Market Overview
The Japan Aerospace and Defense market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained procurement across multi-domain platforms and mission systems, alongside steady modernization of legacy fleets and command networks. Ongoing capability refresh cycles, indigenous development programs, and long-term sustainment contracts underpin consistent demand. Investments remain focused on interoperability, survivability, and secure communications, with program pipelines supported by domestic primes and international collaboration under export compliance frameworks and quality assurance regimes.
Activity concentrates around Tokyo, Aichi, Kanagawa, and Hyogo, where aerospace clusters, shipyards, and advanced electronics ecosystems anchor program execution. Demand concentrates near JSDF bases and testing ranges, supported by mature supplier networks and logistics corridors. The ecosystem benefits from specialized manufacturing, avionics integration, and propulsion expertise, while policy frameworks prioritize secure supply chains, technology safeguarding, and resilience. Port infrastructure, airbases, and space operations facilities further reinforce regional concentration and delivery efficiency.
Market Segmentation
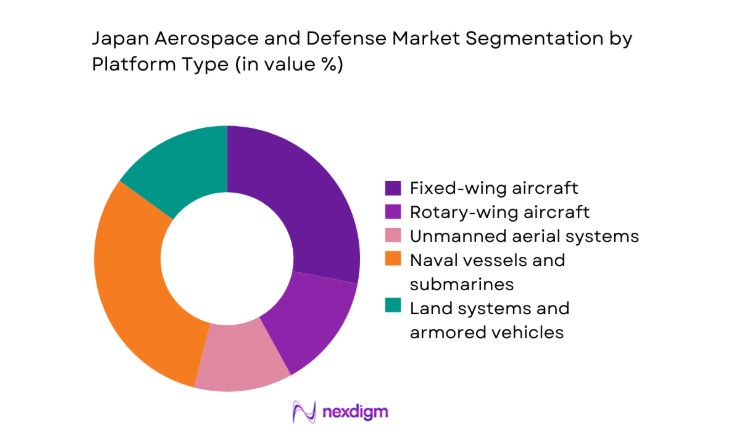
By Platform Type
Fixed-wing and maritime platforms dominate procurement due to persistent airspace monitoring, patrol requirements, and fleet sustainment cycles. Rotary-wing assets remain essential for mobility and disaster response integration, while unmanned systems expand for surveillance and risk mitigation. Naval surface combatants and submarines absorb sustained upgrade spending tied to sensor suites and propulsion reliability. Space and satellite systems gain traction for secure communications and situational awareness, supported by domestic manufacturing depth and allied interoperability standards. Lifecycle modernization programs increasingly bundle training, spares, and software-defined upgrades, reinforcing platform-centric procurement logic and long-term service contracts across programs.
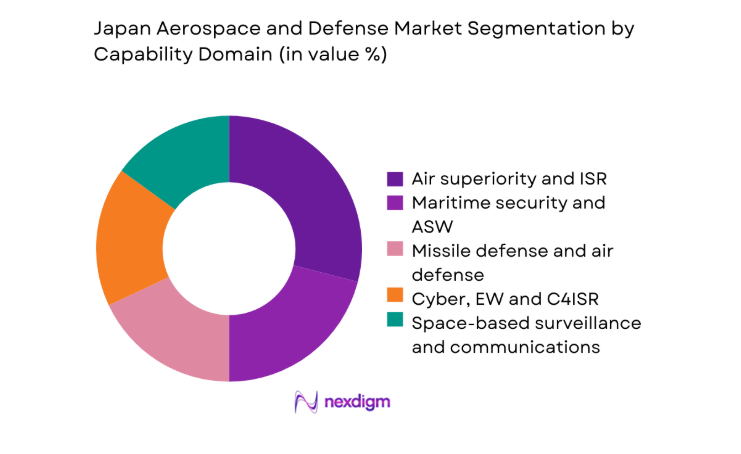
By Capability Domain
ISR and air superiority command priority as sensor fusion and persistent coverage drive mission effectiveness across domains. Missile defense and air defense capabilities attract sustained attention due to layered deterrence requirements and integration with allied networks. Cyber, EW, and C4ISR expand rapidly as digital resilience and secure communications become mission critical. Maritime security and ASW investments track sea-lane protection imperatives. Logistics, MRO, and sustainment remain foundational, with performance-based support and digital twins improving readiness. Capability-domain bundling increasingly aligns procurement with operational outcomes rather than discrete hardware purchases.
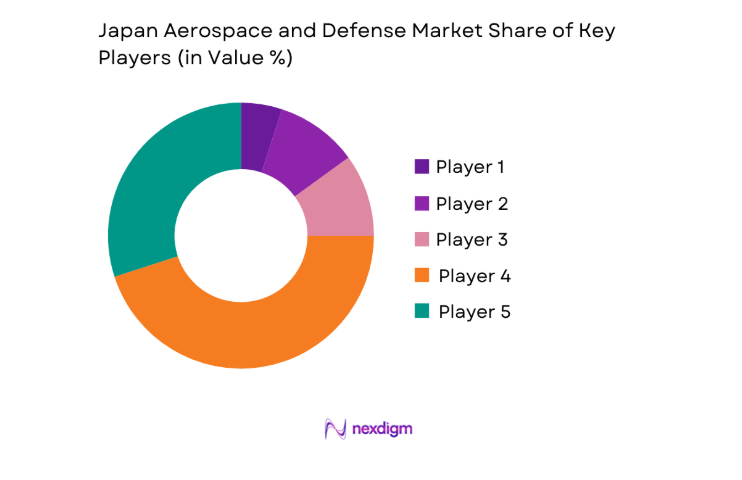
Competitive Landscape
The market features a concentrated set of domestic primes complemented by international integrators operating under co-development and licensed production frameworks. Competition centers on systems integration depth, program execution reliability, secure supply chains, and long-term sustainment capabilities aligned with stringent compliance and interoperability requirements.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries | 1884 | Tokyo | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kawasaki Heavy Industries | 1896 | Kobe | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Subaru Corporation | 1917 | Tokyo | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| IHI Corporation | 1853 | Tokyo | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | 1921 | Tokyo | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Japan Aerospace and Defense Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising defense budget aligned to threat environment in East Asia
Heightened regional security dynamics have driven multi-year budget uplifts and program authorizations supporting readiness, resilience, and deterrence. Parliamentary approvals in 2022 enabled procurement of 42 fixed-wing aircraft and modernization across 16 maritime platforms, while 2023 allocations supported 9 radar upgrades and 24 secure communications nodes. In 2024, 3 new ISR constellations entered integration testing and 12 coastal surveillance sites were hardened. Institutional coordination among defense, space, and cyber agencies expanded joint tasking across 5 commands, accelerating procurement cycles and sustainment contracting. Industrial policy measures approved in 2025 prioritized supplier resilience across 120 tier-two firms, stabilizing delivery schedules nationwide.
JSDF force modernization and multi-domain integration
Multi-domain integration programs are advancing interoperability across air, maritime, land, space, and cyber domains through unified command networks and open architectures. Between 2022 and 2023, 18 command centers completed network modernization, while 2024 saw 27 legacy platforms upgraded with modular mission systems. Joint exercises expanded from 14 to 21 annual iterations by 2025, embedding cross-domain data sharing protocols across 6 operational theaters. Institutional indicators include expanded joint doctrine adoption across 4 service components and standardized interfaces deployed across 33 mission-critical systems. These changes accelerate upgrade demand, software-defined capability insertion, and long-term sustainment contracts across fleets.
Challenges
Complex export controls and technology transfer constraints
Export control regimes and technology safeguards constrain collaborative development, extending approval timelines and limiting subsystem integration pathways. In 2022, compliance reviews delayed 11 cross-border work packages by 6 months, affecting avionics and propulsion modules. By 2023, 19 co-development interfaces required redesign to meet security baselines, while 2024 audits expanded compliance scope across 7 supply-chain tiers. Institutional oversight intensified with 5 additional control committees established by 2025, increasing documentation loads across 48 prime and tier-one programs. These constraints raise integration friction, slow testing cycles, and complicate configuration management across multinational program governance structures.
Lengthy procurement cycles and program approval processes
Procurement approvals remain multi-layered, extending lead times from requirement definition to contract award. In 2022, average cycle durations exceeded 420 days across 13 major programs. Process streamlining in 2023 reduced cycle times for 5 programs, yet 2024 saw 9 initiatives paused pending multi-agency clearance. By 2025, 22 milestone gates governed approvals across capability domains, requiring synchronized sign-offs from defense, finance, and security bodies. These timelines compress supplier planning windows, defer production ramp-ups, and increase inventory holding periods, complicating workforce allocation and supplier cash-flow predictability across long-duration platforms and sustainment contracts.
Opportunities
Next-generation fighter program and associated subsystems
The next-generation fighter initiative catalyzes demand across propulsion, avionics, mission software, sensors, and advanced materials. Between 2022 and 2023, 6 subsystem demonstrators completed flight-representative testing, while 2024 integration trials validated 14 open-architecture interfaces. Institutional indicators include expanded test infrastructure across 3 flight centers and 8 secure labs by 2025, enabling rapid iteration. Supply-chain readiness programs onboarded 36 qualified suppliers to meet quality and security baselines. These conditions create multi-year opportunities for modular upgrades, digital twins, and sustainment analytics across development, test, and operational phases supporting long-term capability insertion.
Maritime patrol and ASW modernization programs
Maritime patrol and ASW modernization programs expand sensor coverage, endurance, and data fusion across sea lanes. From 2022 to 2023, 9 patrol aircraft received sensor upgrades and 4 test ranges added acoustic arrays. In 2024, 11 surface platforms integrated new sonar processing stacks, and 2025 validation expanded multi-static tracking across 3 operational sectors. Institutional drivers include enhanced coordination among maritime, coast guard, and space monitoring units across 7 joint tasking nodes. These programs open opportunities for payload integration, software-defined processing, and sustainment services aligned with readiness metrics and mission availability targets.
Future Outlook
The outlook through 2035 reflects sustained modernization across air, maritime, cyber, and space domains, with greater emphasis on interoperability and resilient supply chains. Program execution will increasingly bundle hardware, software, and sustainment under outcome-based frameworks. Policy alignment and allied coordination are expected to accelerate multi-domain integration while strengthening domestic manufacturing depth. Digital engineering, open architectures, and lifecycle analytics will shape procurement and support models.
Major Players
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Subaru Corporation
- IHI Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Fujitsu Limited
- Toshiba Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Japan Aviation Electronics Industry
- ShinMaywa Industries
- Komatsu Defense Systems
- BAE Systems Japan
- Lockheed Martin Japan
- Boeing Japan
- RTX Japan
Key Target Audience
- Japan Ministry of Defense procurement divisions
- Acquisition, Technology & Logistics Agency program offices
- Japan Self-Defense Forces operational commands
- Prime contractors and Tier-1 subsystem suppliers
- Systems integrators and MRO providers
- Export compliance and security certification bodies
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Program inventories, platform lifecycles, subsystem maturity, and sustainment models were mapped across domains. Operational readiness indicators, integration dependencies, and compliance requirements were prioritized. Policy directives and procurement pathways were screened to define scope boundaries.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Capability demand was structured by platform and mission domain across acquisition and sustainment phases. Supply-chain capacity, test infrastructure availability, and integration readiness were assessed. Program pipelines were organized into near-term upgrades and longer-cycle development streams.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions on interoperability, delivery risk, and sustainment performance were stress-tested with practitioners. Program governance, security controls, and integration workflows were reviewed. Operational feedback loops informed scenario refinement.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into actionable insights aligned with procurement and delivery realities. Cross-domain linkages were reconciled to ensure coherence. Outputs were validated for internal consistency and practical relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope validation for Japan A&D platforms and services, MoD procurement data triangulation and budget cycle analysis, OEM and Tier-1 supplier shipment and backlog tracking)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission profiles across JSDF branches
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Growth Drivers
Rising defense budget aligned to threat environment in East Asia
JSDF force modernization and multi-domain integration
Expansion of missile defense and counterstrike capabilities - Challenges
Complex export controls and technology transfer constraints
Lengthy procurement cycles and program approval processes
High development costs for indigenous platforms - Opportunities
Next-generation fighter program and associated subsystems
Maritime patrol and ASW modernization programs
Growth in unmanned systems and autonomy - Trends
Multi-domain operations and network-centric warfare
Localization of supply chains and trusted supplier programs
Adoption of AI, autonomy and advanced sensors - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Platform Type (in Value %)
Fixed-wing aircraft
Rotary-wing aircraft
Unmanned aerial systems
Naval vessels and submarines - By Capability Domain (in Value %)
Air superiority and ISR
Maritime security and ASW
Missile defense and air defense
Cyber, EW and C4ISR
Space-based surveillance and communications - By Program Phase (in Value %)
New acquisition
Mid-life upgrade and modernization
Maintenance, repair and overhaul
Training and simulation
R&D and prototyping - By Procurement Channel (in Value %)
Domestic prime contractors
Joint development and co-production
Foreign military sales and direct commercial sales
Licensed production and offsets - By End User (in Value %)
Japan Ground Self-Defense Force
Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force
Japan Air Self-Defense Force
- Market share of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (platform portfolio breadth, indigenous manufacturing capability, JSDF program exposure, R&D intensity, systems integration depth, export readiness, MRO network scale, partnership ecosystem strength)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
Subaru Corporation
IHI Corporation
NEC Corporation
Fujitsu Limited
Toshiba Corporation
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
Japan Aviation Electronics Industry
ShinMaywa Industries
Komatsu Defense Systems
BAE Systems Japan
Lockheed Martin Japan
Boeing Japan
RTX Japan
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035