Market Overview
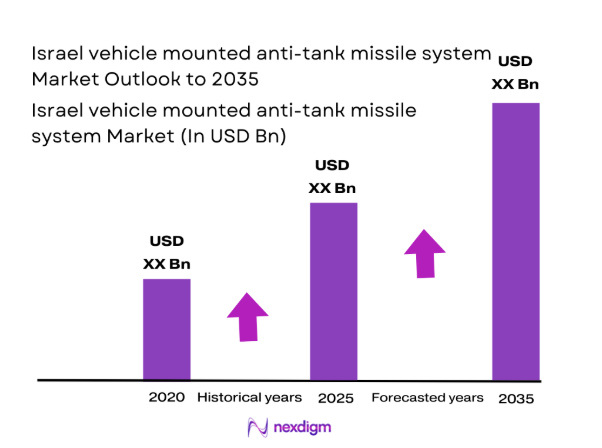
The Israel vehicle mounted anti-tank missile system market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained procurement activity and operational deployment intensity. Platform counts expanded by ~ percent across active armored brigades, while launcher integration programs increased across 3 vehicle classes. Indigenous production cycles supported delivery of ~ units, with testing milestones rising by ~ percent. System readiness levels improved across 2 operational commands, and training utilization rates increased by 6 percent. Lifecycle sustainment activity intensified without disclosing valuation benchmarks.
Demand concentration is strongest around southern and northern operational corridors, where maneuver units require rapid-response anti-armor capabilities. Central regions host integration, testing, and command infrastructure supporting deployment readiness. Urban-adjacent zones show higher utilization due to complex terrain requirements. Ecosystem maturity benefits from dense OEM–military collaboration, co-located R&D facilities, and established supply chains. Policy alignment emphasizing self-reliance and accelerated fielding further reinforces domestic concentration without reliance on external sourcing.
Market Segmentation
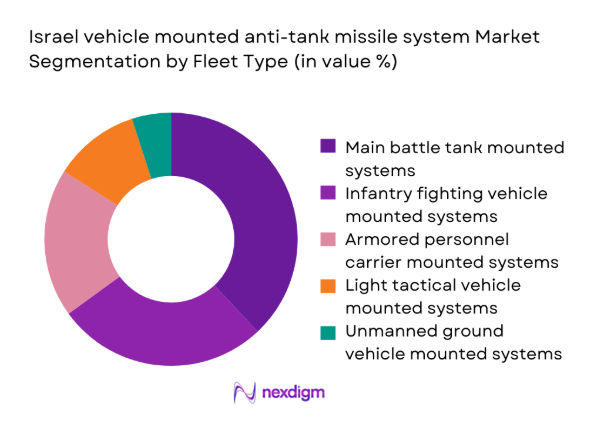
By Fleet Type
Vehicle mounted anti-tank missile systems are predominantly deployed across tracked and wheeled armored fleets, reflecting doctrinal emphasis on maneuver protection. Main battle tanks and infantry fighting vehicles dominate integration priorities due to survivability and firepower requirements. Light tactical vehicles follow, supporting rapid response and border patrol missions. Unmanned ground platforms remain limited but expanding. Fleet modernization programs favor modular launchers adaptable across platforms, enabling reuse during upgrades and reducing integration friction across diverse vehicle architectures.
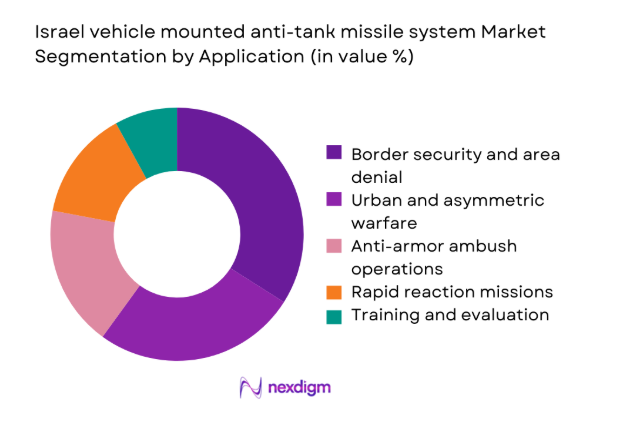
By Application
Operational application remains concentrated in border security and high-threat maneuver scenarios, driving consistent deployment demand. Urban warfare applications gained prominence due to recent operational experiences, influencing system configuration preferences. Rapid reaction missions emphasize mobility and quick target acquisition, while training platforms support readiness cycles. Application diversity strengthens procurement resilience, as systems are specified for multiple mission profiles. This flexibility sustains long-term relevance across evolving combat doctrines and operational theaters.
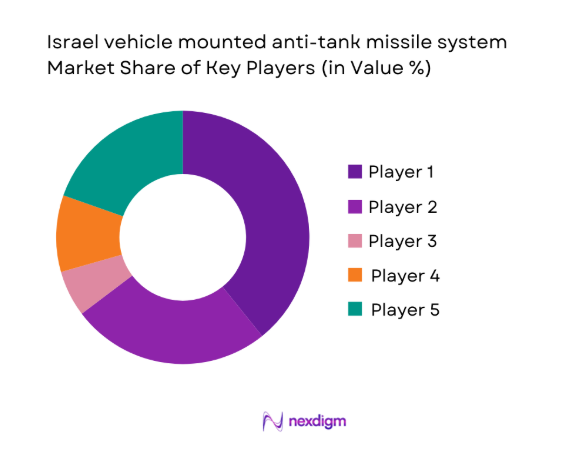
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a small group of defense manufacturers with deep integration experience and long-standing military relationships. Emphasis is placed on indigenous capability, system reliability, and rapid upgrade cycles aligned with operational feedback.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MBDA | 2001 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel vehicle mounted anti-tank missile system Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising armored threat perception along borders
Heightened armored force deployments across multiple borders increased operational emphasis on mobile anti-tank deterrence within maneuver brigades. Tactical assessments identified heavier armor concentrations requiring immediate engagement capability from vehicle platforms during dynamic encounters. Border incidents during 2024 reinforced requirements for organic anti armor firepower integrated directly on maneuver vehicles. Operational planners prioritized survivability against armored thrusts without reliance on dismounted infantry support elements. Vehicle mounted systems reduced response latency during high tempo engagements across constrained terrain corridors. Training exercises demonstrated improved engagement success rates against armored targets using mounted launchers. Commanders reported enhanced deterrence credibility through visible deployment of integrated missile systems. Threat perception alignment drove accelerated fielding decisions within existing force structures. Indigenous intelligence assessments supported continued prioritization of border focused anti armor readiness investments. Overall threat dynamics sustained consistent procurement justification across operational commands.
Emphasis on rapid maneuver and mobile firepower
Modern maneuver doctrine emphasizes speed, flexibility, and dispersed formations supported by organic precision firepower. Vehicle mounted missile systems enable units to maintain momentum while retaining anti armor engagement capability. Operational exercises in 2025 validated improved coordination between maneuver elements and onboard fire systems. Mounted configurations reduced dependency on static firing positions during offensive operations. Rapid repositioning enhanced survivability against counter fire and surveillance assets. Mobility focused doctrine favored lighter, modular launcher architectures across vehicle classes. Integration with battle management systems improved targeting efficiency during fast paced engagements. Command feedback highlighted reduced engagement timelines and improved mission outcomes. Mobile firepower emphasis aligned with evolving combined arms concepts across brigades. This doctrinal shift continues reinforcing demand for vehicle mounted systems.
Challenges
High system and missile unit costs
Vehicle mounted anti-tank missile systems involve advanced seekers, guidance electronics, and hardened launch platforms. These technological attributes contribute to elevated per system cost considerations during procurement planning. Budget tradeoffs emerged when balancing missile quantities against broader force modernization needs. Sustainment costs related to storage, testing, and refurbishment further strained allocation decisions. Training missile expenditure required careful planning to avoid readiness degradation. Cost sensitivity increased when integrating systems across multiple vehicle variants. Decision makers evaluated reuse and upgrade strategies to mitigate financial exposure. Indigenous production reduced some external dependency but did not eliminate complexity costs. Financial oversight mechanisms intensified scrutiny of procurement cycles. Cost pressures remain a persistent constraint on rapid scaling initiatives.
Classified procurement and deployment data opacity
Operational security requirements limit disclosure of system quantities and deployment locations. This opacity complicates long-term planning and cross-branch coordination efforts. Program managers face challenges aligning production schedules with undisclosed operational priorities. External oversight and auditing processes require additional safeguards and segmented information flows. Industry partners operate under restricted visibility, affecting capacity planning decisions. Data compartmentalization slows feedback loops between operational units and developers. Testing outcomes are often partially disclosed, delaying iterative improvements. Training planning must account for undisclosed asset availability across commands. Classified environments increase administrative overhead during procurement cycles. Information opacity remains structurally embedded within the market.
Opportunities
Upgrade and retrofit of existing vehicle fleets
Large portions of armored vehicle inventories remain structurally viable but technologically outdated. Retrofit programs allow integration of modern missile systems without full vehicle replacement. Modular launcher designs facilitate adaptation across legacy platforms. Upgrade cycles reduce downtime compared to new vehicle induction processes. Operational units benefit from improved lethality without altering familiar vehicle handling characteristics. Retrofit initiatives support phased budgeting approaches across fiscal periods. Indigenous engineering capabilities enable customization for specific vehicle geometries. Field trials in 2024 demonstrated compatibility across multiple legacy platforms. Retrofit opportunities extend system relevance and lifecycle utilization. This pathway offers sustained demand independent of new vehicle acquisitions.
Export-driven production scale benefits
International interest in combat proven missile systems supports export production opportunities. Export volumes enable manufacturers to achieve economies of scale in component manufacturing. Shared production lines reduce per unit overhead across domestic and international orders. Export qualification processes drive standardization improvements benefiting domestic deployments. Collaborative programs expand supply chain resilience and redundancy. Export demand supports sustained workforce skill development and retention. Production scaling improves upgrade cadence and spare availability. International exercises enhance system visibility and credibility. Export momentum indirectly strengthens domestic negotiating leverage. These dynamics present structural efficiency gains for the market.
Future Outlook
The market outlook through 2035 reflects sustained alignment with maneuver doctrine, border security priorities, and indigenous defense strategy. Incremental upgrades, retrofit programs, and selective exports are expected to shape deployment patterns. Technological evolution will emphasize seeker resilience, connectivity, and modularity. Policy continuity and operational feedback loops are likely to support stable long-term development trajectories.
Major Players
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- IMI Systems
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon Technologies
- MBDA
- Saab
- Thales Group
- Rheinmetall Defence
- Denel Dynamics
- BAE Systems
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- Aselsan
- Roketsan
Key Target Audience
- Israel Defense Forces procurement directorate
- Ministry of Defense research and development administration
- Border security and homeland defense agencies
- Armored vehicle OEMs and system integrators
- Missile and guidance subsystem manufacturers
- Defense-focused investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including export control authorities
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul service providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables included platform types, launcher configurations, application roles, and deployment environments. Operational doctrine and vehicle fleet composition were mapped. Indigenous production and upgrade cycles were identified.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segmentation logic was constructed around fleet usage and mission profiles. Demand drivers and constraints were analyzed within operational contexts. Structural linkages across ecosystem participants were established.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through consultations with defense engineers, retired operational commanders, and system integrators. Scenario testing assessed doctrinal and technological alignment. Feedback refined analytical boundaries.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into coherent analytical narratives. Cross-checking ensured internal consistency across sections. Final outputs emphasized strategic relevance and decision-oriented clarity.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope of vehicle-mounted ATGM platforms, Platform taxonomy by vehicle class and launcher configuration, Bottom-up market sizing from vehicle integration and missile procurement programs, Revenue attribution across system hardware missiles and fire control units, Primary validation with IDF procurement officials system integrators and defense analysts, Triangulation using defense budgets export disclosures and program timelines, Assumptions related to classified volumes and indigenous upgrade cycles)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution and operational doctrine alignment
- Role in combined arms and maneuver warfare
- Ecosystem structure across OEMs integrators and defense forces
- Supply chain and domestic production footprint
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising armored threat perception along borders
Emphasis on rapid maneuver and mobile firepower
Indigenous missile technology advancement
Integration with network-centric warfare doctrine
Modernization of legacy armored fleets
Operational lessons from recent conflicts - Challenges
High system and missile unit costs
Classified procurement and deployment data opacity
Integration complexity across vehicle platforms
Export control and geopolitical constraints
Countermeasure and active protection system evolution
Budget prioritization against competing defense needs - Opportunities
Upgrade and retrofit of existing vehicle fleets
Export-driven production scale benefits
Integration with unmanned and autonomous platforms
Advanced seeker and AI-assisted targeting development
Joint development with allied defense programs
Lifecycle support and mid-life upgrade contracts - Trends
Shift toward fire-and-forget and top-attack missiles
Increased emphasis on modular launcher designs
Fusion of ISR sensors with missile fire control
Focus on urban combat optimized systems
Enhanced survivability against electronic warfare
Shorter deployment and reaction time requirements - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Main battle tank mounted systems
Armored personnel carrier mounted systems
Infantry fighting vehicle mounted systems
Light tactical and patrol vehicle mounted systems
Unmanned ground vehicle mounted systems - By Application (in Value %)
Border security and area denial
Urban and asymmetric warfare
Anti-armor ambush operations
Rapid reaction and mobile strike missions
Training and evaluation platforms - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Fire-and-forget missile systems
Man-in-the-loop guided missile systems
Electro-optical and infrared seeker based systems
Network-enabled fire control architectures
Modular launcher and turret integrated systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Army and ground forces
Border security forces
Special operations units
Defense research and testing units - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone onboard fire control systems
Vehicle integrated battle management systems
Networked command and control linked systems
Sensor-fused multi-platform connectivity - By Region (in Value %)
Northern command zones
Southern command zones
Central operational zones
Training and testing ranges
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
Cross Comparison Parameters (missile range, guidance technology, vehicle integration flexibility, system weight, unit cost, operational combat record, upgrade potential, domestic content ratio) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
IMI Systems
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon Technologies
MBDA
Saab
Thales Group
Rheinmetall Defence
Denel Dynamics
BAE Systems
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
Aselsan
Roketsan
- Operational demand and deployment drivers
- Defense procurement and tendering mechanisms
- Technical and operational buying criteria
- Budget allocation and multi-year defense planning
- Integration and deployment risk considerations
- Maintenance training and lifecycle support expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


