Market Overview
The Israel Unmanned Underwater Vehicle market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by increasing naval modernization initiatives and expanding autonomous system deployments. Operational fleets recorded more than 120 active underwater missions during recent assessment periods, reflecting rising utilization intensity. Platform upgrades, sensor integration, and endurance enhancements remain key focus areas. Procurement cycles have shortened due to evolving maritime security needs, while local manufacturing capabilities continue expanding. Testing programs and pilot deployments increased across defense-linked coastal zones, reinforcing demand momentum.
The market is primarily concentrated across coastal defense hubs and naval command centers, supported by advanced maritime infrastructure and testing facilities. Southern and central coastal regions dominate deployments due to strategic maritime corridors and operational readiness levels. Strong defense-industrial integration, localized supply chains, and supportive government policies sustain market maturity. Research institutions and defense laboratories further reinforce ecosystem development through technology validation, simulation environments, and continuous platform optimization programs.
Market Segmentation
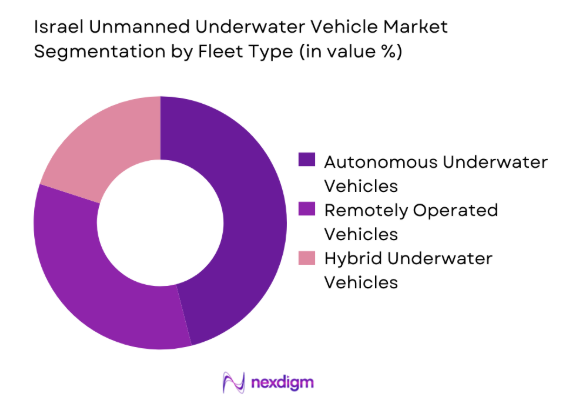
By Fleet Type
Autonomous underwater vehicles dominate fleet deployment due to superior endurance, reduced human risk, and expanding mission adaptability. These systems increasingly support mine countermeasures, seabed surveillance, and reconnaissance operations, driven by growing operational confidence. Remotely operated vehicles maintain relevance for precision interventions and controlled missions requiring real-time oversight. Hybrid platforms are gaining traction for multi-mission flexibility, enabling seamless transitions between autonomous and operator-controlled modes. Continuous investment in propulsion efficiency and navigation accuracy further strengthens fleet diversification and long-term operational reliability.
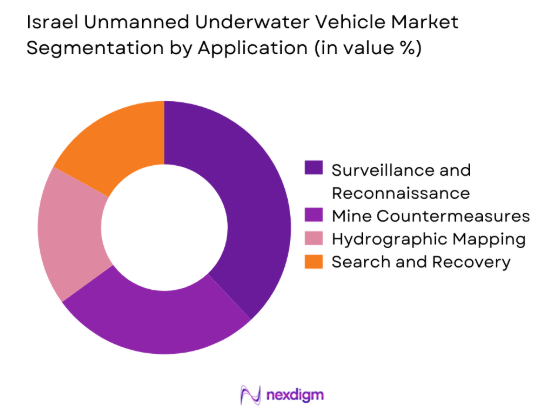
By Application
Surveillance and reconnaissance applications dominate demand due to persistent maritime security requirements and expanding underwater monitoring needs. Mine countermeasure operations represent a significant application area driven by naval readiness priorities. Hydrographic and seabed mapping applications continue growing, supported by offshore infrastructure development. Search and recovery operations maintain steady demand for both defense and civil missions. Multi-role adaptability increasingly influences procurement decisions, encouraging investments in modular payload architectures and mission-configurable platforms.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of domestic defense manufacturers and international technology providers with strong integration capabilities. Market competition centers on system reliability, mission endurance, sensor sophistication, and compliance with naval operational standards. Strategic collaborations and long-term defense contracts shape market positioning, while continuous innovation remains critical for differentiation.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Atlas Elektronik | 1902 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel Unmanned Underwater Vehicle Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising naval modernization programs and asymmetric maritime threat environment
Naval modernization initiatives continue expanding as maritime security threats evolve across strategic coastal zones. Defense planners increasingly prioritize underwater domain awareness to counter asymmetric naval challenges. Fleet upgrades focus on autonomous surveillance and mine detection systems for enhanced readiness. Investment allocation emphasizes multi-mission capabilities supporting persistent underwater monitoring. Technological refresh cycles have accelerated due to evolving operational doctrines. Integration of unmanned platforms strengthens force multiplication across naval operations. Enhanced situational awareness improves response effectiveness during maritime contingencies. Coastal infrastructure protection further reinforces modernization demand. Cross-domain interoperability supports joint naval and air defense coordination. These dynamics collectively reinforce sustained growth across unmanned underwater deployments.
Increasing adoption of autonomous systems for underwater surveillance and security missions
Autonomous platforms are increasingly preferred for prolonged underwater surveillance operations. Reduced human intervention lowers operational risk and mission costs. Advanced navigation algorithms improve mission reliability under complex underwater conditions. Sensor fusion enhances detection accuracy for underwater threats. Deployment flexibility enables rapid response to evolving security requirements. Automation supports continuous monitoring of strategic maritime zones. Operational endurance improvements allow extended mission durations without surface support. Integration with command systems strengthens real-time decision-making. Autonomous capabilities reduce manpower constraints across naval units. These advantages continue driving accelerated adoption across defense applications.
Challenges
High development and integration costs of advanced underwater platforms
Advanced underwater systems require significant investment in engineering and materials development. Integration of sensors, propulsion, and communication modules increases system complexity. Development cycles remain lengthy due to rigorous testing requirements. Customization for specific missions elevates production costs further. Budget constraints limit rapid fleet expansion across operational units. Lifecycle maintenance expenses add to long-term ownership costs. Specialized components require limited supplier ecosystems. Cost optimization remains difficult due to low production volumes. Upgrading legacy systems presents additional financial burdens. These cost pressures constrain broader market penetration.
Operational limitations in complex underwater environments
Underwater environments impose constraints on navigation accuracy and communication reliability. Signal attenuation affects data transmission over extended distances. Variable seabed conditions challenge autonomous maneuvering capabilities. Environmental noise interferes with sensor performance during missions. Battery limitations restrict endurance in deep-water operations. Maintenance complexity increases due to harsh operating conditions. Recovery operations remain resource intensive in adverse environments. Weather variability further impacts deployment consistency. System calibration demands frequent adjustments for accuracy. These operational challenges restrict full utilization potential.
Opportunities
Expansion of autonomous maritime border security initiatives
Maritime border protection initiatives increasingly incorporate autonomous underwater monitoring systems. Governments prioritize persistent surveillance to counter illegal activities and intrusions. Integration with coastal command networks enhances situational awareness. Autonomous systems enable continuous coverage without human fatigue constraints. Expanded maritime patrol zones drive deployment scale. Border security funding supports long-term platform investments. Real-time data analytics improves threat identification capabilities. Collaboration with naval agencies accelerates technology adoption. System interoperability supports multi-layered defense strategies. These initiatives create sustained growth opportunities.
Integration of artificial intelligence in underwater navigation and sensing
Artificial intelligence enhances autonomous decision-making in complex underwater environments. Machine learning algorithms improve obstacle avoidance and route optimization. Adaptive sensing increases detection accuracy for submerged objects. AI-driven analytics reduce false detection rates during missions. Predictive maintenance capabilities improve system reliability. Autonomous learning supports mission efficiency enhancements. Integration with onboard processors enables real-time adjustments. AI adoption reduces operator dependency during extended deployments. Continuous data learning strengthens operational effectiveness. These advancements unlock significant performance gains.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to experience steady expansion driven by continued naval modernization and autonomous technology integration. Advancements in artificial intelligence and sensor miniaturization will enhance operational efficiency. Strategic investments and policy support will strengthen domestic manufacturing capabilities. Collaboration between defense agencies and technology developers will accelerate innovation. Long-term demand will remain anchored in maritime security and surveillance applications.
Major Players
- Elbit Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Atlas Elektronik
- Saab
- Kongsberg Maritime
- Teledyne Marine
- L3Harris Technologies
- Thales Group
- ECA Group
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- BAE Systems
- Bluefin Robotics
- Ocean Infinity
- Lockheed Martin
Key Target Audience
- Israeli Ministry of Defense
- Israeli Navy
- Border Security Agencies
- Offshore Energy Operators
- Port and Harbor Authorities
- Defense System Integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Maritime Security Regulators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key operational, technological, and regulatory variables were identified through structured market scoping. Focus was placed on deployment models, application areas, and system configurations. Data points were aligned with defense procurement frameworks and operational usage patterns.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was developed through segmentation analysis and application mapping. Demand drivers and constraints were evaluated using deployment trends and technology adoption indicators. Cross-validation ensured consistency across segments.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through consultations with defense analysts and system integrators. Operational insights supported refinement of adoption trends. Technical feasibility assessments strengthened analytical accuracy.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into structured insights aligned with market dynamics. Data consistency checks ensured logical coherence. Final outputs were refined for strategic clarity and decision relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for unmanned underwater platforms, defense and commercial segmentation framework development, bottom-up fleet and procurement-based market sizing approach, revenue attribution through platform and subsystem mapping, primary validation with naval operators and defense integrators, data triangulation using contract analysis and deployment tracking, assumption validation based on operational and regulatory constraints)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission deployment landscape
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and integration framework
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising naval modernization programs and asymmetric maritime threat environment
Increasing adoption of autonomous systems for underwater surveillance and security missions
Expansion of offshore infrastructure monitoring requirements
Technological advancements in sensors and autonomous navigation
Growing focus on force multiplication through unmanned systems - Challenges
High development and integration costs of advanced underwater platforms
Operational limitations in complex underwater environments
Regulatory constraints on autonomous defense systems
Limited interoperability between legacy and new-generation systems
Skilled manpower shortages for system operation and maintenance - Opportunities
Expansion of autonomous maritime border security initiatives
Integration of artificial intelligence in underwater navigation and sensing
Export potential to allied naval forces
Dual-use applications in offshore energy and research
Collaborative development programs with international defense partners - Trends
Shift toward modular and scalable UUV platforms
Increased endurance and battery efficiency advancements
Growing use of swarm and networked underwater systems
Emphasis on stealth and low acoustic signature designs
Rising investments in real-time underwater data analytics - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
Remotely Operated Vehicles
Hybrid Underwater Vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Mine countermeasures
Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance
Anti-submarine warfare
Hydrographic survey and seabed mapping
Search and recovery operations - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Tethered systems
Untethered autonomous systems
Hybrid communication systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Naval defense forces
Homeland security agencies
Offshore energy operators
Research and academic institutions - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Acoustic communication
Fiber optic tethered communication
Hybrid communication systems - By Region (in Value %)
Northern Israel
Central Israel
Southern Israel
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology maturity, Operational range, Payload capability, Autonomy level, Integration flexibility, After-sales support, Defense compliance, Cost competitiveness)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Elbit Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elta Systems
Atlas Elektronik
Saab
Kongsberg Maritime
Teledyne Marine
L3Harris Technologies
Thales Group
ECA Group
General Dynamics Mission Systems
BAE Systems
Bluefin Robotics
Ocean Infinity
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


