Market Overview
The KSA Air-to-Air Missiles Market is valued at approximately USD ~ billion in 2023 and is expected to reach a market size of USD ~ billion in 2024. This growth is driven by the significant investments being made by Saudi Arabia in defense modernization, particularly in enhancing the Royal Saudi Air Force’s (RSAF) capabilities. Key factors include Saudi Arabia’s strategic focus on increasing its defense procurement as part of Vision 2030, the growing security challenges in the region, and the country’s efforts to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers by developing indigenous capabilities. Furthermore, air defense systems remain a key priority due to Saudi Arabia’s role as a central power in the Gulf region, contributing to consistent defense spending and upgrades in its missile systems.
Saudi Arabia is the dominant player in the KSA Air-to-Air Missiles Market due to its defense budget allocation and its strategic geopolitical position in the Middle East. The country’s heavy investment in modernizing its military infrastructure, with a focus on advanced air defense systems, has positioned it as a key player in the global air-to-air missile market. Additionally, cities such as Riyadh and Dhahran are central hubs for defense procurement and technology development, where major defense contractors and local manufacturers are based. The dominance is also supported by collaborations with global leaders in defense technology, making Saudi Arabia a focal point in the development and deployment of cutting-edge air-to-air missile systems.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
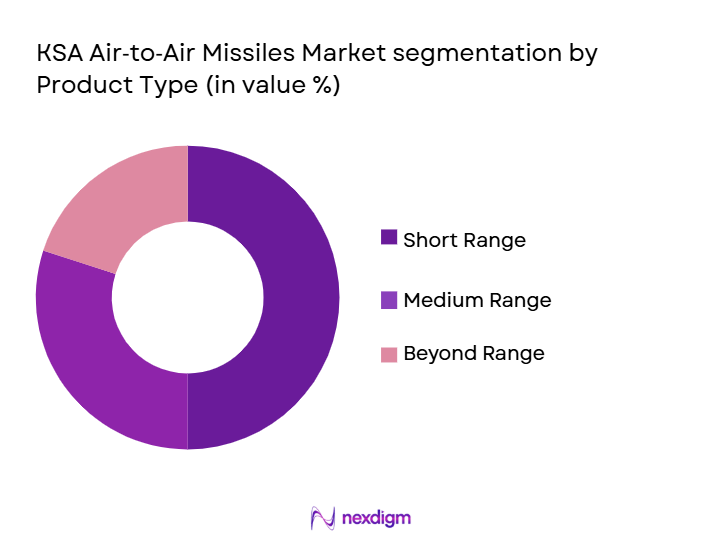
The KSA Air-to-Air Missiles market is segmented by missile range classification, which includes Short-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (SRAAM), Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (MRAAM), and Beyond-Visual-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (BVRAAM). Among these, the MRAAM segment dominates the market in 2024. This is primarily due to the increased demand for medium-range missiles in modern air combat scenarios, where the ability to engage targets beyond the visual range is crucial. MRAAM systems like the AMRAAM (Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile) are commonly integrated into Saudi aircraft fleets, ensuring superior air superiority. The growing preference for MRAAM systems is also influenced by their ability to offer a balance between cost and performance, making them suitable for both defensive and offensive operations.
By Application Type
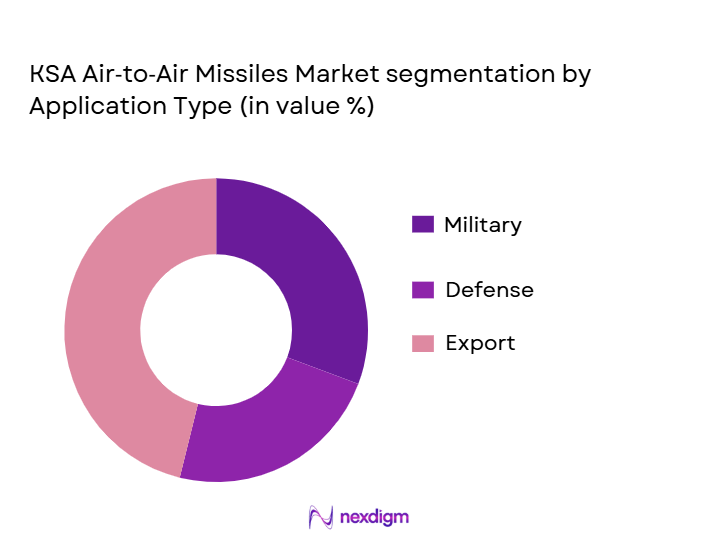
The KSA Air-to-Air Missiles market is also segmented by guidance technology, including Active Radar Homing, Semi-Active Radar Homing, Infrared/Imaging Seekers, and Dual-Mode Seekers. Among these, the Active Radar Homing segment holds the largest market share in 2024. This is due to its superior accuracy and ability to engage targets at extended ranges, making it highly desirable for advanced air defense systems. Missiles equipped with active radar homing, such as the AMRAAM and Meteor, are extensively used by Saudi Arabia’s air force for long-range engagements. The increasing adoption of this technology is attributed to its ability to provide high-performance tracking, minimal reliance on the launching aircraft’s radar, and its effectiveness in challenging environments, including counter-jamming.
Competitive Landscape
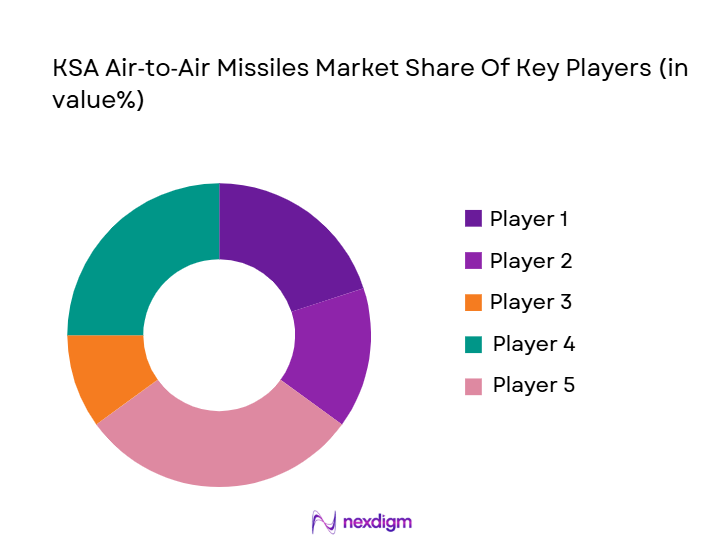
The KSA Air-to-Air Missiles Market is dominated by a few key players, including both global defense giants and local manufacturers. These companies play a significant role in shaping the market landscape, primarily through strategic partnerships, advanced technology integration, and local manufacturing efforts. Companies such as Raytheon Technologies and MBDA are leading the market due to their technological advancements in missile systems. The local players, along with international collaborations, ensure Saudi Arabia’s capability to maintain its air superiority in the region.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Defense Procurement Role | Technology Integration | Partnerships | R&D Investment |
| Raytheon Technologies | 1922 | Waltham, Massachusetts | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MBDA | 2001 | Paris, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | Farnborough, UK | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Haifa, Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | Bethesda, Maryland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Air‑to‑Air Missiles Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Geopolitical Threat Environment
The geopolitical environment in the Middle East significantly influences defense investments in the region. Saudi Arabia, positioned in a politically volatile area, faces ongoing regional conflicts and security threats. According to the Global Peace Index (2024), Saudi Arabia remains in the top 50 countries with high defense spending, primarily due to regional tensions involving Iran and conflicts in Yemen. In 2023, Saudi Arabia’s defense budget was USD ~ billion, which accounts for approximately ~% of its GDP. This high defense expenditure underscores the government’s commitment to securing air defense systems, such as air-to-air missiles, in the face of mounting regional instability.
Defense Modernization
Saudi Arabia’s defense modernization strategy, in alignment with Vision 2030, continues to push the country towards self-sufficiency in defense capabilities. The Kingdom’s National Transformation Program (NTP) allocates significant funds towards upgrading military technology, with a focus on enhancing air defense systems. As of 2024, the country is investing heavily in procuring advanced missile systems. The Saudi military’s increasing reliance on indigenous defense technologies, supported by joint ventures with international defense manufacturers, highlights the commitment to modernizing defense infrastructure. According to the Saudi Ministry of Defense, over ~% of defense spending is directed towards modernization initiatives.
Market Challenges
Export Control Regimes
Export control regimes play a critical role in shaping the Saudi Air-to-Air Missiles Market. Saudi Arabia faces several restrictions on the transfer of sensitive military technology, particularly air-to-air missile systems, due to international treaties and global non-proliferation agreements. As of 2024, the U.S. State Department maintains stringent export controls on defense technologies, impacting Saudi Arabia’s ability to independently procure certain missile systems. For example, technology transfer restrictions on certain radar and missile guidance systems have delayed some of Saudi Arabia’s defense procurement plans. These regulatory frameworks affect the timely acquisition and integration of missile systems in the country.
Technology Transfer Barriers
Technology transfer barriers remain a significant challenge in Saudi Arabia’s pursuit of self-sufficiency in defense technologies. While Saudi Arabia has been proactive in seeking joint ventures with international defense firms, there are substantial challenges in acquiring advanced missile technology. Restrictions on sensitive technology transfer by countries like the U.S. and European powers often hinder the Kingdom’s goal of producing air-to-air missiles indigenously. In 2024, the lack of comprehensive agreements on technology transfer prevented Saudi Arabia from acquiring certain critical missile components, delaying local production efforts and increasing dependency on foreign suppliers.
Opportunities
Indigenous Development Incentives
Saudi Arabia’s defense industry is receiving substantial incentives for indigenous development, which represents a significant opportunity for the air-to-air missile market. As part of Vision 2030, the Saudi government is providing funding and support for domestic defense contractors to design, develop, and manufacture missile systems within the Kingdom. These incentives include financial aid, tax breaks, and preferential procurement policies aimed at boosting local capabilities. In 2024, Saudi Arabia allocated USD ~ billion to support the growth of its defense industry, which is expected to spur innovation in air-to-air missile systems and reduce reliance on foreign technology.
Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances between Saudi Arabia and global defense companies continue to create significant opportunities in the air-to-air missiles market. In 2024, the Kingdom strengthened its partnerships with firms such as Raytheon Technologies and MBDA, ensuring access to cutting-edge missile technologies and R&D. These partnerships are pivotal in enhancing the Kingdom’s technological capabilities and defense systems integration. By leveraging these alliances, Saudi Arabia can gain access to advanced air-to-air missile systems and technologies, accelerating its air defense modernization efforts.
Future Outlook
Over the next decade, the KSA Air-to-Air Missiles Market is expected to witness significant growth. This growth will be propelled by Saudi Arabia’s continued focus on defense modernization and the increasing importance of air superiority in regional security. Advancements in missile technology, including the integration of artificial intelligence for targeting and enhanced guidance systems, will further boost the market. Additionally, the increased demand for advanced missile systems due to rising geopolitical tensions and defense budget allocations will drive future market expansion.
Major Players
- Raytheon Technologies
- MBDA
- BAE Systems
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Lockheed Martin
- Diehl Defence
- Northrop Grumman
- Leonardo
- Thales Group
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- Bharat Dynamics Limited
- Aselsan
- Raytheon Missiles & Defense
- Saab AB
- Hanwha Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies (e.g., Ministry of Defense – Saudi Arabia, U.S. Department of Defense)
- Military contractors and suppliers
- Armed forces and air defense agencies (Royal Saudi Air Force, Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces)
- Aerospace and defense technology firms
- Defense procurement officers
- Air force equipment manufacturers
- Security agencies involved in missile defense technology
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This phase involves constructing a comprehensive map of key players and stakeholders in the KSA Air-to-Air Missiles market. Extensive desk research is conducted to understand the different segments, such as missile range, guidance technology, and regional preferences. Data is collected from primary sources, including defense budgets and government procurement plans.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Here, historical data regarding procurement contracts, missile systems in use, and technological advancements are analyzed. We assess the market demand for different missile categories and the future deployment trends. Our analysis also covers the regional dynamics, including geopolitical factors influencing procurement strategies.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We conduct interviews with defense experts, military planners, and senior professionals from major defense contractors. These consultations help us validate our initial findings and understand the operational challenges and technological shifts in the KSA Air-to-Air Missiles market.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
In the final stage, we synthesize all findings, cross-reference data with industry reports, and prepare actionable insights for stakeholders. Data from multiple sources, including government contracts, defense policy documents, and procurement plans, are integrated into the final analysis, ensuring accuracy and comprehensive coverage.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Defense Procurement Classification, Sizing Approach for Precision Guided Munitions, Value Chain and Supply Chain Assessment, Primary Research Protocol, Defense Budget Data Sources, Limitations and Future Conclusion)
- Definition and scope
- Market dynamics Defense budget allocation, Strategic procurement drivers
- Historical overview Legacy air‑to‑air systems and procurement evolution
- Timeline Major contract awards, policy shifts, indigenous R&D milestones
- Growth drivers
Geopolitical threat environment
Defense modernization
Aircraft fleet upgrades - Market challenges
Export control regimes
Technology transfer barriers
Supply chain bottlenecks - Trends
Localization of manufacturing
Integration with 5th gen fighters
Multi‑sensor seekers - Opportunities
Indigenous development incentives
Strategic alliances
Offset programs - Government regulations (Foreign Military Sales policies, Export/Import controls)
- SWOT analysis
- Porter’s 5 Forces
- By Value, 2020‑2025
- By Volume, 2020‑2025
- By Average Price, 2020‑2025
- By Missile Range Classification (In value %)
Short‑Range
Medium‑Range
Beyond‑Visual‑Range
Extended Range - By Guidance Technology (In value %)
Active radar homing
Semi‑active
Infrared/Imaging - By Platform Integration (In value %)
Fighter aircraft integrated
Ground launch adapters
Airborne platforms AWD/AEW - By End User (In value %)
Royal Saudi Air Force
Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces
Export/Allied use - By Technology Maturity (In value %)
Legacy systems
Next‑gen systems
Indigenous development
- Market share of major players
- Cross comparison parameters (Company overview; Strategic alliances; Product portfolio breadth [air‑to‑air missile variants]; Guidance technologies supported; Production capacity; Localization footprint; R&D investment; Revenue concentration in KSA; Government partnerships; Authorized licenses; Intellectual property holdings; After‑sales support capability; Integration support services; Export control compliance)
- SWOT analysis of key players
- Pricing analysis of major players
- Detailed profile of major players
RTX / Raytheon
Lockheed Martin
MBDA Meteor & related systems
Diehl Defence (IRIS‑T)
Thales Group Missile subsystems
Northrop Grumman
BAE Systems Air warfare solutions
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Leonardo S.p.A.
Bharat Dynamics Limited
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
KAI / Hanwha Seeker/integration partners
Aselsan Guidance & subsystems
Roketsan Regional partnerships
Saab AB
- Operational capability requirements
- Budgeting and procurement cycles
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) demands
- Platform compatibility demands
- Threat perception and rules of engagement
- Decision hierarchy in defense acquisitions
- By value 2026‑2035
- By volume 2026‑2035
- By average price 2026‑2035


