Market Overview
The Israel Sudan Satellite Transponder market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by expanding satellite communication deployments across defense, broadcasting, and broadband connectivity segments. In recent periods, satellite payload utilization increased steadily, driven by higher transponder leasing volumes and growing data transmission requirements. The market recorded stable operational demand in 2024 and 2025, supported by increased satellite capacity utilization and modernization of existing orbital assets. Government-backed satellite programs and regional connectivity projects have contributed to consistent demand patterns across multiple frequency bands.
Israel remains the dominant hub due to advanced satellite infrastructure, established aerospace capabilities, and strong government backing for space communications. Sudan shows growing activity driven by connectivity expansion, defense communication needs, and limited terrestrial infrastructure. Regional demand concentration is influenced by security requirements, cross-border communication needs, and growing satellite broadband adoption. The ecosystem benefits from a combination of government agencies, private satellite operators, and regional telecom providers supporting long-term service continuity and infrastructure resilience.
Market Segmentation
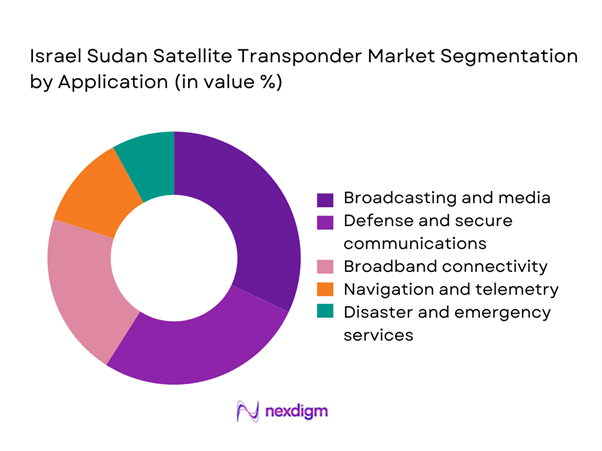
By Application
The broadcasting and media segment holds a dominant position due to continuous demand for satellite-based television distribution and signal redundancy. Defense and secure communications represent a significant share, driven by surveillance requirements and encrypted communication needs. Broadband connectivity applications are expanding steadily, particularly in underserved regions where terrestrial networks remain limited. Navigation and telemetry applications maintain stable demand supported by aviation and maritime operations. Emergency and disaster response services also contribute consistently, supported by government preparedness initiatives and regional connectivity requirements.
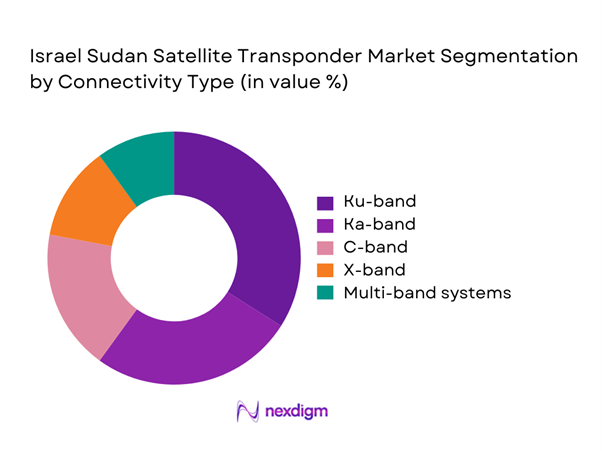
By Connectivity Type
Ku-band connectivity remains dominant due to widespread adoption in broadcasting and data transmission applications. Ka-band usage continues to expand, supported by higher throughput requirements and modern satellite payloads. C-band maintains relevance for legacy broadcasting and weather resilience. X-band is primarily used for military and government communications, reflecting steady institutional demand. Multi-band hybrid systems are gaining traction as operators seek flexible capacity allocation across applications.
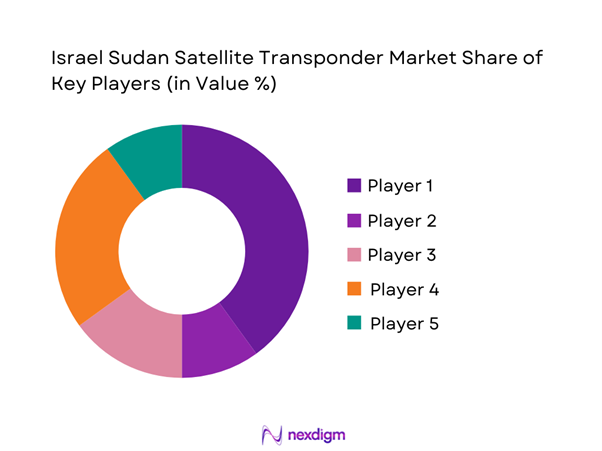
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of regional satellite operators, global satellite service providers, and aerospace manufacturers supporting transponder deployment and operations. Market competition is shaped by satellite fleet ownership, spectrum access, service reliability, and long-term leasing capabilities. Companies compete through technological capability, orbital coverage, service uptime, and regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Spacecom | 1992 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Gilat Satellite Networks | 1987 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SES | 1985 | Luxembourg | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Eutelsat | 1977 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Sudan Satellite Transponder Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising defense and surveillance satellite demand
Defense modernization programs increasingly rely on satellite transponders for secure communications and surveillance coverage. Governments continue prioritizing encrypted data transmission capabilities to strengthen national security infrastructure. Satellite-based reconnaissance applications are expanding due to geopolitical considerations and border monitoring requirements. Enhanced situational awareness needs are driving continuous investment in satellite capacity. Military communication reliability requirements are increasing dependence on dedicated transponder resources. Cross-border security coordination further accelerates demand for stable satellite links. Defense agencies prioritize redundancy and uptime, supporting long-term transponder leasing contracts. Satellite-based intelligence systems are increasingly replacing terrestrial alternatives in remote zones. The need for real-time data transmission sustains steady demand growth. These factors collectively reinforce defense-driven expansion across the regional satellite ecosystem.
Expansion of broadband connectivity in remote regions
Remote connectivity expansion continues to drive satellite transponder utilization across underserved areas. Limited terrestrial infrastructure accelerates reliance on satellite-based broadband delivery. Government initiatives increasingly prioritize digital inclusion and rural connectivity programs. Satellite links provide rapid deployment advantages compared to fiber-based alternatives. Increasing mobile backhaul requirements further strengthen satellite demand. Remote enterprise operations rely on consistent connectivity for operational continuity. Satellite broadband supports education, healthcare, and public service accessibility. Demand remains resilient due to geographic and infrastructural constraints. Growing data consumption amplifies bandwidth utilization across satellite networks. This expansion sustains long-term capacity leasing and service contracts.
Challenges
High satellite deployment and launch costs
Satellite deployment involves significant capital investment and extended development timelines. Launch costs remain a substantial barrier for new satellite programs. Manufacturing complexity increases overall project risk and financial exposure. Delays in satellite deployment affect service availability and revenue realization. Insurance and risk mitigation further elevate overall project expenses. Limited access to affordable launch services constrains expansion plans. Cost overruns impact long-term return on investment projections. Smaller operators face barriers entering capital-intensive satellite markets. These cost pressures restrict rapid market scaling. Financial risk remains a key challenge affecting investment decisions.
Spectrum allocation and orbital slot constraints
Spectrum availability remains tightly regulated and increasingly congested. Orbital slot allocation processes involve lengthy international coordination requirements. Competition for limited frequency bands intensifies operational complexity. Regulatory delays can slow satellite deployment timelines significantly. Spectrum interference risks increase with growing satellite density. Coordination challenges affect cross-border service delivery capabilities. Regulatory compliance costs continue to rise across jurisdictions. Limited spectrum flexibility constrains service scalability. Satellite operators face increasing administrative burdens. These factors collectively limit rapid expansion opportunities.
Opportunities
Expansion of HTS and VHTS platforms
High throughput satellites enable significantly improved data transmission efficiency. Operators increasingly invest in advanced payload technologies to enhance capacity utilization. HTS platforms support growing broadband and enterprise connectivity demand. VHTS systems enable cost-effective bandwidth scaling across regions. Enhanced spectral efficiency improves service economics and coverage quality. Advanced beamforming capabilities allow flexible capacity allocation. These platforms support emerging digital services and applications. Technological maturity improves long-term operational reliability. Growing adoption supports sustained market expansion opportunities. HTS evolution strengthens competitive positioning across satellite operators.
Growth in government-led satellite programs
Government investment in national satellite programs continues to expand steadily. Strategic communication independence drives public sector satellite procurement. Defense, disaster management, and connectivity initiatives fuel demand growth. Public funding reduces financial risk for satellite deployment projects. Long-term contracts provide stable revenue visibility for operators. Government-backed programs encourage local ecosystem development. Increased collaboration with private operators enhances service delivery. Policy support strengthens domestic satellite capabilities. Regional cooperation initiatives further boost project volumes. These programs create sustained growth opportunities across the market.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to maintain stable growth supported by rising connectivity needs and defense communication requirements. Continued investments in satellite modernization and spectrum efficiency will shape long-term development. Expansion of high-throughput platforms and government-backed initiatives will drive sustained demand. Regional cooperation and technological upgrades are likely to strengthen overall market resilience through the forecast period.
Major Players
- Spacecom
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Gilat Satellite Networks
- SES
- Eutelsat
- Intelsat
- Arabsat
- Yahsat
- Thales Alenia Space
- Airbus Defence and Space
- L3Harris Technologies
- Lockheed Martin
- Boeing Defense Space & Security
- Hughes Network Systems
- Sudatel
Key Target Audience
- Satellite operators and service providers
- Defense and military communication agencies
- Government and regulatory bodies such as national space agencies
- Telecommunications service providers
- Broadcasting and media networks
- Infrastructure investment firms
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Emergency response and disaster management agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope, application segments, satellite types, and connectivity models were identified through structured industry mapping. Demand drivers and operational parameters were analyzed to establish study boundaries. Regulatory and technological variables were incorporated to reflect market complexity.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Qualitative and quantitative data were synthesized to assess market structure and performance trends. Segmentation frameworks were developed based on application, connectivity, and usage patterns. Market dynamics were evaluated using industry-specific analytical models.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through expert interactions with satellite operators, engineers, and policy specialists. Assumptions were tested against real-world deployment scenarios. Feedback was incorporated to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Data triangulation techniques were applied to refine insights. Market narratives were aligned with observed industry developments. Final outputs were structured to support strategic decision-making and investment evaluation.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and satellite transponder scope alignment, Payload and bandwidth segmentation logic across GEO MEO and LEO assets, Capacity-based market sizing using MHz and transponder leasing benchmarks, Revenue attribution across commercial and government satellite programs, Primary validation through satellite operators and ground segment integrators)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and capacity utilization patterns
- Satellite ecosystem structure
- Value chain and service delivery model
- Regulatory and spectrum governance environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising defense and surveillance satellite demand
Expansion of broadband connectivity in remote regions
Growing need for secure communication links
Increasing satellite-based broadcasting requirements
Modernization of legacy satellite fleets - Challenges
High satellite deployment and launch costs
Spectrum allocation and orbital slot constraints
Political and regulatory uncertainties
Long satellite development and replacement cycles
Dependence on foreign satellite manufacturing - Opportunities
Expansion of HTS and VHTS platforms
Growth in government-led satellite programs
Cross-border connectivity and data backhaul demand
Private sector participation in satellite leasing
Adoption of software-defined payloads - Trends
Shift toward high throughput and flexible payloads
Increased use of Ka-band frequencies
Integration of satellite and terrestrial networks
Rising demand for secure military communications
Adoption of satellite-as-a-service models - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
GEO satellites
MEO satellites
LEO constellations
High Throughput Satellites
Government-owned satellite assets - By Application (in Value %)
Broadcasting and media distribution
Defense and secure communications
Broadband and data connectivity
Navigation and telemetry
Disaster recovery and emergency response - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Bent-pipe transponders
Digital transparent processors
Software-defined payloads
Regenerative payload systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense and homeland security
Telecommunications operators
Broadcast media companies
Aviation and maritime connectivity
Government and public sector - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
C-band
Ku-band
Ka-band
X-band
Multi-band hybrid systems - By Region (in Value %)
Israel
Sudan
Cross-border regional coverage
Rest of Middle East and North Africa
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Satellite fleet size, Transponder capacity, Frequency band coverage, Geographic footprint, Contract duration models, Pricing structure, Government contract exposure, Technology capability)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Spacecom
Israel Aerospace Industries
Gilat Satellite Networks
SES
Eutelsat
Intelsat
Arabsat
Yahsat
Thales Alenia Space
Airbus Defence and Space
L3Harris Technologies
Lockheed Martin
Boeing Defense Space & Security
Hughes Network Systems
Sudatel
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


