Market Overview
The Japan submarine propulsion systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained naval modernization investments and technology upgrades. In 2024 and 2025, fleet induction activity increased, supported by stable defense allocations and domestic manufacturing emphasis. Adoption of lithium-ion propulsion and advanced control systems expanded across new platforms. Production volumes remained aligned with long-term fleet replacement cycles. Industrial participation intensified across propulsion components, energy storage, and integration systems. Demand stability was reinforced through multi-year defense acquisition planning.
The market is primarily concentrated in coastal industrial regions supporting naval shipbuilding and defense electronics ecosystems. Strong infrastructure in Kanto, Kansai, and Chubu supports propulsion manufacturing, testing, and integration. Demand is driven by operational requirements of the maritime defense forces and indigenous development mandates. Policy emphasis on self-reliance has strengthened domestic supplier participation. Mature logistics, skilled engineering workforce, and long-term naval programs sustain consistent demand. Regional clustering enables efficient coordination across shipyards, suppliers, and defense agencies.
Market Segmentation
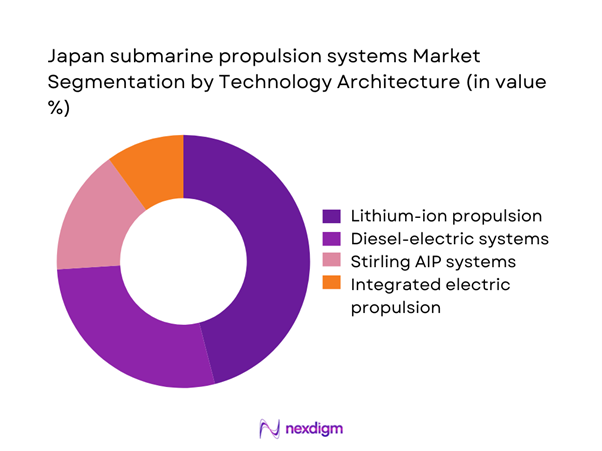
By Technology Architecture
The market is dominated by lithium-ion battery propulsion systems due to superior energy density and operational endurance advantages. Diesel-electric configurations continue to support legacy platforms undergoing upgrades. Stirling-based air-independent propulsion maintains relevance in select submarines, particularly for extended submerged endurance. Integrated electric propulsion systems are gaining adoption due to improved acoustic stealth and efficiency. Technology selection is influenced by mission profiles, endurance requirements, and lifecycle cost considerations. Ongoing investments in battery safety and energy management systems continue to reshape procurement preferences across new submarine programs.
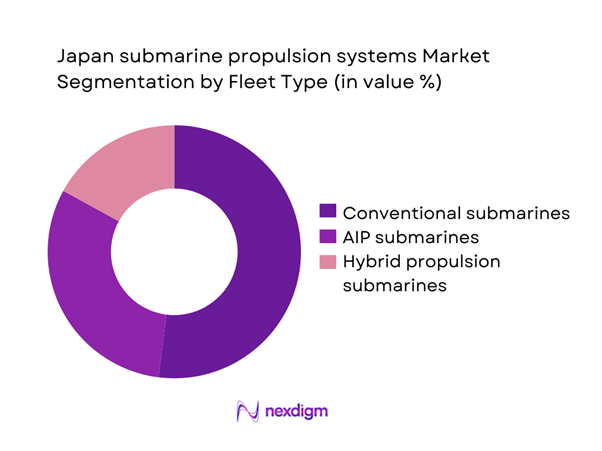
By Fleet Type
Conventional diesel-electric submarines dominate fleet composition due to their operational versatility and cost efficiency. Air-independent propulsion submarines represent a growing share, driven by endurance enhancement needs. Hybrid propulsion platforms are increasingly incorporated in next-generation designs. Fleet modernization programs prioritize reliability, reduced acoustic signatures, and extended operational range. Replacement of aging vessels continues to support steady procurement volumes. The fleet mix reflects evolving maritime security strategies and increased emphasis on undersea deterrence capabilities.
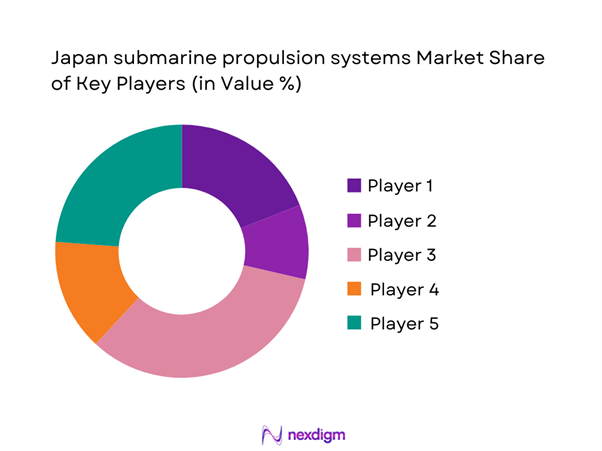
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by a concentrated group of domestic manufacturers supported by specialized component suppliers. High entry barriers exist due to regulatory controls, technological complexity, and long qualification cycles. Collaboration between shipbuilders and propulsion technology providers shapes market positioning. Competitive differentiation is driven by system integration capability, reliability performance, and lifecycle support expertise.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries | 1884 | Tokyo | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kawasaki Heavy Industries | 1896 | Kobe | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Japan Marine United | 2013 | Yokohama | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| IHI Corporation | 1853 | Tokyo | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Toshiba Energy Systems | 2017 | Kawasaki | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Japan submarine propulsion systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising maritime security requirements in the Indo-Pacific
Increasing regional maritime tensions continue to elevate strategic importance of undersea defense capabilities across national security planning. Naval modernization initiatives emphasize enhanced stealth, endurance, and operational readiness to address evolving maritime threat scenarios. Submarine fleets receive prioritization due to deterrence value and surveillance effectiveness across contested maritime zones. Defense policy alignment supports sustained procurement of advanced propulsion technologies. Growing focus on undersea domain awareness reinforces propulsion reliability requirements. Investment continuity remains consistent through long-term defense planning cycles. Indigenous manufacturing strengthens strategic autonomy and reduces external dependency. Technological upgrades aim to ensure superiority in underwater maneuverability and endurance. Operational readiness metrics increasingly guide propulsion system specifications. These factors collectively sustain propulsion system demand growth.
Fleet modernization and replacement of aging submarines
Aging submarine fleets necessitate systematic replacement to maintain operational effectiveness and safety standards. Replacement programs emphasize advanced propulsion to improve submerged endurance and acoustic performance. Fleet modernization schedules drive consistent procurement cycles across multiple years. New platforms integrate advanced energy storage and propulsion management systems. Legacy vessels undergoing midlife upgrades also require propulsion system retrofits. Modernization initiatives align with evolving operational doctrines and threat assessments. Fleet renewal supports stable industrial output for propulsion manufacturers. Integration of modern propulsion technologies enhances platform lifecycle value. Maintenance efficiency improves through standardized propulsion architectures. These factors collectively reinforce propulsion system demand.
Challenges
High development and integration costs
Submarine propulsion systems require significant capital investment for research, testing, and certification processes. High engineering complexity increases development timelines and cost structures. Integration with hull systems demands extensive customization and validation. Specialized materials and components elevate procurement expenses. Testing requirements under extreme operational conditions further increase development burden. Budget constraints can delay adoption of advanced propulsion technologies. Cost overruns pose risks to program timelines and procurement planning. Limited production volumes restrict economies of scale. Long development cycles impact return on investment predictability. These factors constrain rapid market expansion.
Complexity of indigenous propulsion technology development
Developing indigenous propulsion technologies requires deep technical expertise and long-term investment commitment. Integration challenges arise from coupling propulsion systems with combat management architectures. Achieving acoustic stealth standards demands extensive iterative testing. Limited availability of specialized suppliers affects development timelines. Technology maturation cycles extend beyond typical procurement horizons. Knowledge transfer constraints slow innovation scalability. Regulatory compliance adds additional development complexity. High reliability standards necessitate prolonged validation phases. Workforce specialization remains a limiting factor. These complexities collectively hinder rapid technological advancement.
Opportunities
Next-generation submarine development programs
Next-generation submarine initiatives create strong demand for advanced propulsion architectures. Program specifications emphasize endurance, efficiency, and reduced acoustic signatures. Development programs encourage adoption of next-generation battery and propulsion technologies. Long-term procurement commitments provide visibility for system suppliers. Integration of digital monitoring systems enhances propulsion performance management. Indigenous development priorities open opportunities for domestic technology innovation. Collaboration across defense research organizations accelerates system maturity. Modular propulsion designs improve upgrade flexibility. Emerging designs support improved lifecycle management. These programs present sustained growth opportunities.
Upgrades of legacy propulsion systems
Legacy submarine fleets require propulsion upgrades to meet evolving operational requirements. Retrofit programs extend vessel service life while improving performance metrics. Upgrades focus on energy efficiency and reduced maintenance burden. Integration of modern control systems enhances operational reliability. Retrofit activities offer recurring revenue opportunities for system suppliers. Modernization programs align with budget optimization strategies. Incremental upgrades reduce the need for full platform replacement. Enhanced safety standards drive propulsion system replacements. Digital monitoring improves predictive maintenance outcomes. These factors create consistent retrofit demand.
Future Outlook
The market outlook remains positive as naval modernization continues through the forecast period. Emphasis on indigenous capability development will support sustained investment in propulsion technologies. Technological advancements in energy storage and system integration are expected to shape future platforms. Policy alignment with maritime security objectives will continue to drive procurement activity. Collaboration between industry and defense agencies will further strengthen market stability.
Major Players
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Japan Marine United
- IHI Corporation
- Toshiba Energy Systems
- Hitachi Ltd.
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Wärtsilä
- Rolls-Royce
- BAE Systems
- Saab Group
- Kongsberg Gruppen
- L3Harris Technologies
- Thales Group
- Siemens Energy
Key Target Audience
- Naval defense procurement agencies
- Ministry of Defense Japan
- Maritime Self-Defense Force logistics divisions
- Shipbuilding and integration companies
- Defense equipment suppliers
- Maintenance and overhaul providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including ATLA
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope was defined based on propulsion technologies, fleet composition, and defense procurement structures. Key performance parameters and application areas were identified to establish analytical boundaries.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was structured using fleet deployment patterns, technology adoption trends, and procurement cycles. Segmentation logic was applied to reflect real-world operational classification.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through consultations with naval engineers, defense planners, and system integrators. Assumptions were refined through iterative cross-verification.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation of qualitative and quantitative inputs. Final outputs were structured to reflect industry dynamics and strategic relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and propulsion system scope for Japanese submarines, fleet and platform segmentation logic aligned to JMSDF programs, bottom-up market sizing using shipyard output and retrofit cycles, revenue attribution across propulsion hardware and integration services, primary validation through naval engineers and defense procurement experts, triangulation using defense budgets and shipbuilding order books, assumptions linked to fleet renewal timelines and indigenous technology adoption)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and operational deployment patterns
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and industrial base
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising maritime security requirements in the Indo-Pacific
Fleet modernization and replacement of aging submarines
Adoption of lithium-ion battery propulsion technology
Increased defense spending and naval self-reliance policies
Technological advancement in quiet propulsion systems - Challenges
High development and integration costs
Complexity of indigenous propulsion technology development
Long procurement and certification cycles
Export restrictions and technology transfer limitations
Maintenance complexity and lifecycle cost management - Opportunities
Next-generation submarine development programs
Upgrades of legacy propulsion systems
Growth in domestic defense manufacturing
Advancements in energy-dense battery technologies
Collaboration with allied naval technology partners - Trends
Shift from Stirling AIP to lithium-ion propulsion
Increased automation in propulsion control systems
Focus on acoustic stealth and efficiency
Integration of digital monitoring and diagnostics
Lifecycle-based procurement models - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Conventional diesel-electric submarines
Air-independent propulsion submarines
Lithium-ion battery powered submarines
Hybrid propulsion platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Propulsion and power generation
Energy storage and management
Propulsion control and automation
Auxiliary propulsion systems - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Diesel-electric propulsion
Stirling engine AIP
Lithium-ion battery propulsion
Integrated electric propulsion - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Naval defense forces
Defense shipbuilding yards
Maintenance, repair, and overhaul providers
Defense research and testing agencies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone propulsion control systems
Integrated platform management systems
Networked combat system interfaces - By Region (in Value %)
Kanto region
Kansai region
Chubu region
Kyushu region
Other coastal defense regions
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology capability, propulsion efficiency, integration expertise, local manufacturing presence, defense certifications, lifecycle support capability, R&D investment, contract value)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
Japan Marine United
IHI Corporation
Toshiba Energy Systems
Hitachi Ltd.
MAN Energy Solutions
Wärtsilä
Rolls-Royce
BAE Systems
Saab Group
Kongsberg Gruppen
L3Harris Technologies
Thales Group
Siemens Energy
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


