Market Overview
The Israel Supersonic and Hypersonic Weapons market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by sustained defense modernization programs and strategic deterrence investments. The market reflects steady development activity across propulsion systems, guidance technologies, and high-speed weapon integration platforms. Demand remains concentrated around advanced strike capabilities and rapid response systems. Development programs emphasize survivability, accuracy, and penetration capabilities. Investment activity is driven by long-term national security priorities. Technology validation and prototype testing remain central to program advancement.
Israel’s market dominance is supported by dense defense infrastructure, mature aerospace ecosystems, and centralized procurement mechanisms. Key activity clusters are concentrated around major defense manufacturing corridors and military research centers. Strong integration between defense agencies and domestic manufacturers accelerates development cycles. Policy alignment favors indigenous development and limited reliance on imports. Secure testing environments and controlled deployment zones further support advanced weapon experimentation. Long-term strategic doctrine continues to shape system requirements and deployment priorities.

Market Segmentation
By Weapon Type
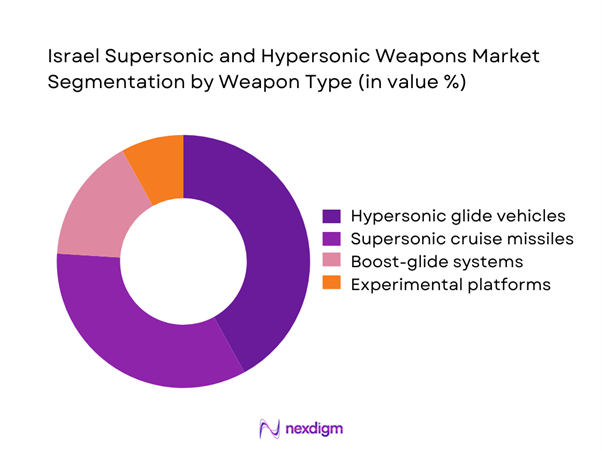
The market is dominated by hypersonic glide vehicles and advanced supersonic cruise systems due to their operational flexibility and penetration capability. Hypersonic platforms receive strong development focus owing to their maneuverability and reduced interception probability. Supersonic missiles continue to play a critical role in tactical operations and rapid strike missions. Research programs emphasize propulsion efficiency and thermal protection systems. Experimental platforms account for a smaller share but remain strategically significant. Integration readiness and deployment adaptability influence segment dominance.
By Launch Platform
Air-launched systems lead adoption due to deployment flexibility and integration with existing aircraft fleets. Surface-launched platforms maintain strategic relevance for rapid response and area denial operations. Naval-launched variants are gaining traction with increasing maritime security priorities. Platform selection depends on mission profile, range requirements, and survivability expectations. Integration complexity and operational doctrine strongly influence platform selection trends.

Competitive Landscape
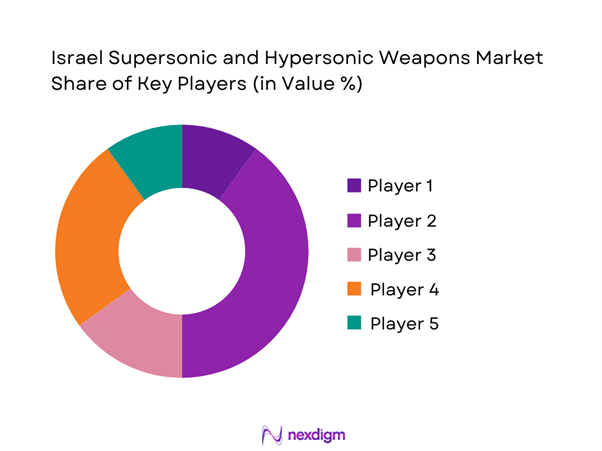
The competitive landscape is characterized by a small number of highly specialized defense manufacturers supported by national research institutions. Competition is driven by technological depth, system integration capability, and long-term defense partnerships rather than volume production. Entry barriers remain high due to regulatory restrictions and development complexity.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| IMI Systems | 1933 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elta Systems | 1967 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Supersonic and Hypersonic Weapons Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising regional threat perception
Heightened regional security tensions continue to drive accelerated investment in advanced strike and deterrence technologies. Strategic planners prioritize rapid response capabilities to counter evolving aerial and missile threats. Defense doctrine increasingly emphasizes preemptive and defensive strike readiness. Regional instability reinforces continuous modernization of weapon systems. Military planners focus on maintaining technological superiority against emerging adversaries. Operational readiness requirements stimulate ongoing testing and validation programs. Threat simulations influence procurement and development roadmaps. Strategic deterrence remains a central national defense objective. Enhanced surveillance capabilities support targeting precision improvements. Sustained security challenges ensure long-term demand stability.
Increased defense modernization spending
Modernization programs emphasize replacing legacy platforms with advanced high-speed weapon systems. Budget allocations increasingly favor indigenous development to strengthen technological independence. Investment flows support propulsion research and guidance system enhancements. Defense planning prioritizes multi-domain operational capabilities. Funding supports integration of hypersonic systems with existing command networks. Modernization initiatives encourage collaborative development across defense agencies. Long-term procurement planning enhances program continuity. Capability upgrades aim to reduce interception vulnerability. Advanced materials research benefits system durability. Modernization spending remains a structural growth driver.
Challenges
High development and testing costs
Hypersonic weapon development requires extensive testing infrastructure and specialized engineering expertise. High failure rates during early-stage testing increase program risk. Specialized materials and propulsion systems elevate development complexity. Testing facilities require strict safety and environmental compliance. Extended validation cycles delay operational deployment. Cost-intensive simulations are required for aerodynamic modeling. Limited availability of testing corridors constrains timelines. Engineering talent shortages increase development pressure. Program delays impact procurement schedules. Financial risk management remains a persistent challenge.
Export restrictions and international compliance constraints
Stringent export controls limit technology sharing and international collaboration. Compliance with international arms regulations restricts market expansion opportunities. Licensing requirements delay cross-border program execution. Technology transfer limitations affect joint development initiatives. Regulatory oversight increases documentation and audit burdens. Geopolitical considerations influence approval timelines. Export constraints reduce economies of scale. Compliance costs affect program budgeting. International treaties impose operational limitations. Regulatory uncertainty complicates long-term planning.
Opportunities
Expansion of indigenous hypersonic programs
Domestic development initiatives enable greater control over critical technologies. Indigenous programs reduce reliance on foreign suppliers. National research institutions support accelerated innovation cycles. Local manufacturing enhances supply chain resilience. Government backing strengthens long-term program viability. Domestic testing facilities improve development efficiency. Skill development programs enhance engineering capabilities. Indigenous systems align with strategic autonomy objectives. Local sourcing improves security compliance. Program scalability supports future export potential.
Integration with missile defense ecosystems
Hypersonic systems increasingly integrate with layered defense architectures. Interoperability with radar and command systems enhances mission effectiveness. Integration improves threat detection and response coordination. Networked systems enable real-time data exchange. Defense planners prioritize multi-layered protection strategies. Integration enhances survivability against countermeasures. Combined systems improve interception probability. Digital integration supports adaptive mission planning. System interoperability reduces operational risk. Integrated architectures enhance overall defense resilience.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to maintain steady momentum driven by sustained defense modernization and evolving security doctrines. Continued investment in propulsion and guidance technologies will shape next-generation capabilities. Strategic focus on indigenous development will remain strong. Integration with broader defense ecosystems will deepen. Long-term outlook reflects sustained technological advancement and controlled expansion.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- IMI Systems
- Elta Systems
- Aeronautics Group
- UVision Air
- BlueBird Aero Systems
- Israel Shipyards
- RT LTA Systems
- Cyclone Ltd
- SIBAT
- Tomer Ltd
- Elron Electronic Industries
- IWI
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defense procurement divisions
- Israeli Air Force strategic planning units
- Naval defense procurement agencies
- National missile defense organizations
- Government research and development authorities
- Defense system integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Defense export control and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key parameters including system types, deployment platforms, and operational roles were identified through defense program mapping. Market boundaries were defined based on weapon classification and deployment scope. Data points were aligned with national defense planning frameworks.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segment-level analysis was conducted using platform-based and application-based classification models. Development pipelines and deployment patterns were assessed to establish structural market behavior. Data consistency was ensured through cross-validation.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry specialists and defense analysts were consulted to validate technology trajectories. Program assumptions were reviewed against operational feasibility. Expert inputs refined segmentation logic and growth assumptions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation of technical, strategic, and operational data. Assumptions were stress-tested for consistency. Final insights were structured to support decision-making relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope alignment, weapon system taxonomy and segmentation logic, platform-level market sizing and validation approach, program-wise revenue attribution modeling, primary interviews with defense officials and industry experts, triangulation using defense budgets and contract disclosures, assumption mapping based on classified-to-open source reconciliation)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and mission usage landscape
- Defense ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and industrial base
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising regional threat perception
Increased defense modernization spending
Emphasis on long-range precision strike capabilities
Technological advancements in propulsion and materials
Expansion of indigenous defense manufacturing
Strategic deterrence requirements - Challenges
High development and testing costs
Export restrictions and international compliance constraints
Complexity of hypersonic propulsion systems
Limited testing infrastructure
Long development and certification cycles
Geopolitical sensitivity of deployments - Opportunities
Expansion of indigenous hypersonic programs
Integration with missile defense ecosystems
Dual-use technology advancements
International defense collaborations
AI-enabled guidance and targeting systems
Next-generation propulsion breakthroughs - Trends
Shift toward hypersonic glide vehicle development
Increased focus on survivability and maneuverability
Integration with multi-domain operations
Rising investment in scramjet research
Enhanced electronic counter-countermeasures
Greater emphasis on domestic supply chains - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Program Value, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Air-launched weapons
Surface-launched weapons
Sea-launched weapons
Experimental and test platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Strategic strike
Precision tactical strike
Missile defense penetration
Deterrence and second-strike capability - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Supersonic cruise missiles
Hypersonic glide vehicles
Hypersonic cruise missiles
Boost-glide systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Air force
Navy
Strategic defense forces
Defense R&D establishments - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone guidance systems
Network-enabled weapon systems
Integrated C4ISR-linked platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Central Israel defense clusters
Southern Israel testing corridors
Northern operational zones
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology maturity, propulsion capability, range performance, integration capability, program scale, defense contracts, R&D intensity, export readiness)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Israel Military Industries (IMI Systems)
Aeronautics Group
Tomcar Defense
BlueBird Aero Systems
Elta Systems
SIBAT
Israel Shipyards
UVision Air
RT LTA Systems
Elron Electronic Industries
Cyclone Ltd.
Israel Weapon Industries (IWI)
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Program Value, 2026–2035


