return realization for stakeholders. Budgetary constraints affect smaller program participation. Risk mitigation requirements increase redundancy needs. Cost pressures limit rapid experimentation cycles. These factors collectively restrain faster commercialization of space robotics technologies.
Complexity of space-grade robotic validation
Validation of robotic systems in simulated space environments requires advanced testing infrastructure. Replicating microgravity and radiation exposure conditions remains technically challenging. Certification processes involve multiple regulatory and safety assessments. Limited access to orbital testing opportunities slows iteration cycles. High failure costs necessitate extensive pre-launch verification. Software validation for autonomous behavior adds further complexity. Interoperability testing with satellites requires precise synchronization. Long validation cycles delay deployment readiness. Resource-intensive testing increases overall project risk exposure. These constraints hinder rapid scaling of robotic deployments.
Opportunities
Growth in in-orbit servicing missions
Expanding satellite constellations increase demand for refueling, repair, and repositioning services. In-orbit servicing reduces replacement frequency and extends asset lifecycles. Governments increasingly support debris mitigation initiatives requiring robotic intervention. Commercial operators seek cost-effective maintenance alternatives to satellite replacement. Technological improvements enable more complex servicing operations. Modular satellite designs enhance robotic compatibility. Mission success stories build operator confidence in servicing robotics. Policy frameworks increasingly support sustainability-oriented space operations. Investment interest grows around life-extension capabilities. These trends create strong long-term growth potential.
International collaboration on space robotics
Cross-border space programs enable technology sharing and joint mission execution. Collaborative projects reduce development risks and accelerate innovation cycles. Access to international launch platforms enhances mission flexibility. Joint research initiatives expand testing and validation opportunities. Harmonized standards facilitate interoperability of robotic systems. Partnerships improve funding stability and knowledge exchange. Shared mission objectives strengthen political and economic alignment. Collaborative frameworks support scalable deployment strategies. Exposure to global markets improves commercialization prospects. These factors collectively enhance growth opportunities.
Future Outlook
The Israel space robots market is expected to experience steady advancement driven by defense modernization and expanding satellite operations. Increased emphasis on autonomous capabilities and mission reliability will shape future system development. International cooperation and private sector participation are likely to strengthen. Regulatory clarity and sustained investment support long-term technological progress. The market is positioned for gradual expansion aligned with evolving space infrastructure needs.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Elbit Systems
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- SpaceIL
- Roboteam
- Aeronautics Group
- UVision Air
- BlueBird Aero Systems
- Astroscale Israel
- Honeywell Aerospace Israel
- OHB Israel
- Thales Alenia Space Israel
- Airobotics
- Elta Systems
- Orbit Communication Systems
Key Target Audience
- Government space agencies
- Defense procurement authorities
- Satellite operators
- Aerospace system integrators
- Private space exploration companies
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Ministry of Defense and Israel Space Agency
- Commercial satellite service providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope was defined through technology classification, application mapping, and mission type differentiation. Core variables included system architecture, deployment models, and end-use alignment.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was structured through segmentation analysis, technology mapping, and ecosystem evaluation. Demand drivers and operational trends were examined to establish market structure.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through expert interviews, program reviews, and technology benchmarking. Assumptions were refined using domain-specific operational feedback.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation, consistency checks, and analytical modeling. Final outputs reflect validated insights and structured market interpretation.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and space robotics scope delineation, mission-class and orbital segment taxonomy development, bottom-up market sizing using satellite and robotic mission counts, revenue attribution across hardware software and services, primary interviews with space agency and defense robotics experts, data triangulation using launch manifests and program budgets, assumption mapping based on technology readiness and mission cadence)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission deployment pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and system integration framework
- Regulatory and space governance environment
- Growth Drivers
Increasing satellite servicing demand
Rising defense-led space robotics investments
Miniaturization and AI integration in space systems
Expansion of Israel’s commercial space ecosystem
Growing need for on-orbit maintenance and inspection - Challenges
High development and mission deployment costs
Complexity of space-grade robotic validation
Limited launch availability and high dependency on partners
Regulatory and mission approval constraints
Long development and ROI cycles - Opportunities
Growth in in-orbit servicing missions
International collaboration on space robotics
Dual-use applications across defense and commercial sectors
Advancement in autonomous navigation systems
Emergence of space debris management missions - Trends
AI-driven autonomy in space robotics
Modular robotic platform development
Increased public-private partnerships
Rising demand for robotic life-extension services
Integration of robotics with small satellite missions - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Orbital servicing robots
Planetary exploration robots
On-orbit assembly robots
Inspection and maintenance robots
Autonomous docking robots - By Application (in Value %)
Satellite servicing and life extension
Space debris inspection and mitigation
Planetary surface exploration
In-orbit assembly and manufacturing
Defense and surveillance missions - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Autonomous robotic systems
Tele-operated robotic systems
AI-enabled adaptive robotics
Hybrid human-robot control systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Government and space agencies
Defense and intelligence
Commercial satellite operators
Research institutions and universities
Private space exploration companies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Ground-controlled communication
Inter-satellite link based control
AI-driven autonomous operation
Hybrid communication architecture
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology capability, mission heritage, system integration depth, autonomy level, defense certification, commercial readiness, pricing strategy, partnership network)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
Elbit Systems
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
SpaceIL
Roboteam
Aeronautics Group
UVision Air
Israel Space Agency (ISA)
Lockheed Martin Israel
Thales Alenia Space Israel
OHB Israel
BlueBird Aero Systems
Airobotics
Astroscale Israel
Honeywell Aerospace Israel
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


