Market Overview
The Israel unmanned ground vehicle market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by rising deployment volumes and sustained defense modernization priorities. Recent operational deployments exceeded ~ units, reflecting increased utilization across reconnaissance, logistics, and tactical support missions. Fleet modernization programs, combined with elevated security requirements, continue to stimulate platform upgrades and autonomous capability integration. Procurement cycles remain active, with multi-year acquisition planning sustaining stable demand levels across military and homeland security users.
Market activity is concentrated around central defense hubs, border regions, and advanced testing zones where operational readiness and rapid deployment are essential. Strong integration between defense forces, technology developers, and systems integrators has created a mature ecosystem. Infrastructure readiness, battlefield digitization, and advanced command systems reinforce adoption. Supportive policy frameworks and sustained investment in indigenous defense manufacturing further strengthen long-term market stability and deployment scalability.
Market Segmentation
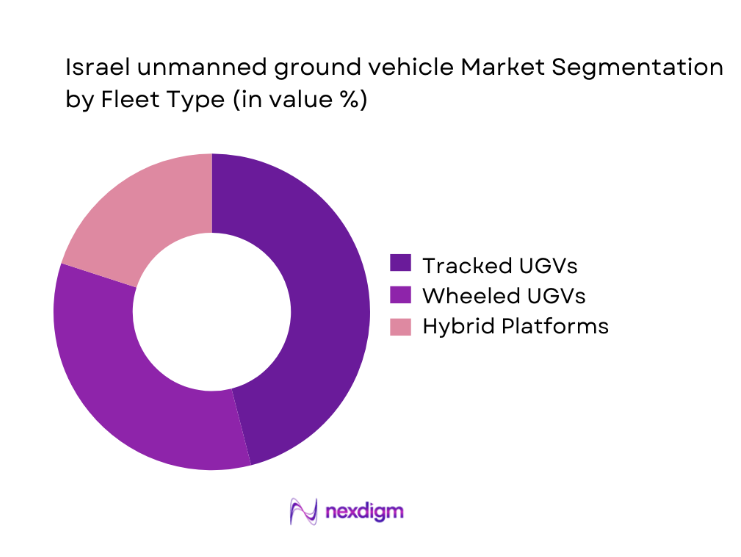
By Fleet Type
Tracked and hybrid unmanned ground vehicles dominate deployment due to superior mobility across uneven terrain and combat environments. Wheeled platforms maintain relevance for logistics and surveillance roles where speed and endurance are prioritized. Hybrid configurations combining tracked mobility with modular payloads are increasingly adopted to support multi-mission flexibility. Defense planners favor platforms capable of rapid reconfiguration, enabling efficient use across border patrol, reconnaissance, and combat support operations. Continuous upgrades in mobility systems and power management enhance operational effectiveness across varied terrain conditions.
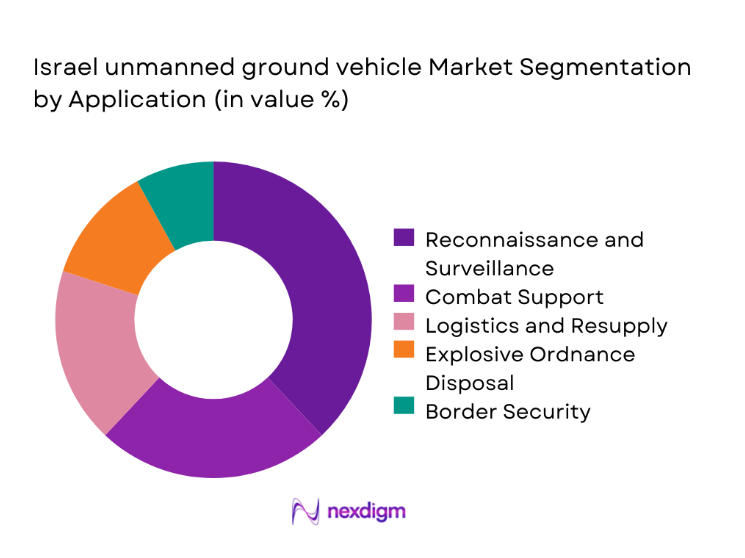
By Application
Reconnaissance and surveillance represent the largest application segment due to persistent intelligence requirements and border monitoring needs. Combat support platforms are increasingly adopted to reduce soldier exposure in high-risk operations. Logistics and resupply applications are expanding as autonomous transport reliability improves. Explosive ordnance disposal remains a critical niche, driven by urban security demands. Border security and perimeter monitoring continue to generate consistent demand due to evolving threat environments and terrain complexity.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by strong domestic innovation, close military collaboration, and a focus on mission-specific platform development. Companies compete on system reliability, autonomy levels, integration capability, and lifecycle support. Technological differentiation, rapid prototyping, and defense-grade compliance remain critical competitive factors.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Roboteam | 2009 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| IMI Systems | 1933 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel unmanned ground vehicle Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising border security and asymmetric warfare threats
Escalating border tensions have intensified demand for unmanned systems capable of persistent surveillance and rapid response. Military planners increasingly prioritize unmanned solutions to reduce personnel exposure in volatile environments. Operational incidents have highlighted the need for continuous monitoring across complex terrains and urban areas. UGVs provide extended operational endurance without fatigue constraints. Their deployment supports early threat detection and situational awareness improvements. Border security agencies have expanded patrol coverage using unmanned platforms. Integration with command networks enhances real-time decision-making accuracy. The shift toward asymmetric warfare necessitates adaptable and remotely operated systems. Enhanced sensing capabilities improve threat identification accuracy under challenging conditions. These factors collectively reinforce sustained procurement momentum.
Increasing adoption of unmanned combat support systems
Combat units increasingly rely on unmanned platforms for logistics, reconnaissance, and tactical support functions. These systems reduce direct soldier involvement in high-risk missions. Enhanced autonomy enables extended mission duration with minimal human intervention. Military modernization programs emphasize force multiplication through unmanned technologies. Integration with digital battlefield management systems improves coordination efficiency. Operational feedback indicates improved mission success rates using unmanned support assets. Reliability improvements have increased acceptance among field commanders. Modular payload designs allow rapid mission reconfiguration. Interoperability with existing defense infrastructure supports scalable deployment. Continued innovation sustains rising adoption across operational theaters.
Challenges
High system development and integration costs
Advanced unmanned ground systems require significant investment in hardware, software, and testing. Development cycles are extended due to stringent military performance requirements. Integration with existing command architectures increases engineering complexity. Customization for specific mission profiles elevates cost structures. Maintenance and lifecycle support further add to total ownership expenses. Budget constraints can delay large-scale deployment programs. Cost overruns may impact long-term procurement planning. Smaller defense units face affordability challenges. Continuous technology upgrades increase financial commitments. These factors collectively constrain rapid market expansion.
Limited autonomy in complex terrain
UGV performance remains constrained in unpredictable and cluttered environments. Navigation challenges persist in urban and underground settings. Sensor limitations affect obstacle detection accuracy. Terrain variability reduces operational reliability during missions. Communication latency impacts autonomous decision-making processes. Environmental interference can degrade system responsiveness. Human intervention remains necessary in high-complexity scenarios. Software refinement requires extensive field testing. Terrain mapping accuracy affects mission success rates. These limitations restrict full autonomy deployment potential.
Opportunities
Expansion of autonomous logistics platforms
Military logistics operations increasingly adopt unmanned solutions for supply transport. Autonomous platforms reduce exposure of personnel in contested zones. Improved navigation algorithms support longer autonomous missions. Logistics automation enhances operational efficiency and response time. Modular cargo systems enable flexible deployment scenarios. Demand for resupply automation continues to rise. Integration with aerial platforms creates multi-domain logistics networks. Energy-efficient designs improve mission endurance. Autonomous convoys support sustained operations in remote areas. This segment presents strong long-term growth potential.
Export potential to allied defense markets
International defense cooperation creates opportunities for technology exports. Allied nations seek proven unmanned ground solutions for modernization. Combat-tested platforms offer strong credibility in global markets. Export demand benefits from standardized interoperability requirements. Collaborative development programs enhance market accessibility. Technology transfer agreements expand international footprint. Regional security concerns drive procurement interest. Customizable platforms meet varied operational doctrines. Government-backed export initiatives support market penetration. Global partnerships strengthen long-term revenue prospects.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to experience steady advancement driven by autonomy improvements, operational digitization, and expanding defense requirements. Continued investment in artificial intelligence and sensor fusion will enhance system effectiveness. Cross-domain integration and export-oriented development will shape competitive strategies. Policy support and technological maturity are expected to sustain long-term growth momentum.
Major Players
- Elbit Systems
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Roboteam
- IMI Systems
- Rheinmetall
- Milrem Robotics
- QinetiQ
- Northrop Grumman
- General Dynamics Land Systems
- Textron Systems
- Leonardo
- Oshkosh Defense
- HDT Global
- Teledyne FLIR
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defense procurement divisions
- Israel Defense Forces modernization units
- Border security and homeland security agencies
- Defense system integrators
- Military logistics and support commands
- Autonomous systems developers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including defense export authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Platform classifications, mission profiles, autonomy levels, and deployment environments were identified through structured defense capability mapping. Operational doctrines and procurement frameworks guided variable selection. Emphasis was placed on system lifecycle characteristics and integration requirements.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segmentation structures were constructed using application and fleet logic aligned with military deployment practices. Deployment density and platform utilization patterns informed analytical modeling. Comparative assessment focused on capability depth rather than commercial metrics.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through consultations with defense technology specialists and system integrators. Operational feedback from training and deployment exercises informed refinement. Cross-validation ensured internal consistency across analytical dimensions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into coherent market narratives emphasizing operational relevance. Analytical insights were reviewed for logical consistency and clarity. Final outputs prioritize decision-oriented understanding for strategic stakeholders.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope of unmanned ground vehicles in Israeli defense and security use, platform and mission-based segmentation logic for UGV classification, bottom-up market sizing using defense procurement and deployment data, revenue attribution across OEMs and subsystem suppliers, primary validation through defense integrators and military technology experts, triangulation using government tenders and export disclosures, assumptions based on classified program proxy indicators)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission deployment landscape
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and system integration flow
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising border security and asymmetric warfare threats
Increasing adoption of unmanned combat support systems
Technological advancements in AI and autonomy
Operational risk reduction for military personnel
Growing defense modernization budgets
Integration of UGVs into multi-domain operations - Challenges
High system development and integration costs
Limited autonomy in complex terrain
Cybersecurity and electronic warfare vulnerabilities
Regulatory and ethical constraints on autonomous weapons
Maintenance complexity in harsh environments
Interoperability issues with legacy systems - Opportunities
Expansion of autonomous logistics platforms
Export potential to allied defense markets
Integration with UAV and C4ISR systems
Development of swarm-enabled UGVs
Urban warfare and tunnel detection applications
Dual-use adoption for civilian security roles - Trends
Shift toward autonomous and semi-autonomous platforms
Increased use of AI-driven perception systems
Modular payload architectures
Integration of remote weapon stations
Enhanced focus on survivability and stealth
Growing collaboration between defense startups and OEMs - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Tracked UGVs
Wheeled UGVs
Hybrid mobility platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Reconnaissance and surveillance
Combat and armed support
Logistics and resupply
Explosive ordnance disposal
Border patrol and perimeter security - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Teleoperated systems
Semi-autonomous systems
Autonomous navigation systems
AI-enabled perception platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense forces
Homeland security
Border security agencies
Critical infrastructure protection - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Line-of-sight communication
Beyond-line-of-sight communication
Satellite-enabled control
Mesh network enabled systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northern Israel
Southern Israel
Central Israel
Border and conflict-prone zones
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (product portfolio strength, autonomy level, defense contracts, geographic reach, technology integration, production capability, pricing strategy, after-sales support)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Roboteam
IMI Systems
Rheinmetall
Milrem Robotics
QinetiQ
General Dynamics Land Systems
Northrop Grumman
Textron Systems
Leonardo
Oshkosh Defense
HDT Global
Teledyne FLIR
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


