Market Overview
The Israel Unmanned Sea Systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by active fleet deployment, sustained defense modernization, and expanding maritime surveillance programs. The market shows stable momentum with increased platform deliveries, growing system upgrades, and steady procurement cycles. Adoption levels increased during the recent period due to heightened coastal monitoring needs, multi-mission capability demand, and autonomous technology maturity. Operational utilization expanded across surveillance, mine countermeasures, and patrol missions, supported by consistent defense allocations and naval digitization initiatives.
The market is primarily concentrated along Israel’s Mediterranean coastline, supported by strong naval infrastructure and defense manufacturing ecosystems. Coastal command centers, naval bases, and defense technology clusters form the operational backbone. Demand concentration remains high in areas supporting border security, offshore infrastructure protection, and maritime intelligence. Strong government backing, advanced naval R&D capabilities, and an established defense supply chain further reinforce regional dominance and sustained system deployment across maritime zones.
Market Segmentation
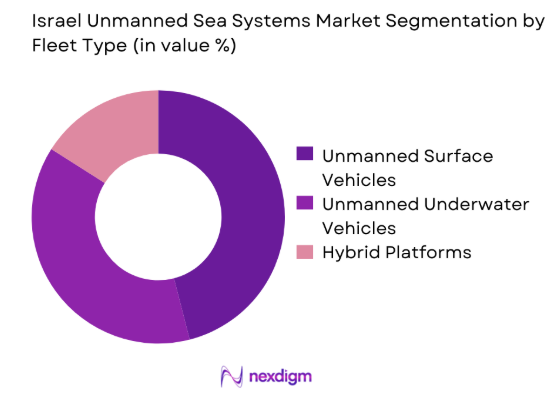
By Fleet Type
Unmanned surface vehicles dominate deployment due to versatility, endurance, and operational adaptability across patrol and reconnaissance missions. Their ability to integrate sensors, communication modules, and weapon payloads supports wide mission coverage. Unmanned underwater vehicles follow closely, driven by mine detection and seabed monitoring requirements. Hybrid platforms are gradually emerging, supported by multi-role mission concepts and modular architectures. Fleet investment decisions are strongly influenced by mission duration, autonomy levels, and integration compatibility with existing naval assets.
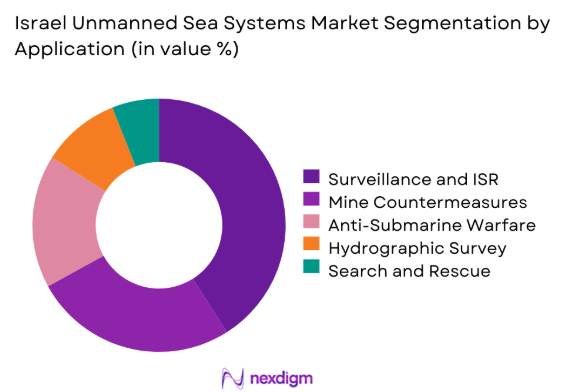
By Application
Surveillance and intelligence missions represent the dominant application due to persistent border monitoring requirements. Mine countermeasure operations follow as naval safety priorities increase around ports and shipping lanes. Anti-submarine warfare applications continue expanding with improved sensor payloads and autonomous navigation. Hydrographic surveying remains essential for infrastructure planning and coastal management. Search and rescue operations are gradually integrating unmanned platforms to reduce operational risks and enhance coverage efficiency.
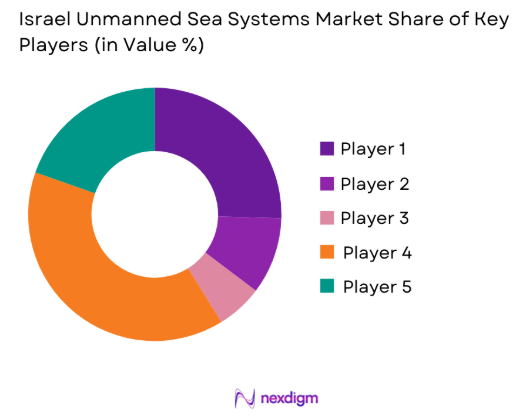
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a mix of domestic defense leaders and specialized maritime technology providers. Competition is driven by platform autonomy, system reliability, integration capability, and long-term support offerings. Vendors emphasize modular designs, mission flexibility, and compliance with naval standards. Strategic collaborations with defense agencies and continuous product upgrades define competitive positioning across the ecosystem.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Shipyards | 1959 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Aeronautics Group | 1997 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Unmanned Sea Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising maritime security threats in eastern Mediterranean
Maritime security threats increased during 2024 and 2025, driving higher naval surveillance activity and unmanned deployment frequency. Regional tensions elevated demand for persistent monitoring platforms supporting coastal awareness and offshore asset protection. Unmanned systems provide continuous coverage with reduced human exposure and improved endurance. Defense planners emphasized autonomous patrol capabilities to strengthen maritime domain awareness. Increased vessel traffic intensified monitoring requirements across commercial and strategic sea lanes. Integration with coastal command networks improved operational responsiveness. Cross-domain surveillance coordination expanded reliance on autonomous surface and subsurface platforms. Unmanned fleets supported real-time intelligence fusion across naval command structures. Operational efficiency improvements reinforced procurement interest among defense agencies. These factors collectively strengthened market expansion dynamics.
Increasing adoption of autonomous naval surveillance platforms
Autonomous surveillance platforms experienced rising adoption due to advancements in navigation and sensor technologies. Improved autonomy enabled longer missions with minimal human intervention. Naval operators prioritized persistent ISR capabilities to enhance situational awareness. Autonomous systems reduced operational fatigue and improved data accuracy. Integration with command networks enhanced real-time decision-making efficiency. Increased reliability supported expanded mission profiles across patrol and reconnaissance tasks. Reduced manpower dependency aligned with modern naval operational strategies. Autonomous deployment supported rapid response requirements during maritime incidents. Fleet modernization programs increasingly favored autonomous capabilities. These developments sustained strong adoption momentum.
Challenges
High system integration and validation complexity
System integration complexity remains a significant challenge for unmanned sea system deployment. Multiple sensor fusion requirements complicate platform validation processes. Compatibility issues arise between legacy naval systems and autonomous technologies. Certification procedures extend deployment timelines significantly. Testing requirements increase operational costs and development durations. Interoperability validation demands extensive simulation and sea trials. Cybersecurity integration adds additional design complexity. Command and control synchronization requires continuous system updates. Technical failures during trials impact procurement confidence. These challenges constrain rapid scalability across fleets.
Regulatory and operational restrictions in contested waters
Operational deployment faces regulatory constraints within sensitive maritime zones. International maritime laws limit autonomous operations in contested regions. Navigation safety compliance imposes strict operational protocols. Restricted waters reduce mission flexibility for autonomous platforms. Regulatory uncertainty affects cross-border deployment planning. Approval processes delay operational readiness timelines. Rules regarding autonomous engagement remain under development. Coordination with manned vessels introduces operational complexity. Environmental compliance requirements add further constraints. These limitations impact mission scalability and deployment flexibility.
Opportunities
Expansion of unmanned fleet modernization programs
Fleet modernization initiatives continue expanding across naval forces to replace aging assets. Unmanned platforms offer scalable alternatives to traditional vessels. Modernization programs emphasize modularity and mission adaptability. Increased defense funding allocations support fleet renewal strategies. Lifecycle cost advantages strengthen unmanned system adoption. Integration with digital naval architectures enhances operational efficiency. Autonomous platforms enable faster deployment cycles. Interoperability with allied systems improves regional coordination. Modernization plans prioritize long-endurance capabilities. These trends create sustained growth opportunities.
Integration of AI-enabled autonomous navigation
Artificial intelligence integration enhances navigation accuracy and mission autonomy. AI-based decision systems improve obstacle avoidance and route optimization. Machine learning enables adaptive mission planning under dynamic conditions. Enhanced data processing supports faster threat identification. Autonomous learning reduces operator workload significantly. AI-driven platforms improve endurance and operational reliability. Advanced analytics support predictive maintenance planning. AI integration aligns with next-generation naval strategies. Development investments accelerate system intelligence levels. These advancements unlock long-term operational advantages.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to maintain steady expansion driven by continued naval modernization and autonomous technology integration. Increased emphasis on maritime security and surveillance will support sustained system deployment. Technological advancements in autonomy and sensor fusion will further enhance operational effectiveness. Strategic partnerships and government-backed programs are expected to reinforce long-term growth momentum.
Major Players
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Israel Shipyards
- Aeronautics Group
- BlueBird Aero Systems
- Ocean Aero
- L3Harris Technologies
- Thales Group
- Saab AB
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Kongsberg Gruppen
- BAE Systems
- Teledyne Marine
- General Dynamics
Key Target Audience
- Israeli Ministry of Defense
- Israeli Navy Procurement Directorate
- Maritime Border Security Agencies
- Coastal Surveillance Authorities
- Offshore Infrastructure Operators
- Defense System Integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Defense export control and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope was defined through platform classification, mission profiles, and deployment environments. Key variables included fleet size, autonomy levels, and operational roles. Data parameters were structured to reflect defense procurement realities.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was developed using bottom-up assessment of active programs and platform deployments. Segmentation logic was validated through operational use cases and defense planning frameworks.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through expert consultations with naval engineers and defense analysts. Operational feasibility and adoption patterns were cross-checked for consistency.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All findings were consolidated using triangulation techniques. Final insights were structured to ensure analytical consistency and strategic relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Operational Scope Mapping, Platform and Mission Taxonomy Structuring, Bottom-Up Fleet and Program Level Market Estimation, Revenue Attribution by Platform and Deployment Model, Primary Validation with Naval and Defense Program Stakeholders, Cross-Verification Through Program Budget and Procurement Analysis, Assumption Normalization and Data Triangulation)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and mission deployment landscape
- Ecosystem and value chain structure
- Defense procurement and regulatory framework
- Growth Drivers
Rising maritime security threats in eastern Mediterranean
Increasing adoption of autonomous naval surveillance platforms - Challenges
High system integration and validation complexity
Regulatory and operational restrictions in contested waters - Opportunities
Expansion of unmanned fleet modernization programs
Integration of AI-enabled autonomous navigation - Trends
Increased deployment of modular payload systems
Growing interoperability with manned naval platforms - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Unit Economics, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Unmanned Surface Vehicles
Unmanned Underwater Vehicles
Hybrid Autonomous Platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance
Mine Countermeasures
Anti-Submarine Warfare
Maritime Border Security
Hydrographic and Survey Missions - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Remote Operated Systems
Semi-Autonomous Systems
Fully Autonomous Systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Naval Defense Forces
Homeland Security Agencies
Port and Coastal Authorities
Research Institutions - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Line of Sight Control
Satellite Communication
Hybrid Communication Architecture - By Region (in Value %)
Northern Coastal Zone
Central Coastal Zone
Southern Maritime Zone
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Platform maturity, Autonomy level, Mission flexibility, Integration capability, Naval certification, After-sales support, Export readiness, Cost efficiency)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Israel Shipyards
Aeronautics Group
BlueBird Aero Systems
Saildrone
Ocean Aero
L3Harris Technologies
Thales Group
Saab AB
Leonardo S.p.A.
Kongsberg Gruppen
BAE Systems
Teledyne Marine
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Unit Economics, 2026–2035


