Market Overview
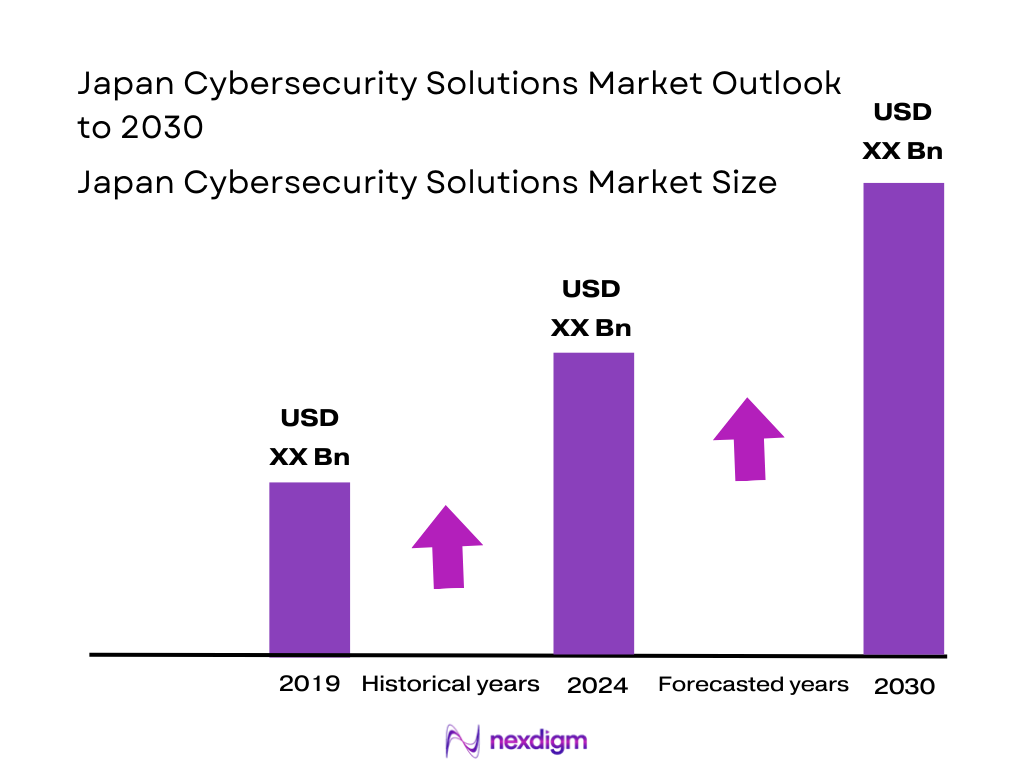
The Japan Cybersecurity Solutions Market is valued at USD 8.65 billion, based on recent country‑level industry analysis and historical trends indicating robust growth backed by regulatory mandates and rising threat levels. This valuation reflects a comprehensive analysis of historical data, enterprise investments, and government stimulus driving demand for advanced security solutions.
The market is dominated by major metropolitan regions such as Tokyo, Osaka–Kansai, and Chubu manufacturing belt, due to their concentration of critical infrastructure, financial institutions, high‑tech industries, and proactive cybersecurity initiatives. These hubs command leading adoption driven by regulatory urgency and digital transformation momentum.
Market Segmentation
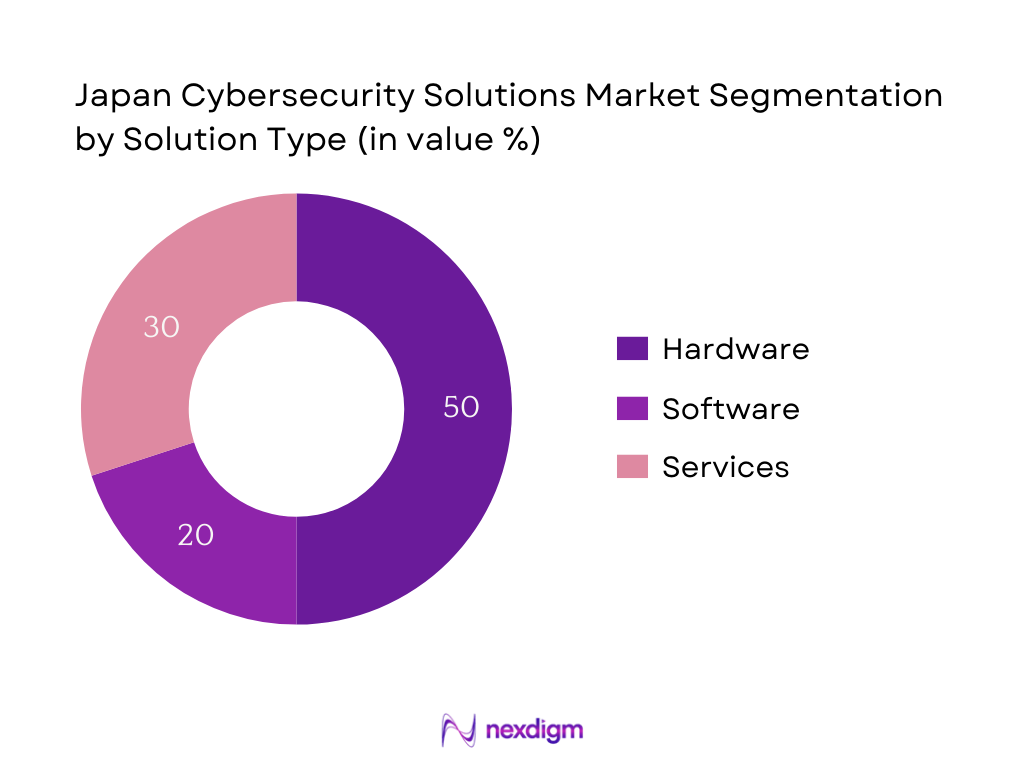
By Solution Type
The Japan Cybersecurity Solutions Market is segmented into hardware, software, and services. The hardware sub‑segment dominates, holding the largest share, as enterprises and government entities continue investing heavily in robust physical devices such as firewalls, intrusion detection appliances, and hardware security modules. This preference stems from the high reliability and regulatory compliance associated with hardware-based defense, especially amid growing concerns over physical tampering and critical infrastructure protection.
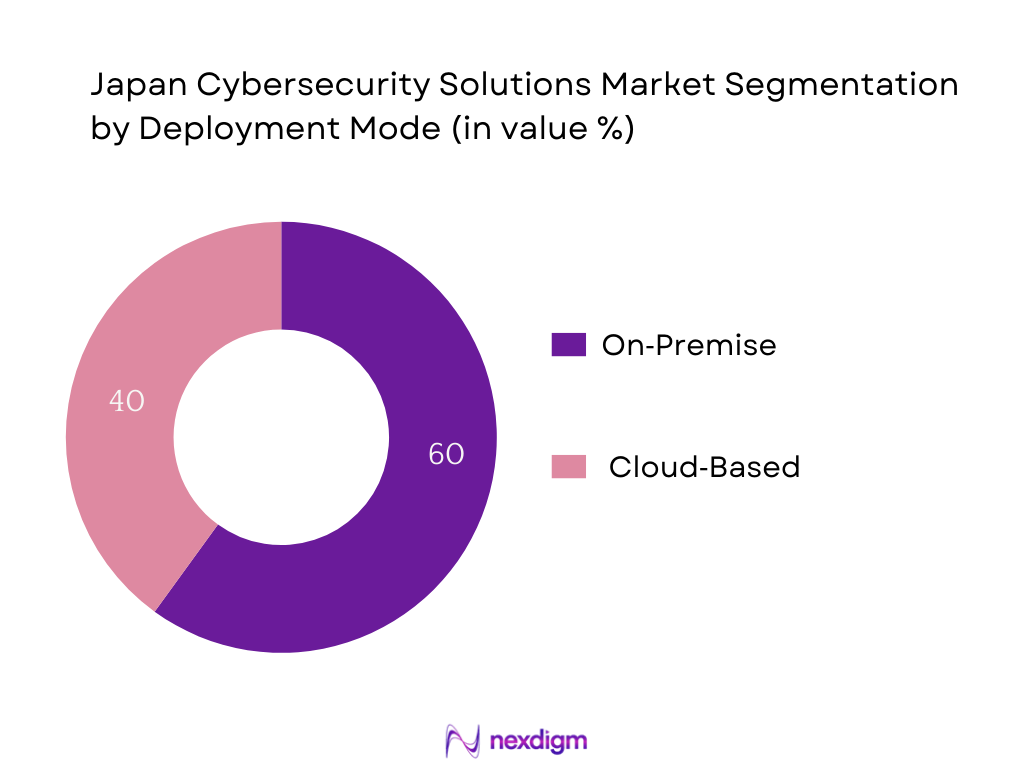
By Deployment Mode
The segmentation includes on‑premise and cloud‑based deployments. On‑premise remains the dominant deployment model, favored by organizations that prioritize data sovereignty, operational control, and strict compliance with privacy regulations. However, cloud deployments are rapidly gaining traction due to scalability and agility.
Competitive Landscape
The Japan cybersecurity solutions market is highly competitive, featuring both domestic champions and global technology firms strategically positioned to serve Japan’s rigorous regulatory and threat environment. The competitive landscape is shaped by major players such as Trend Micro, NEC, Fujitsu, NTT Data, and global vendors like Cisco, IBM Japan, Palo Alto Networks, and Fortinet. These players consolidate the market, leveraging integrated platforms, compliance-centric services, and localized R&D to cater to Japan’s complex security needs.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Local R&D Presence | Compliance Certifications | Enterprise Deployments in Japan | Managed Services Offering | Government Contracts |
| Trend Micro | 1988 | Tokyo, Japan | – | – | – | – | – |
| NEC Corporation | 1899 | Tokyo, Japan | – | – | – | – | – |
| Fujitsu | 1935 | Tokyo, Japan | – | – | – | – | – |
| NTT Data | 1988 | Tokyo, Japan | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cisco Japan | 1984 | Tokyo, Japan | – | – | – | – | – |
Japan Cybersecurity Solutions Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Strong Economic Scale Amplifying Cybersecurity Investment
Japan’s macroeconomic indicators reflect substantial scale: nominal GDP was US $4,110 billion in 2024, slightly down from US $4,213 billion in 2023, with GDP per capita at US $33,138. These figures exhibit a mature and extensive economy that underpins substantial digital transformation across industries such as manufacturing, finance, and services. The sheer economic magnitude necessitates resilient cybersecurity capabilities, prompting both private and public sectors to intensify investment. This systemic need, stirred by expansive digital infrastructure overlaid on a high‑GDP economy, fuels adoption of cybersecurity solutions capable of operating at enterprise scale.
Digital Infrastructure Modernization and Regulatory Emphasis
Japan’s manufacturing hubs—particularly in Kanto, Kansai, and Chubu—are actively adopting smart factory guidelines issued by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). These emphasize cybersecurity in operational technology (OT) environments, directly referencing increased cyber attack risks against factory systems. Alongside, nominal GDP of US $4,110 billion and per capita GDP of US $33,138 reflect an economy undergoing digital modernization. This economic scale and regulatory push reinforce embedded cybersecurity investments in physically and digitally integrated infrastructure.
Market Challenges
Cybersecurity Talent Shortage Amid Labor Constraints
Japan’s working-age population has declined to approximately 59.4 percent of total population in 2024, one of the lowest rates among OECD nations. This demographic contraction constricts the cybersecurity talent pool. Even as annual nominal GDP remains robust at US $4,110 billion, organizations face shortages in skilled cybersecurity professionals to implement, manage, and respond to threats across national and enterprise infrastructure. The labor force constraints thus pose a structural bottleneck for market growth, limiting human capacity essential for deploying and managing cybersecurity solutions.
Complex Cybersecurity Regulation for Foreign Vendors
Japan’s Cybersecurity Strategy framework—under the Basic Act on Cybersecurity—imposes tailored responsibilities on government, private sector, and digital infrastructure operators. This regulatory architecture creates a complex compliance landscape for foreign cybersecurity vendors, who must align with Japan’s standards such as NISC and APPI guidelines. While nominal GDP of US $4,110 billion signals strong economic opportunity, navigating Japan’s regulatory nuance, including multi-year cybersecurity strategies and sector-specific guidelines, presents a persistent complexity for non-domestic entrants.
Opportunities
Zero Trust Architecture Adoption Fueled by Advanced Infrastructure
Japan’s economy, with nominal GDP of US $4,110 billion and GDP per capita of US $33,138, is anchored on expansive digital transformation across critical sectors. The prevalence of cyber incidents—such as 861 critical infrastructure breaches in fiscal year 2023—is accelerating interest in Zero Trust frameworks. This modern approach enables granular access controls and segmented trust zones, fitting Japan’s large-scale, high‑value digital environments. Organizations are increasingly exploring Zero Trust as a future‑ready strategy to reduce the surface of attack and reinforce integrity in corporate and critical infrastructure networks.
AI and ML Enhancing Threat Detection Capabilities
While exact AI-related cybersecurity incident data in Japan is emerging, global reports emphasize AI’s role both as threat enabler and as a tool for advanced defense. Amid Japan’s economic environment—nominal GDP US $4,110 billion, per capita GDP US $33,138—there is rising interest in AI/ML-based cybersecurity systems capable of detecting and responding to evolving threats at scale. Enterprises are exploring machine learning for anomaly detection, behavior profiling, and automated response. This builds on macroeconomic stability to support deployment of intelligent cybersecurity solutions that augment human-limited resources and counter increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Future Outlook
Over the coming years, Japan’s Cybersecurity Solutions Market is expected to continue its strong growth trajectory, driven by intensifying cyber threats, ongoing digital transformation initiatives, and deepening regulatory pressure for enhanced national and enterprise cybersecurity.
Major Players
- Trend Micro
- NEC Corporation
- Fujitsu
- NTT Data
- IBM Japan
- Cisco Japan
- Palo Alto Networks
- Fortinet
- Hitachi Systems
- Cybertrust Japan
- LAC Co., Ltd.
- Kaspersky Japan
- Acalvio Technologies
- Akamai Technologies
- Cyber Security Cloud, Inc.
Key Target Audience
- Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) of large enterprises and public institutions
- Security procurement leads at major manufacturing and BFSI firms
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms (e.g. SoftBank Vision Fund)
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
- Cyber Risk Management Officers at financial institutions
- Infrastructure Security Heads in energy/utilities sectors
- Managed Security Service Providers (MSPs) looking to expand in Japan
- Corporate Strategy Teams at global cybersecurity vendors planning Japan entry
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map encompassing all major stakeholders within the Japan Cybersecurity Solutions Market. This is underpinned by extensive desk research, gathering secondary data from proprietary industry reports, government publications, and regulatory documents to define variables such as solution deployment, compliance norms, and institutional demand.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile and analyze historical data, including cybersecurity expenditures, component segmentation (hardware, software, services), deployment trends, and vertical usage patterns. The approach assesses revenue generation by segment and deployment type, ensuring accuracy in estimating the 2024 market size of USD 8.65 billion.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses around region dominance, segment leadership, and deployment preferences are validated through interviews with industry experts, including CISOs at major institutions, cybersecurity vendors, and government representatives. These insights refine data reliability and context.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
In the final phase, we cross-verify bottom-up expenditure data with enterprise-level inputs from vendor sales channels and public budget disclosures. This ensures that the derived market size, segmentation distribution, and future outlook are accurate and reflect actual market dynamics in Japan.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Digital Threat Landscape in Japan
- National Cybersecurity Timeline and Milestones
- Cybersecurity Value Chain and Ecosystem Stakeholders
- ICT and Internet Penetration Benchmarks
- Market Role in Japan’s Digital Transformation Goals
- Growth Drivers
Cyber Attack Frequency in Critical Infrastructure
Digital Japan 2025 Plan and Cybersecurity Budgeting
Enterprise Cloud Migration and SaaS Integration
Cybersecurity Talent Gap and MSP Outsourcing
Escalating Ransomware and Malware Cases - Market Challenges
Shortage of Cybersecurity Professionals
Complex Regulatory Environment for Foreign Vendors
Cost Sensitivity in SME Adoption
Fragmented Procurement Channels - Opportunities
Zero Trust Architecture Adoption
AI and ML in Threat Detection & Response
Regulatory Tech (RegTech) Integration for Compliance
Deeper Penetration of XDR Solutions
Cyber Insurance Collaboration Models - Trends
Increased Cybersecurity Budget Allocation
SOC-as-a-Service Adoption in Tier-2 Cities
Consolidation in Cybersecurity Vendors
Rise of Threat Intelligence Exchanges (ISACs) - Government Regulations
Act on the Protection of Personal Information (APPI)
NISC’s National Cybersecurity Strategy
Guidelines by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
METI Cybersecurity Guidelines for Business - Stakeholder Ecosystem Mapping
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Spend per Organization, 2019-2024
- By Cyber Incident Response Expenditure, 2019-2024
- By Solution Type (In Value %)
Network Security
Endpoint Security
Cloud Security
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) - By Deployment Type (In Value %)
On-Premise
Cloud-Based
Hybrid - By End-Use Industry (In Value %)
BFSI
Government & Public Sector
Manufacturing
Healthcare
IT & Telecom - By Organization Size (In Value %)
SMEs
Large Enterprises
Public Institutions - By Region (In Value %)
Kanto
Kansai
Chubu
Tohoku
Kyushu
- Market Share of Major Players (By Value and Solution Type)
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Product Offerings, Number of Enterprise Deployments in Japan, Japan-based Clients, Local R&D/Tech Support Presence, Cybersecurity Certification Portfolio, Local Market Revenue, Cyber Readiness Score, M&A Activity, Threat Response Time, Patent Landscape)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Technology Benchmarking: Response Time, Accuracy, SOC Automation
- Strategic Alliances and OEM Integrations
- Detailed Company Profiles
Trend Micro
NEC Corporation
Fujitsu
Hitachi Systems
NTT Data
SoftBank Technology
IBM Japan
Cisco Japan
Palo Alto Networks
Fortinet
Cyber Reason Japan
Kaspersky Japan
LAC Co. Ltd.
Rapid7
Check Point Software Japan
- Industry-Wise Security Maturity
- End-User Risk Appetite and Tech Readiness
- Budget Allocation Models (Capex vs Opex)
- Cyber Audit and Compliance Preferences
- Digital Identity and IAM Prioritization
- Enterprise Procurement Journey and Buying Center Roles
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Spend per Organization, 2025-2030
- By Cyber Incident Response Expenditure, 2025-2030


