Market Overview
The Japan Naval Gas Turbine market is valued at approximately USD ~billion in 2024, driven by Japan’s significant investment in modernizing its naval fleet and the growing need for advanced propulsion technologies. As the Japanese government continues to prioritize defense and maritime security, particularly in the context of the East China Sea and regional tensions, the demand for reliable and high-performance gas turbines for naval ships and submarines has risen. The market’s growth is also fueled by technological advancements in gas turbine systems, which offer enhanced fuel efficiency, greater power output, and reduced emissions. Moreover, Japan’s collaboration with global defense manufacturers, such as Rolls-Royce and General Electric, further supports the market’s expansion, making it a key player in the global naval propulsion industry.
Japan is the leading player in the naval gas turbine market within the Asia-Pacific region, with key activities centered in cities such as Tokyo, Yokohama, and Kobe. Tokyo, as the political and economic capital, is at the core of defense policy and procurement decisions, influencing the demand for advanced naval propulsion systems. Yokohama and Kobe are home to major shipyards and defense contractors, which are integral to the development and integration of gas turbines in naval vessels. Japan’s strategic focus on maintaining a technologically advanced and self-reliant military has led to the continued dominance of these cities, ensuring Japan’s position as a leader in naval defense technology.
Market Segmentation
By System Type
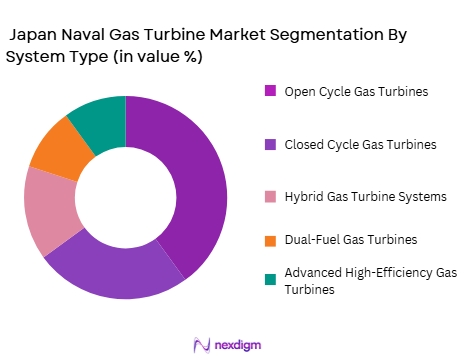
The Japan Naval Gas Turbine market is segmented by system type into Open Cycle Gas Turbines, Closed Cycle Gas Turbines, Hybrid Gas Turbine Systems, Dual-Fuel Gas Turbines, and Advanced High-Efficiency Gas Turbines. Among these, Open Cycle Gas Turbines dominate the market. These turbines are widely used in the Japanese Navy for their operational simplicity, high power output, and rapid start-up capabilities, which are essential for military operations where quick deployment is critical. The efficiency of open-cycle turbines in producing high thrust at relatively lower costs makes them the preferred choice for Japan’s surface combatants and amphibious assault ships. As the Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force continues to modernize its fleet, the dominance of open-cycle gas turbines is expected to persist, although there is growing interest in hybrid and dual-fuel systems for their environmental benefits.
By Platform Type
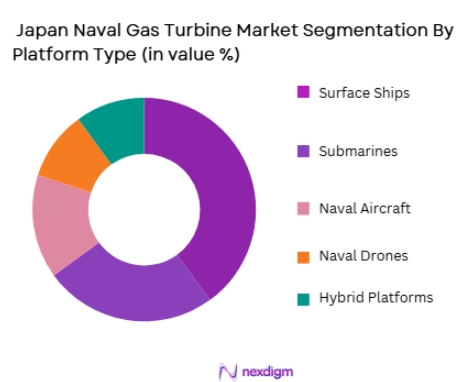
The Japan Naval Gas Turbine market is also segmented by platform type into Surface Ships, Submarines, Naval Aircraft, Naval Drones, and Hybrid Platforms. Surface Ships lead the market, as they represent the majority of Japan’s naval fleet and require powerful and reliable propulsion systems to maintain operational readiness. Gas turbines provide the high-speed performance necessary for Japan’s advanced destroyers, frigates, and amphibious vessels, all of which play a key role in Japan’s naval strategy. The demand for high-performance turbines is particularly strong in Japan’s surface combatants, which are equipped with multi-role systems designed for both offensive and defensive operations. Furthermore, the strategic importance of surface ships in maintaining Japan’s defense posture in the Indo-Pacific region ensures their dominance in the market for naval turbines.
Competitive Landscape
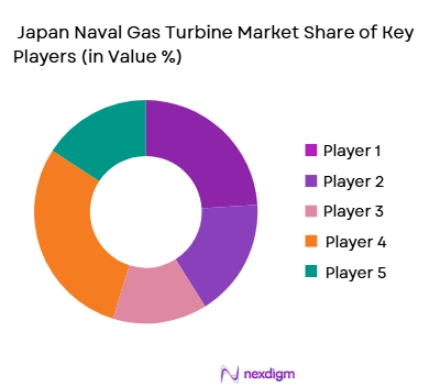
The Japan Naval Gas Turbine market is dominated by several key global and local players, who supply advanced propulsion systems to the Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF) and other defense contractors. Leading companies such as Rolls-Royce, General Electric, and MTU Friedrichshafen provide cutting-edge gas turbines for naval vessels, while local manufacturers like Kawasaki Heavy Industries and IHI Corporation play a critical role in supplying and integrating these systems into Japan’s fleet. The competition in the market is characterized by ongoing technological innovation, partnerships with the Japanese government, and the continuous demand for fuel-efficient, high-performance turbines.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Key Product Categories | Market Focus | R&D Investment | Government Contracts |
| Rolls-Royce Japan | 1904 | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| General Electric Japan | 1892 | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MTU Friedrichshafen GmbH | 1909 | Friedrichshafen, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kawasaki Heavy Industries | 1896 | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Japan Naval Gas Turbine Market Analysis
Growth Drivers:
Increased Defense Spending and Fleet Modernization
Japan’s rising defense spending is a key driver of growth in the naval gas turbine market. As Japan’s defense strategy evolves to address regional security concerns, including tensions in the East China Sea and North Korea, the Japanese government has committed to modernizing its naval fleet. Gas turbines are a critical component of this modernization effort, as they provide the high-performance propulsion systems required for Japan’s advanced surface combatants, submarines, and amphibious vessels. These turbines are essential for improving the operational range, speed, and overall effectiveness of Japan’s naval assets, making them a top priority in the country’s defense budget. The Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF) continues to upgrade its fleet with advanced gas turbines to enhance its maritime security capabilities and ensure readiness in potential conflict scenarios.
Technological Advancements in Turbine Efficiency and Sustainability
Technological innovations in gas turbine technology, such as advancements in fuel efficiency and emissions reduction, are driving growth in the Japan Naval Gas Turbine market. Japan’s commitment to sustainability, alongside its need for more energy-efficient propulsion systems, has led to the development of turbines that consume less fuel while delivering high power output. This is particularly important as naval fleets seek to lower operational costs and meet stricter environmental regulations. Moreover, the introduction of hybrid and dual-fuel turbines is increasing their appeal, as these systems can operate on both conventional fuels and alternative energy sources, further enhancing their performance and environmental benefits.
Market Challenges:
High Initial Costs and Maintenance Expenses
One of the main challenges in the Japan Naval Gas Turbine market is the high initial cost of purchasing and installing advanced gas turbines, as well as the ongoing maintenance expenses. While gas turbines offer superior performance and reliability, they come with substantial upfront investments and require specialized maintenance to ensure peak efficiency. These turbines often involve complex engineering and integration processes, which can raise installation and operational costs. Additionally, routine maintenance and the need for spare parts can be costly, particularly for the high-tech turbines used in advanced naval platforms. Managing these costs while maintaining fleet readiness remains a significant challenge for Japan’s defense budget.
Dependency on International Suppliers for Key Technologies
Despite significant progress in domestic manufacturing, Japan still relies on international suppliers for advanced turbine technologies. Companies like Rolls-Royce, General Electric, and MTU Friedrichshafen provide key components for Japan’s naval gas turbines, creating a dependency that exposes the country to potential supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and delays in procurement. This reliance on foreign technology also raises concerns related to technology transfer and national security. As Japan aims to increase self-sufficiency in defense production, reducing its dependency on foreign turbine manufacturers will be crucial for ensuring the long-term stability and sustainability of its naval operations.
Opportunities:
Export Potential for Advanced Gas Turbines
Japan has significant opportunities to expand its influence in the global naval gas turbine market. The demand for high-performance and fuel-efficient turbines is rising in several countries, particularly in the Asia-Pacific and Europe, as nations modernize their naval fleets. Japan, with its strong technological expertise and established defense industry, has the potential to become a leading exporter of advanced gas turbines. Exporting these turbines could not only boost the country’s defense sector but also strengthen its strategic alliances with allied nations seeking to upgrade their naval propulsion systems. By tapping into emerging markets, Japan could position itself as a global supplier of high-efficiency naval turbines.
Collaboration with Global Defense Contractors for Technological Innovation
Another opportunity lies in strengthening collaborations with global defense contractors and technology providers to drive further innovation in the naval gas turbine market. These collaborations can facilitate access to cutting-edge technologies, including hybrid systems, advanced materials, and AI-driven turbine performance monitoring systems. Working with international partners also enables Japan to remain at the forefront of the naval propulsion sector, ensuring that its own defense industry benefits from the latest advancements in turbine technology. Such partnerships could also open up opportunities for joint research and development, which would enhance Japan’s technological capabilities while fostering stronger defense relations with key international allies.
Future Outlook
Over the next decade, the Japan Naval Gas Turbine market is expected to show steady growth, driven by Japan’s continued focus on enhancing its naval defense capabilities and fleet modernization efforts. With increasing regional security concerns and ongoing technological advancements, the demand for high-efficiency, fuel-flexible, and reliable gas turbines will continue to rise. The Japanese government’s emphasis on maintaining a technologically superior defense force in the Indo-Pacific region will contribute significantly to the market’s expansion. As a result, the naval gas turbine market in Japan is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% from 2026 to 2035.
Major Players
- Rolls-Royce Japan
- General Electric Japan
- MTU Friedrichshafen GmbH
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- IHI Corporation
- Siemens Japan
- Wärtsilä Japan
- Pratt & Whitney Japan
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Kongsberg Gruppen
- Lockheed Martin Japan
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Navantia Japan
- Thales Japan
- L3 Technologies Japan
Key Target Audience
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
- Naval Defense Contractors
- Energy & Propulsion Technology Manufacturers
- Private Sector Defense Technology Companies
- International Defense Forces
- Naval Equipment Suppliers
- Defense Procurement Agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first step involves identifying the key factors influencing the Japan Naval Gas Turbine market, such as defense spending, technological advancements in turbines, and Japan’s geopolitical strategy. Secondary data sources, including government publications and defense industry reports, are utilized to gather relevant information.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical market data on naval turbine installations, defense budgets, and technological developments are analyzed. Market trends and segmentation, such as system and platform types, are examined to understand the dynamics driving the market’s growth.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses regarding growth drivers, challenges, and opportunities are tested through expert interviews with industry professionals and stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, and government officials. These insights help refine projections and validate assumptions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves synthesizing the collected data to provide a comprehensive report on the market, integrating insights from both secondary and primary sources. Expert feedback is incorporated to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the market analysis.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Increasing defense budget and naval modernization efforts
Technological advancements in turbine efficiency and reliability
Rising demand for high-power propulsion systems for naval vessels - Market Challenges
High integration and maintenance costs of advanced turbines
Dependency on international suppliers for turbine technologies
Challenges in adapting turbines for next-generation naval platforms - Market Opportunities
Export potential for advanced naval gas turbines to global markets
Collaborations with international turbine manufacturers for technological innovation
Growing demand for fuel-efficient turbines and hybrid systems - Trends
Adoption of high-efficiency turbines in naval propulsion systems
Emergence of dual-fuel and hybrid gas turbines in naval applications
Increased focus on digital monitoring and predictive maintenance systems - Government regulations
Japan’s Defense Procurement Regulations
National Maritime Safety and Emission Standards
Japan’s National Security and Defense Technology Guidelines - SWOT analysis
- Porters 5 forces
- By Market Value,2020-2025
- By Installed Units,2020-2025
- By Average System Price,2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier,2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Open Cycle Gas Turbines
Closed Cycle Gas Turbines
Hybrid Gas Turbine Systems
Dual-Fuel Gas Turbines
Advanced High-Efficiency Gas Turbines - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Surface Ships
Submarines
Naval Aircraft
Naval Drones
Hybrid Platforms - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
New Installations
Upgrades
Retrofits
Modular Systems
Custom Integrations - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF)
Defense Contractors
Government Agencies
Private Sector / Civilian Applications
International Defense Forces - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct Procurement
Third-Party Resellers
Online Platforms
Government Tenders
OEMs
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology innovation, Market penetration rate, Cost of maintenance, Supplier diversification, Operational efficiency)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Competitors
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Rolls-Royce Japan
General Electric Japan
MTU Friedrichshafen GmbH
Wärtsilä Japan
Siemens Japan
Pratt & Whitney Japan
MAN Energy Solutions
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
IHI Corporation
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Kongsberg Gruppen
Navantia Japan
Thales Japan
L3 Technologies Japan
Babcock International Group
- Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force’s focus on fleet modernization
- Government agencies’ emphasis on energy-efficient and cost-effective naval propulsion
- Private sector investment in hybrid propulsion technologies
- International collaborations with defense forces for turbine integration
- Forecast Market Value,2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units,2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier,2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform,2026-2035