Market Overview
The Japan Airport Ground Support Vehicles Market market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by an active fleet base of ~ vehicles deployed across major aviation hubs and regional terminals. Recent procurement cycles added ~ vehicles to operational fleets, driven by modernization programs and replacement of aging diesel assets. Annual capital deployment toward fleet upgrades reached nearly USD ~ million, reflecting growing focus on efficiency and emissions compliance. Service and maintenance spending also crossed USD ~ million, indicating a mature aftermarket ecosystem sustaining long-term fleet performance.
The market shows strong concentration around major aviation clusters such as Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya, where dense passenger traffic, advanced ground handling ecosystems, and multi-terminal airport infrastructures create sustained demand for modern support vehicles. These regions benefit from early adoption of low-emission technologies, strong airline alliances, and policy-backed sustainability mandates. Secondary airports across Kyushu and Hokkaido are gradually upgrading fleets, but large metropolitan hubs continue to dominate due to higher utilization intensity, superior financing access, and stronger partnerships with global equipment manufacturers.
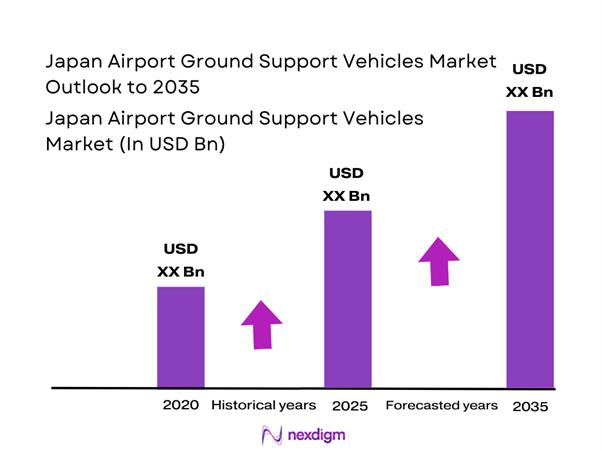

Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
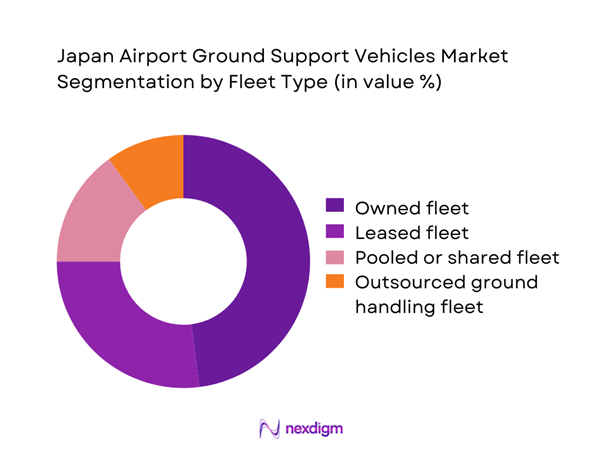
Owned fleets dominate the Japan Airport Ground Support Vehicles Market as major airlines and airport authorities prioritize long-term asset control and lifecycle cost optimization. Ownership models enable operators to align fleet specifications with terminal layouts, aircraft mix, and operational tempo, ensuring higher reliability during peak traffic periods. Large airports prefer in-house fleets to maintain service continuity and reduce dependency on third-party availability. Leasing and pooled fleets remain relevant among regional airports and seasonal operators, but strategic control, customization flexibility, and predictable maintenance planning continue to make owned fleets the preferred structure across primary aviation hubs.
By Technology Architecture
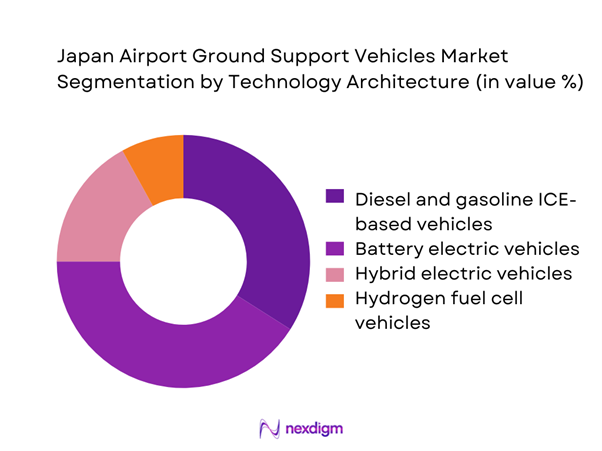
Battery electric vehicles lead technology adoption as airports accelerate decarbonization strategies and align with national sustainability objectives. Electric platforms offer lower operating noise, reduced emissions, and predictable maintenance cycles, making them well-suited for high-frequency baggage and towing operations. Hybrid systems continue to serve as transitional solutions where charging infrastructure remains limited, particularly at secondary airports. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are still at an early stage but attract pilot deployments in innovation-focused hubs. Overall, technology selection increasingly reflects long-term environmental compliance rather than short-term cost considerations.
Competitive Landscape
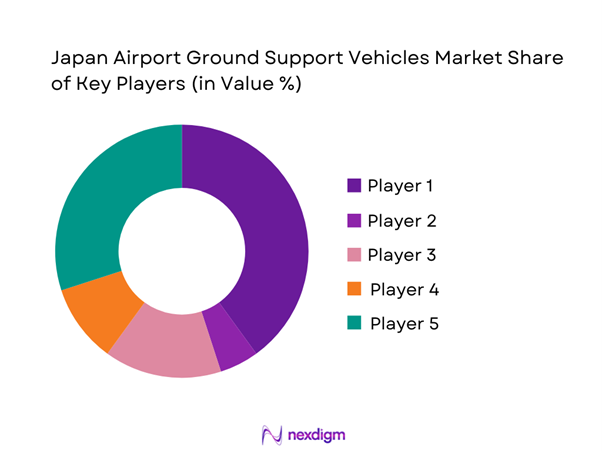
The Japan Airport Ground Support Vehicles Market exhibits moderate concentration, with a mix of global equipment manufacturers and strong domestic engineering firms shaping competitive dynamics. Large players dominate high-value contracts at major airports, while regional suppliers and niche specialists serve smaller terminals and customized operational needs.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Toyota Industries Corporation | 1926 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| JBT AeroTech | 1947 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| TLD | 1946 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Textron GSE | 1923 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Goldhofer AG | 1705 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Japan Airport Ground Support Vehicles Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising air passenger traffic and airport capacity expansion
Sustained growth in air travel has pushed several Japanese airports to operate above designed handling thresholds, requiring rapid scaling of ground operations. Over the recent period, passenger throughput expanded by ~ million travelers, compelling airports to deploy an additional ~ vehicles to maintain turnaround efficiency. Cargo throughput also increased by ~ tons, driving demand for specialized loaders and tractors. Capital allocations for terminal and apron expansion exceeded USD ~ million, indirectly stimulating fleet procurement. These structural shifts elevate baseline demand for ground support vehicles as airports prioritize operational resilience and congestion mitigation.
Shift toward low-emission and electric ground support fleets
Environmental mandates have accelerated the transition toward electric and low-emission ground support vehicles across major airports. Recent fleet renewal programs replaced nearly ~ diesel units with electric alternatives, supported by sustainability budgets totaling USD ~ million. Charging infrastructure installations reached ~ points across large hubs, enabling continuous electric operations. Annual emissions reduction targets translated into procurement of ~ electric vehicles per major airport cluster. This policy-driven shift is embedding electrification as a core growth engine for equipment manufacturers aligned with clean mobility strategies.
Challenges
High upfront cost of electric and hydrogen GSE
The transition to advanced propulsion technologies introduces significant capital pressure for operators. The average acquisition outlay for electric and hydrogen-powered units remains higher by USD ~ million across large fleet renewal cycles. Airports upgrading more than ~ vehicles face cumulative investment requirements exceeding USD ~ million, stretching capital budgets and extending payback timelines. Smaller regional airports, operating fleets below ~ vehicles, encounter greater financial constraints, slowing adoption. These economic barriers limit the pace of fleet transformation despite strong environmental incentives.
Limited charging and refueling infrastructure at regional airports
While major hubs have deployed over ~ charging points, many regional airports operate with fewer than ~ functional units, restricting large-scale electrification. Hydrogen refueling remains confined to pilot locations with fewer than ~ operational stations nationwide. Infrastructure rollout programs account for USD ~ million annually, yet geographic disparities persist. Operators managing fleets of ~ vehicles or more face operational risks due to downtime and range limitations. This uneven infrastructure maturity constrains uniform technology adoption across the national airport network.
Opportunities
Fleet electrification programs at major Japanese airports
Large-scale electrification initiatives at flagship airports create sustained procurement pipelines for advanced ground support vehicles. Recent tenders cover replacement of ~ vehicles over multi-year cycles, backed by public and private funding exceeding USD ~ million. Centralized fleet management programs aim to standardize equipment across terminals, increasing order volumes per contract. These initiatives also generate aftermarket demand for ~ charging systems and digital fleet monitoring tools. Manufacturers aligned with turnkey electrification solutions are positioned to capture long-term revenue streams from these structured modernization programs.
Adoption of autonomous and semi-autonomous GSE
Automation pilots are reshaping operational models in high-traffic airports, where labor optimization and safety enhancement are strategic priorities. Trial deployments of ~ autonomous tugs and baggage tractors have demonstrated productivity gains across ~ daily movements. Investment in intelligent mobility platforms reached USD ~ million, supporting integration of sensors, AI navigation, and fleet orchestration systems. As airports seek to scale these pilots, demand is emerging for ~ automated units per major hub, opening new growth corridors for technology-driven equipment providers.
Future Outlook
The Japan Airport Ground Support Vehicles Market is set to evolve toward a technology-centric ecosystem, where electrification, automation, and digital fleet management converge. Through the coming decade, sustainability mandates and smart airport programs will redefine procurement priorities, favoring integrated solutions over standalone equipment. Regional airports are expected to follow the lead of metropolitan hubs as infrastructure matures. Competitive differentiation will increasingly depend on service depth, software integration, and lifecycle support capabilities.
Major Players
- Toyota Industries Corporation
- JBT AeroTech
- TLD
- Textron GSE
- Goldhofer AG
- Mallaghan Engineering
- Kalmar Motor AB
- MULAG Fahrzeugwerk
- ShinMaywa Industries
- IHI Transport Machinery
- Weihai Guangtai Airport Equipment
- Tronair
- Clyde Machines
- ITW GSE
- Guinault
Key Target Audience
- Airport authorities and airport operating companies
- Airline ground operations and fleet management teams
- Ground handling service providers
- Air cargo terminal operators
- MRO service providers for airport equipment
- Investments and venture capital firms focused on mobility and infrastructure
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism and Civil Aviation Bureau
- Local government agencies overseeing airport sustainability programs
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core demand indicators were mapped across fleet age profiles, airport traffic intensity, and infrastructure readiness. Technology adoption patterns and regulatory compliance thresholds were assessed to define market boundaries. Stakeholder priorities were identified across operators, service providers, and equipment manufacturers.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Operational data points were structured around procurement cycles, replacement rates, and service lifecycles. Comparative assessment of propulsion technologies and automation maturity supported segmentation logic. Regional deployment patterns were evaluated to build a coherent national market framework.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were refined through structured consultations with airport operations leaders and fleet managers. Technology roadmaps were cross-validated with engineering teams and sustainability officers. Policy alignment and infrastructure rollout scenarios were stress-tested through expert reviews.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into integrated market narratives linking demand drivers with supply capabilities. Strategic insights were structured around investment priorities, risk factors, and opportunity pathways. Final outputs were aligned to decision-maker requirements across public and private stakeholders.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, airport ground support vehicle taxonomy across tugs loaders and service units, market sizing logic by airport traffic and GSE fleet deployment, revenue attribution across vehicle sales leasing and maintenance services, primary interview program with airports ground handlers and fleet managers, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and usage pathways in airport ground handling
- Ecosystem structure and stakeholder roles
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory and safety environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising air passenger traffic and airport capacity expansion
Shift toward low-emission and electric ground support fleets
Government incentives for airport decarbonization
Increasing outsourcing of ground handling services
Modernization of aging airport vehicle fleets
Growing focus on operational efficiency and turnaround time reduction - Challenges
High upfront cost of electric and hydrogen GSE
Limited charging and refueling infrastructure at regional airports
Fragmented procurement across airlines and handlers
Long replacement cycles for existing fleets
Complex certification and safety compliance requirements
Supply chain constraints for specialized components - Opportunities
Fleet electrification programs at major Japanese airports
Adoption of autonomous and semi-autonomous GSE
Expansion of smart airport initiatives and digital fleet management
Growth in air cargo operations and dedicated cargo hubs
Leasing and GSE-as-a-service business models
Retrofit and conversion of legacy vehicles to electric - Trends
Rapid penetration of battery electric baggage tractors and loaders
Integration of telematics for predictive maintenance
Standardization of GSE platforms across airline alliances
Use of AI-based dispatch and fleet optimization tools
Collaboration between airports and OEMs on sustainability targets
Increasing demand for modular and multi-use GSE designs - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Owned fleet
Leased fleet
Pooled or shared fleet
Outsourced ground handling fleet - By Application (in Value %)
Baggage and cargo handling
Passenger boarding and mobility assistance
Aircraft towing and pushback
Catering and cabin service support
Ground power and pre-conditioned air
Maintenance and service support - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Diesel and gasoline ICE-based vehicles
Battery electric vehicles
Hybrid electric vehicles
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Airport operators
Airlines
Ground handling service providers
MRO service providers
Dedicated air cargo operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone non-connected vehicles
Telematics-enabled vehicles
IoT-connected smart GSE
Integrated fleet management platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Kanto region
Kansai region
Chubu region
Kyushu region
Hokkaido region
Chugoku and Shikoku region
Okinawa region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (product portfolio breadth, electric vehicle readiness, local service footprint, fleet management software capability, customization flexibility, pricing competitiveness, aftersales support strength, regulatory compliance track record)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
TLD
JBT AeroTech
Textron GSE
Toyota Industries Corporation
IHI Transport Machinery
ShinMaywa Industries
Mallaghan Engineering
Goldhofer AG
Kalmar Motor AB
MULAG Fahrzeugwerk
Weihai Guangtai Airport Equipment
Tronair
Clyde Machines
ITW GSE
Guinault
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection processes
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and operational risk factors
- Post-purchase service and lifecycle support expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


