Market Overview
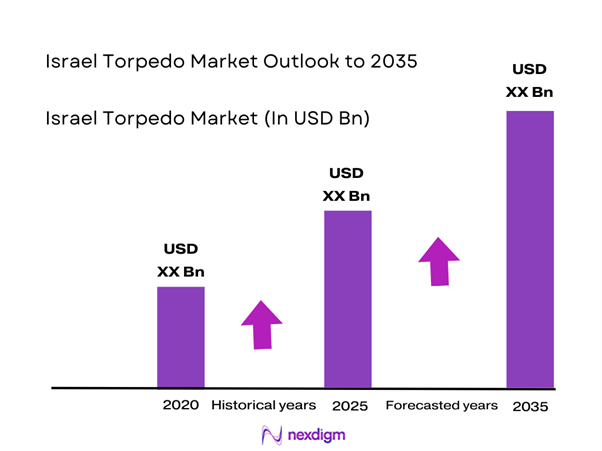
The Israel Torpedo market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by consistent naval modernization programs and rising underwater defense requirements. Deployment volumes remained stable across recent cycles, with ~ units operationally active and incremental additions observed through platform upgrades. Demand momentum is influenced by fleet renewal activities, underwater threat mitigation priorities, and increasing emphasis on indigenous defense capabilities. Technological upgrades and lifecycle extensions continue to support sustained procurement activity without abrupt fluctuations.
Israel’s torpedo ecosystem is concentrated around coastal naval bases and submarine-operating zones with advanced maintenance infrastructure. Demand concentration is driven by naval command centers, defense manufacturing clusters, and testing ranges located along strategic maritime corridors. The ecosystem benefits from a mature defense-industrial base, strong system integration capabilities, and close coordination between military operators and domestic suppliers. Regulatory oversight and defense procurement policies further shape adoption patterns and upgrade cycles.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
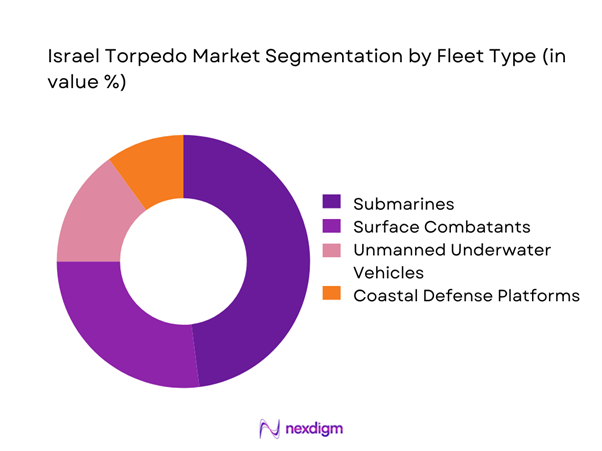
The fleet type segmentation is dominated by submarine-based deployments due to Israel’s emphasis on underwater deterrence and strategic maritime surveillance. Submarine fleets account for the majority of torpedo integration owing to their stealth requirements and extended operational ranges. Surface combatants maintain a smaller but consistent share, primarily for anti-submarine and coastal defense roles. Unmanned underwater platforms are emerging gradually, driven by reconnaissance and mine countermeasure applications. The segmentation reflects a shift toward high-endurance platforms rather than volume-based fleet expansion.
By Application
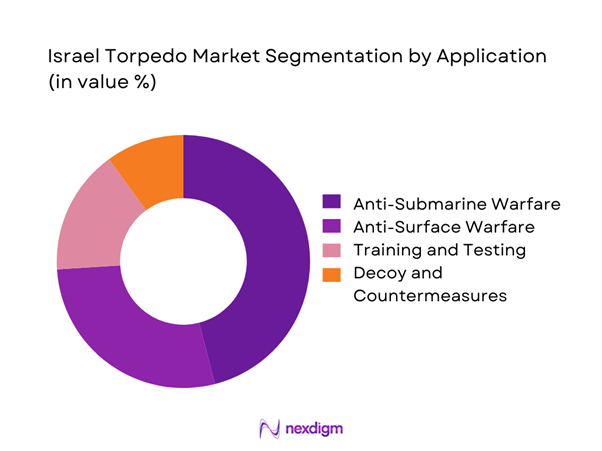
Application-based segmentation is led by anti-submarine warfare due to persistent regional maritime security challenges. Anti-surface warfare represents a secondary share, supported by naval deterrence strategies and patrol requirements. Training and testing applications maintain steady demand linked to crew readiness and system validation cycles. Decoy and countermeasure deployment remains niche but growing, reflecting increasing focus on survivability and electronic warfare preparedness.
Competitive Landscape
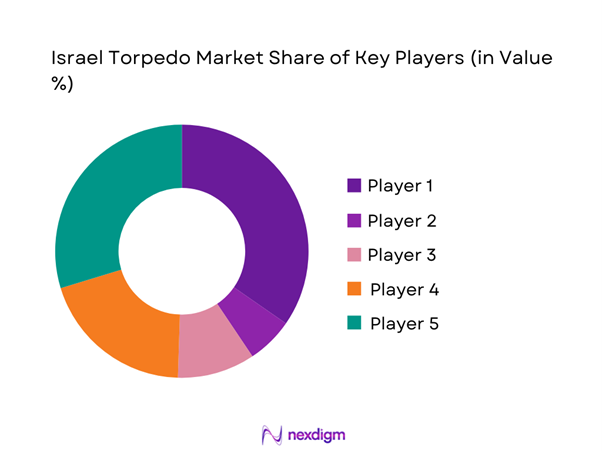
The competitive environment is characterized by a limited number of highly specialized defense manufacturers with strong technological depth. Market participation is shaped by long-term defense contracts, high entry barriers, and stringent regulatory oversight. Companies compete primarily on system reliability, integration capability, and lifecycle support rather than price alone.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo S.p.A. | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab AB | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Torpedo Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising maritime security threats in Eastern Mediterranean
Growing regional maritime tensions have intensified naval surveillance and underwater defense priorities across Israel’s operational waters. Increased submarine activity and asymmetric naval threats have elevated the importance of torpedo readiness and response capability. Naval patrol frequencies expanded during 2024, reinforcing demand for reliable underwater weapons systems. Enhanced maritime domain awareness initiatives further supported torpedo system deployment and modernization. Regional security cooperation frameworks indirectly increased operational readiness expectations. Defense planning increasingly emphasizes underwater dominance as a strategic deterrent. Training intensity rose to maintain combat preparedness amid evolving threat profiles. Operational doctrines now prioritize rapid response and underwater engagement capabilities. Continuous monitoring requirements are reinforcing long-term procurement stability. Strategic maritime protection remains a central driver for torpedo system investments.
Expansion of submarine and naval combat fleet
Israel’s submarine fleet modernization programs have accelerated demand for advanced torpedo integration and compatibility. Fleet expansion initiatives emphasized stealth capabilities and extended underwater endurance. Newer platforms require next-generation torpedo systems with improved guidance accuracy. Fleet upgrades during 2024 and 2025 sustained procurement activity across supporting systems. Naval combat doctrine increasingly favors multi-role underwater engagement capabilities. Platform modernization cycles directly influence torpedo replacement and upgrade timelines. Integration requirements have increased collaboration between naval engineers and system suppliers. Fleet readiness objectives prioritize reliable and scalable underwater weapon systems. Long-term naval planning continues to support sustained torpedo system demand. Operational flexibility remains a key outcome of fleet expansion strategies.
Challenges
High development and testing costs
Torpedo system development involves extensive testing cycles and specialized underwater validation infrastructure. High engineering complexity increases development timelines and resource requirements. Testing environments require controlled maritime zones and advanced instrumentation. Validation processes often extend across multiple operational phases. Cost pressures limit rapid innovation and constrain experimentation with emerging technologies. Smaller production volumes further elevate per-unit development expenditures. Compliance with military performance standards adds additional cost layers. Testing redundancy requirements increase overall program expenditure. Budgetary scrutiny influences prioritization of new development initiatives. These factors collectively slow commercialization cycles.
Export control and regulatory restrictions
Stringent export controls restrict international collaboration and limit market expansion opportunities. Regulatory approval processes introduce delays across procurement and deployment stages. Compliance requirements vary significantly across export destinations, increasing administrative complexity. Technology transfer limitations restrict joint development initiatives. Licensing approvals often require extended evaluation periods. Regulatory oversight impacts supplier selection and contract structuring. Security clearance processes further constrain operational flexibility. Policy shifts can affect long-term planning certainty. Export restrictions reduce economies of scale for manufacturers. These constraints collectively affect market scalability.
Opportunities
Development of next-generation smart torpedoes
Advancements in guidance systems enable higher accuracy and adaptive targeting capabilities. Smart torpedo development aligns with evolving naval combat requirements. Integration of artificial intelligence enhances threat discrimination and engagement efficiency. Development programs emphasize reduced acoustic signatures and improved propulsion efficiency. Modular architectures support future upgrades without full system replacement. Innovation efforts focus on interoperability with existing naval platforms. Research initiatives during 2024 and 2025 supported prototype advancements. Enhanced sensing technologies improve operational effectiveness in complex environments. These developments strengthen long-term capability expansion. Technological leadership presents significant strategic value.
Integration with unmanned naval platforms
Growing adoption of unmanned underwater vehicles creates new deployment opportunities for torpedo systems. Autonomous platforms require lightweight and digitally integrated weapon solutions. Integration enhances operational reach while reducing human risk exposure. Unmanned systems enable extended surveillance and strike capabilities. Development programs increasingly prioritize compatibility with remote platforms. Testing activities during 2024 demonstrated successful integration trials. Operational doctrines are evolving to include unmanned strike coordination. This integration expands tactical flexibility and mission diversity. Cost efficiency improves through reduced manpower requirements. The trend supports sustained innovation investment.
Future Outlook
The Israel torpedo market is expected to maintain steady advancement through continued naval modernization and evolving maritime security priorities. Technological innovation, particularly in autonomous and smart weapon systems, will shape future procurement strategies. Policy alignment and defense collaboration will further influence development trajectories. Long-term demand is expected to remain stable, supported by strategic defense planning and fleet sustainment initiatives.
Major Players
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Elbit Systems
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Saab AB
- Thales Group
- Naval Group
- BAE Systems
- Raytheon Technologies
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- L3Harris Technologies
- Ultra Electronics
- Atlas Elektronik
Key Target Audience
- Naval defense procurement authorities
- Ministry of Defense acquisition departments
- Naval operations and fleet commanders
- Defense manufacturing companies
- System integrators and technology suppliers
- Maritime security agencies
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including defense export authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core market parameters were defined based on platform deployment, application scope, and technology integration levels. Data points were aligned with naval procurement structures and operational usage patterns.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segment-wise evaluation was conducted using platform classification, application mapping, and technology adoption assessment. Market behavior was analyzed through operational demand indicators.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through structured consultations with defense experts and naval technology specialists. Assumptions were refined using operational feasibility checks.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated inputs were synthesized into coherent insights, ensuring consistency across segments and alignment with observed market dynamics.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Operational Scope for Naval Torpedo Systems, Platform-Based Segmentation and Classification Framework, Bottom-Up and Top-Down Market Sizing Methodology, Revenue Attribution by Program and Procurement Cycle, Primary Interviews with Naval Officers and Defense Contractors, Cross-Verification Using Defense Budgets and Contract Databases, Assumptions and Limitations Related to Classified Procurement Data)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and deployment environment
- Defense ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and sourcing dynamics
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising maritime security threats in Eastern Mediterranean
Expansion of submarine and naval combat fleet
Increased defense modernization budgets
Technological upgrades toward autonomous weapons
Growing emphasis on underwater domain awareness
Strategic deterrence requirements - Challenges
High development and testing costs
Export control and regulatory restrictions
Limited domestic production scale
Complex integration with legacy naval platforms
Long procurement and approval cycles
Dependence on specialized components - Opportunities
Development of next-generation smart torpedoes
Integration with unmanned naval platforms
Export potential to allied naval forces
Advancements in propulsion and guidance systems
Joint development programs with allied nations
Simulation and training system demand - Trends
Shift toward electric and low-noise propulsion
Increased use of AI-enabled targeting
Modular torpedo architecture adoption
Emphasis on interoperability with NATO systems
Growing investment in countermeasure-resistant designs
Lifecycle extension and upgrade programs - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Submarines
Surface Combatants
Unmanned Underwater Vehicles
Coastal Defense Platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Anti-Submarine Warfare
Anti-Surface Warfare
Training and Testing
Decoy and Countermeasure Deployment - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Heavyweight Torpedoes
Lightweight Torpedoes
Electric Propulsion Systems
Wire-Guided and Autonomous Systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Naval Defense Forces
Homeland Security and Coastal Protection
Defense R&D Organizations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Wire-Guided
Fiber-Optic Guided
Autonomous / AI-Enabled
Hybrid Guidance Systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northern Naval Command
Mediterranean Coast
Red Sea Operational Zone
Training and Testing Facilities
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology maturity, Product range, Platform compatibility, R&D intensity, Pricing strategy, Export footprint, Contract size, After-sales support)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
Elbit Systems
Atlas Elektronik
Leonardo S.p.A.
Saab AB
Thales Group
Naval Group
L3Harris Technologies
BAE Systems
Raytheon Technologies
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
Ultra Electronics
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


