Market Overview
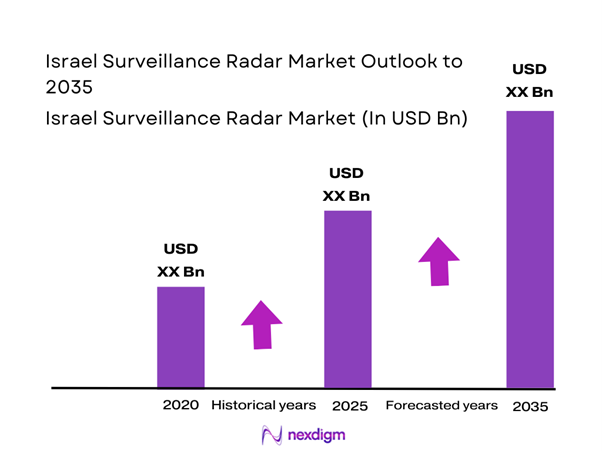
The Israel Surveillance Radar Market current size stands at USD ~ million, reflecting sustained defense procurement activity and radar modernization initiatives. Demand intensity remains elevated due to persistent border monitoring requirements and multi-layered aerial threat detection priorities. Procurement volumes during recent periods show stable ordering patterns supported by long-term defense planning cycles. Technology refresh programs emphasize sensor accuracy, network integration, and rapid deployment capabilities across terrain types. Spending distribution favors domestically produced systems complemented by selective international technology collaboration agreements.
Core demand originates from southern and northern border zones with dense surveillance infrastructure requirements. Urban centers supporting command integration act as coordination hubs for radar data processing. Defense industrial clusters enable rapid customization, maintenance access, and system upgrades. High operational readiness expectations shape procurement cycles and lifecycle support models. Regulatory oversight and security clearances influence deployment pace and vendor participation. Geopolitical sensitivity reinforces prioritization of resilient and secure surveillance architectures.
Market Segmentation
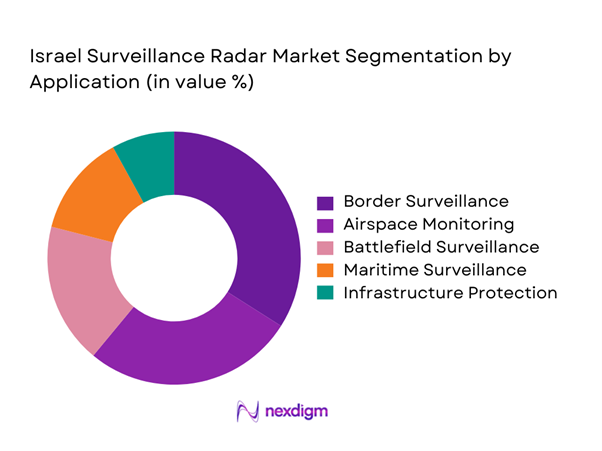
By Application
Border and perimeter surveillance dominates deployment due to persistent monitoring requirements across land and maritime boundaries. Airspace surveillance applications maintain strong demand driven by layered air defense doctrines and early-warning integration needs. Battlefield surveillance systems are increasingly deployed for real-time situational awareness and tactical coordination. Critical infrastructure protection applications continue expanding around energy assets and transportation corridors. Maritime surveillance adoption is supported by coastal monitoring programs and offshore asset protection priorities. The application mix reflects operational readiness objectives rather than commercial demand dynamics.
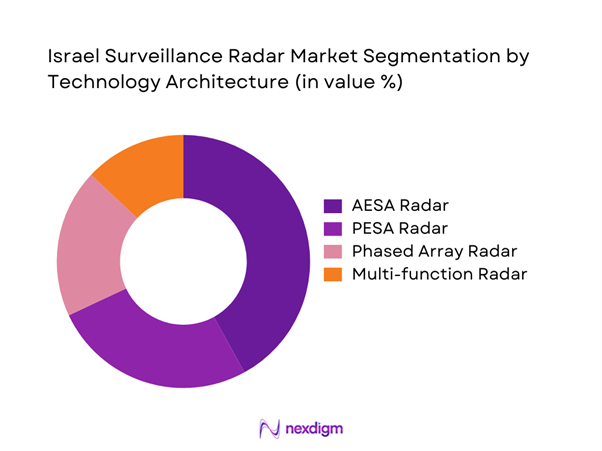
By Technology Architecture
Active electronically scanned array systems dominate adoption due to superior tracking accuracy and multi-target handling capabilities. Passive electronically scanned arrays retain relevance in cost-sensitive and legacy upgrade deployments. Phased array systems continue to support wide-area surveillance and missile detection requirements. Multi-function radar architectures gain traction as defense forces prioritize platform consolidation and reduced system complexity. Technology selection is increasingly influenced by interoperability and software-defined upgrade potential rather than standalone performance metrics.
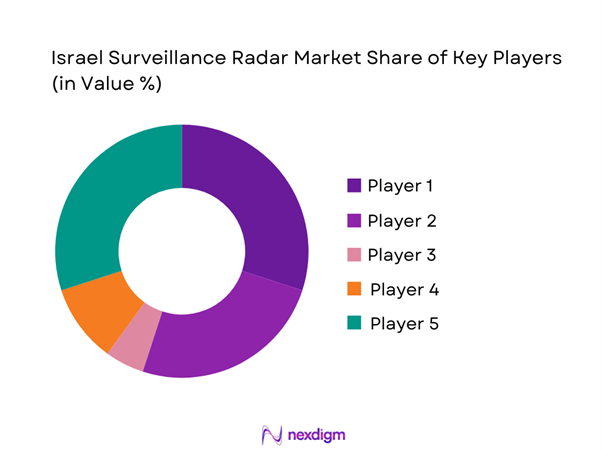
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a concentrated group of defense-focused manufacturers with deep integration into national security programs. Market positioning depends on technological depth, system reliability, and long-term service capabilities. Domestic suppliers maintain strong advantages through established defense relationships and regulatory alignment.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Elta Systems | 1967 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hensoldt | 2017 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Surveillance Radar Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising border security and threat detection requirements
Border surveillance intensity increased during 2024 due to heightened cross-border activity and regional instability. Continuous monitoring demands accelerated deployment of advanced radar platforms across sensitive zones. Multi-layer detection systems gained importance to counter low-altitude and unmanned threats effectively. Operational doctrines emphasized persistent surveillance rather than periodic monitoring approaches. Sensor fusion capabilities were increasingly prioritized to improve response coordination. Investment momentum remained strong across land and coastal surveillance programs. Defense planners favored systems offering real-time data transmission reliability. Technological readiness influenced faster replacement of legacy radar installations. Interoperability with command networks strengthened procurement justification. National security imperatives consistently reinforced surveillance radar modernization programs.
Modernization of Israel Defense Forces surveillance infrastructure
Modernization initiatives accelerated as aging radar assets required replacement with digitally integrated platforms. Command-and-control modernization programs drove compatibility requirements for new surveillance systems. Digital transformation strategies emphasized data fusion and automated threat recognition capabilities. Infrastructure upgrades supported faster deployment and reduced maintenance downtime. Integration with air defense and missile systems became a strategic priority. Procurement planning increasingly favored modular and upgradeable architectures. Enhanced processing power enabled improved detection accuracy under complex operational conditions. Training frameworks evolved alongside system modernization programs. Interoperability standards influenced procurement selection criteria. Long-term readiness objectives sustained continuous infrastructure modernization investments.
Challenges
High development and lifecycle costs of radar systems
Advanced radar systems require extensive research investment and prolonged development cycles. Component sourcing complexity increases overall system integration expenditure. Maintenance requirements elevate long-term operational cost burdens significantly. Lifecycle upgrades demand specialized technical expertise and recurring resource allocation. Budget constraints affect procurement timelines and fleet expansion strategies. Customization requirements further elevate engineering and validation expenses. Sustainment contracts contribute to long-term financial commitments. Testing and certification phases extend deployment schedules. Technology obsolescence risks necessitate frequent upgrades. Cost optimization remains a persistent procurement challenge.
Export control and regulatory restrictions
Export regulations impose strict limitations on technology transfer and system configuration. Compliance requirements increase administrative complexity for manufacturers and buyers. Approval timelines often delay international collaboration initiatives. Sensitive technology classifications restrict broader market participation opportunities. Regulatory oversight influences system design and feature availability. Licensing processes vary across jurisdictions, complicating export planning. Policy changes introduce uncertainty into long-term supply agreements. Security clearance protocols slow cross-border cooperation. Documentation requirements increase operational overhead. Regulatory alignment remains a critical barrier to market expansion.
Opportunities
Deployment of AI-enabled radar analytics
Artificial intelligence integration enhances target recognition accuracy and response speed. Automated analytics reduce operator workload and improve situational awareness. Machine learning models support adaptive threat classification capabilities. AI-driven processing enables faster decision-making during high-density surveillance operations. Predictive analytics improve early-warning effectiveness across complex environments. Data-driven optimization enhances system reliability and uptime. Software-centric upgrades extend platform lifecycle value. AI integration aligns with digital defense modernization objectives. Continuous learning models improve performance under evolving threat conditions. Technology adoption strengthens overall surveillance efficiency.
Growth in unmanned and autonomous surveillance platforms
Unmanned platforms increase demand for lightweight and adaptive radar systems. Autonomous surveillance expands operational reach without increased personnel deployment. Integration with aerial and ground drones enhances coverage flexibility. Radar miniaturization supports deployment across diverse unmanned platforms. Autonomous operations require advanced sensing and navigation capabilities. Surveillance persistence improves through coordinated unmanned deployments. System interoperability becomes critical for multi-platform operations. Cost efficiencies arise from reduced manpower requirements. Autonomous surveillance aligns with future battlefield concepts. Market potential expands with increased unmanned system adoption.
Future Outlook
The market outlook remains positive as defense modernization and border security priorities continue shaping procurement strategies. Technological convergence between radar, analytics, and command systems will accelerate adoption. Policy emphasis on surveillance resilience supports sustained investment momentum. Innovation in autonomous and AI-enabled systems will further redefine operational capabilities. Long-term demand stability is supported by evolving regional security dynamics.
Major Players
- Elta Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Hensoldt
- Thales Group
- Raytheon Technologies
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Leonardo
- Saab AB
- BAE Systems
- Indra Sistemas
- ASELSAN
- IAI Tamam
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defense procurement divisions
- Israel Defense Forces surveillance units
- Border security and homeland protection agencies
- Naval and air force command authorities
- Defense system integrators
- Radar component manufacturers
- Government and regulatory bodies including defense export authorities
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope definition focused on surveillance radar applications, platform types, and deployment environments. Core demand indicators were mapped across defense and security use cases.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data modeling incorporated platform adoption trends, procurement cycles, and technology integration patterns. Segment-level dynamics were structured using deployment and application logic.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through defense technology experts, system integrators, and operational stakeholders. Assumptions were refined based on operational feasibility assessments.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation of qualitative insights and quantitative indicators. Final outputs reflect realistic market behavior and deployment trends.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Defense Surveillance Radar Scope Mapping, Radar Technology Taxonomy and Platform Classification, Bottom-Up Market Sizing Using Program and Contract Analysis, Revenue Attribution by Platform and Deployment Type, Primary Validation Through Defense OEMs and Military Experts, Data Triangulation Using Procurement Budgets and Radar Install Base, Assumptions and Limitations Linked to Classified Programs)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and defense usage landscape
- Ecosystem and stakeholder structure
- Supply chain and localization dynamics
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising border security and threat detection requirements
Modernization of Israel Defense Forces surveillance infrastructure
Increasing adoption of AESA and multi-mission radar systems
Expansion of integrated air and missile defense programs
Growing demand for real-time situational awareness - Challenges
High development and lifecycle costs of radar systems
Export control and regulatory restrictions
Complex system integration requirements
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities in networked radars
Dependence on defense budget cycles - Opportunities
Deployment of AI-enabled radar analytics
Growth in unmanned and autonomous surveillance platforms
Export potential to allied defense markets
Upgrades of legacy radar installations
Integration with space-based surveillance assets - Trends
Shift toward multi-function and software-defined radars
Increased use of gallium nitride technology
Network-centric warfare and sensor fusion adoption
Rising demand for mobile and rapid-deployment radar systems
Integration with missile defense and counter-UAS systems - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Ground-based surveillance radars
Airborne surveillance radars
Naval surveillance radars
Space-based and high-altitude radar systems - By Application (in Value %)
Border and perimeter surveillance
Airspace monitoring and air defense
Maritime domain awareness
Battlefield surveillance and target tracking
Critical infrastructure protection - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Active electronically scanned array radar
Passive electronically scanned array radar
Phased array radar
Multi-function radar systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense forces
Homeland security agencies
Border security forces
Intelligence and surveillance agencies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone radar systems
Network-centric and C4ISR-integrated systems
AI-enabled sensor fusion systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northern Israel
Southern Israel
Central Israel
Coastal and maritime zones
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Radar range capability, Technology maturity, Platform compatibility, System integration capability, Pricing and contract structure, Local manufacturing presence, After-sales support strength, Export footprint)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Elta Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Hensoldt
Thales Group
Raytheon Technologies
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
Leonardo
Saab AB
BAE Systems
Indra Sistemas
ASELSAN
IAI Tamam
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service and upgrade expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


