Market Overview
The KSA Automatic Emergency Braking market is valued at USD ~ billion, derived from aggregated factory-fit ADAS system revenues, OEM option pricing disclosures, and Tier-1 shipment data compiled across passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles. Industry shipment data indicates that more than ~ new vehicles equipped with some form of forward collision mitigation system were registered nationally, supported by rising safety feature standardization. Regulatory alignment with UNECE vehicle safety mandates, increasing insurance-driven safety requirements, and OEM platform consolidation around ADAS domain controllers have collectively driven the market’s revenue expansion. Growth is further reinforced by escalating urban traffic density and rising adoption of semi-autonomous braking functions in mid-segment vehicles.
The market is dominated by Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dammam, driven primarily by high vehicle ownership density, concentration of premium dealerships, and government fleet procurement programs. Riyadh leads due to centralized government and corporate fleets mandating ADAS-equipped vehicles, while Jeddah’s dominance is supported by urban congestion intensity and port-led commercial vehicle inflows. The Eastern Province benefits from logistics, oil & gas fleet requirements, and higher penetration of safety-equipped SUVs and LCVs. Dominance is structural rather than price-led, rooted in regulatory enforcement intensity, fleet renewal cycles, and OEM distribution priorities rather than consumer preference alone.
Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Type
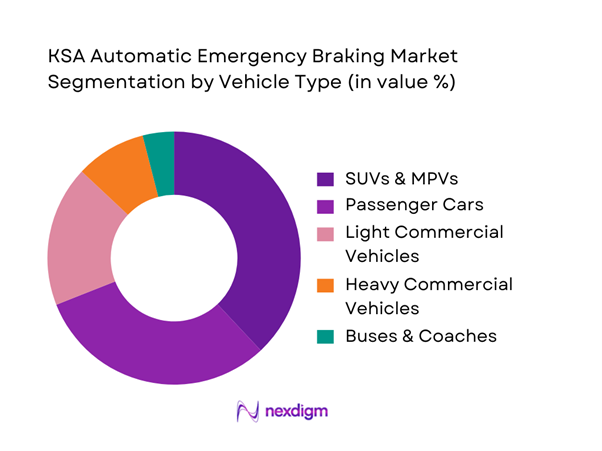
The KSA Automatic Emergency Braking market is segmented by vehicle type into Passenger Cars, SUVs/MPVs, Light Commercial Vehicles, Heavy Commercial Vehicles, and Buses & Coaches. Among these, SUVs and MPVs dominate AEB penetration. This dominance is driven by their high utilization in family transport, government procurement, and ride-hailing platforms where safety ratings directly influence purchasing decisions. OEMs increasingly bundle AEB as standard in SUV trims due to higher ASP tolerance and compliance readiness. Additionally, SUVs operate across mixed-speed corridors where AEB effectiveness is more demonstrable, reinforcing regulatory and insurer preference for AEB-equipped platforms.
By Sensor Technology
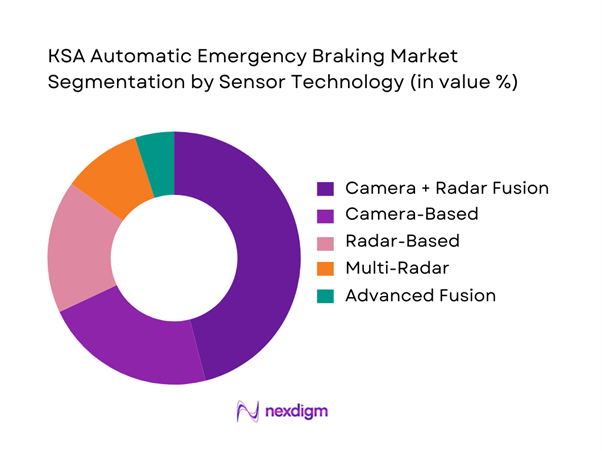
Based on sensor architecture, the market is segmented into Camera-Based Systems, Radar-Based Systems, Camera-Radar Fusion Systems, Multi-Radar Systems, and Advanced Fusion (Camera + Radar + LiDAR). Camera-Radar fusion systems dominate the market due to their superior detection reliability in high-speed and low-visibility conditions common across Saudi highways. Fusion systems reduce false braking events, a critical requirement for fleet operators and insurers. OEMs increasingly prefer fusion due to compliance alignment with UNECE test protocols and better performance in pedestrian and vehicle cut-in scenarios. Cost optimization at the Tier-1 level has also reduced the historical price premium of fusion systems, accelerating adoption across mid-segment vehicles.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Automatic Emergency Braking market is moderately consolidated, dominated by global Tier-1 automotive suppliers with deep OEM integration and homologation experience. Companies such as Bosch, Continental, and ZF benefit from long-term platform contracts and strong GCC regulatory familiarity. Asian suppliers such as Denso and Hyundai Mobis have strengthened their position through aggressive OEM partnerships and cost-efficient sensor architectures. Competition is driven less by pricing and more by validation performance, software robustness, and localization readiness, particularly calibration and aftersales support.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | Core Sensor Tech | OEM Coverage | Localization | Software Stack | Validation Capability | KSA Presence |
| Bosch | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Continental | 1871 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ZF | 1915 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Denso | 1949 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Valeo | 1923 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Road Safety Policy Push
Saudi Arabia’s road-safety agenda is being reinforced by the sheer scale and persistence of serious crashes on its road network, which keeps AEB adoption on the “must-have” path for OEMs, fleets, and regulators. National road-transport statistics record ~ serious traffic accidents, ~ fatalities, and ~ injuries in 2024, with intracity crashes accounting for ~, a pattern that directly aligns with AEB’s strongest real-world value in rear-end conflicts, stop-and-go traffic, and intersection approach risks. On the demand-side, the vehicle base is expanding, with registered and roadworthy vehicles reaching ~ and new vehicle registrations hitting ~ units versus ~ in 2023, meaning more new-model fitment opportunities where AEB is packaged with ADAS suites. Macroeconomically, the operating environment supports technology add-ons, with Saudi GDP reported at USD ~–USD ~ and GDP per capita around USD ~–USD ~, sustaining affordability for safety-feature penetration in new vehicle purchases and higher-spec trims where AEB is standard.
OEM Standardization of ADAS
OEM standardization is accelerating because the Kingdom’s new-vehicle inflow is large enough to justify “Saudi-ready” ADAS packaging strategies at scale, and because OEMs increasingly treat AEB as a baseline component within broader ADAS bundles including camera and radar sensing, braking actuation, and electronic stability integration. The national market’s intake of new vehicles is evidenced by ~ newly registered vehicles in 2024, up from ~, alongside a total parc of ~ registered and roadworthy vehicles, numbers that matter because OEMs prioritize standardization when the addressable installed base and replacement cycle can sustain consistent calibration, parts, and service tooling. At the same time, driver base expansion supports higher ADAS exposure, with ~ first-time driving licenses and ~ renewed licenses issued in the same period, indicating a broadening and renewing driver population interacting with dense urban roads where OEMs typically push safety features as default. From a macro lens, Saudi Arabia’s economic scale, with GDP around USD ~–USD ~, supports a premiumization trend in passenger vehicles and SUVs where AEB is more often embedded across trim ladders as part of brand safety positioning and regulatory alignment.
Challenges
Sensor Performance in Harsh Environmental Conditions
AEB performance in Saudi Arabia is challenged by the operating environment that stresses sensors and perception stacks, as extreme heat, blown dust, glare, and variable visibility conditions can degrade detection of vehicles, lane edges, and vulnerable road users. For context on heat load, temperatures up to ~ have been recorded during peak seasonal periods, conditions that can affect sensor thermals, lens clarity, and electronic reliability for front-facing camera modules and radar units. Road safety stakes remain high in these conditions, with ~ serious traffic accidents, ~ fatalities, and ~ injuries, meaning any sensor degradation has non-trivial safety implications and raises OEM validation requirements for KSA-specific tuning. The Kingdom’s large parc of ~ registered and roadworthy vehicles also means that a wide diversity of vehicle maintenance states and windshield or bumper conditions can affect sensor alignment and contamination levels in real-world use. On the macro side, the economy’s scale, with GDP per capita around USD ~–USD ~, increases vehicle usage intensity and exposure time on roads, further amplifying the importance of robust sensor performance under harsh local conditions.
Software Validation Complexity
Validating AEB software in Saudi Arabia is complex because the driving environment combines high-speed corridors, dense urban merges, and a wide spectrum of road-user behaviors, forcing OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers to expand scenario libraries, edge-case testing, and calibration loops. The hard justification is visible in outcomes, with ~ serious traffic accidents and ~ injuries indicating a large and diverse crash surface where AEB must avoid both false negatives and false positives, especially in mixed traffic flows. The in-city concentration, with ~ of serious accidents occurring within cities, implies frequent junction interactions and cut-ins, which are among the most software-sensitive AEB scenarios. Meanwhile, the fleet and cross-border context, with ~ passengers through land ports and ~ tons of road-freight imports, adds exposure to buses, coaches, heavy vehicles, and mixed traffic at corridor choke points, increasing the variety of braking interactions that software must handle safely. Macroeconomically, the population scale of about ~ expands the diversity of daily road interactions, which raises the bar for validation depth before OEMs confidently standardize AEB across high-volume trims.
Opportunities
VRU and Junction AEB Expansion
A major growth path for KSA AEB is expanding from basic vehicle-to-vehicle scenarios into VRU and junction-aware AEB, including pedestrian and cyclist detection, turning conflicts, and cross-traffic braking, because Saudi crash exposure is concentrated where these capabilities matter most in dense city roads and intersections. The fact that ~ of serious traffic accidents occur within cities strengthens the strategic case for junction AEB and VRU AEB as the next value step beyond highway-style forward collision mitigation. The market context is large and expanding, with ~ registered and roadworthy vehicles, ~ newly registered vehicles, and ~ first-time driving licenses indicating growing urban traffic volumes and increasing interactions among new drivers, commuters, and mixed vehicle types. High social cost remains visible in outcomes, with ~ fatalities and ~ injuries, which keeps safety feature upgrades commercially and institutionally relevant. The opportunity therefore lies in positioning next-generation AEB as a city-safety enabler aligned with the Kingdom’s urban mobility realities and the rising density of daily traffic interactions.
Brake-by-Wire Integration
Brake-by-wire integration is an attractive opportunity for KSA AEB because it enables faster and more precise brake actuation control, supports redundancy architectures required by advanced ADAS, and improves integration with stability control and future automated functions. The business logic is grounded in scale and usage intensity, as Saudi Arabia has ~ registered and roadworthy vehicles and adds ~ newly registered vehicles in the year, an installed base large enough to support supplier localization strategies, standardized platform deployment, and scalable service tooling for by-wire braking systems. The safety challenge remains significant, with ~ serious traffic accidents and ~ injuries, which underlines the potential benefit of tighter braking control loops that by-wire architectures can provide, particularly in stop-and-go urban traffic where AEB interventions are frequent and timing-critical. Macro capacity also supports adoption readiness, with GDP reported around USD ~–USD ~, indicating an economy with the capital depth and industrial investment runway needed for more advanced vehicle electronics and safety systems to become mainstream in new-vehicle platforms.
Future Outlook
Over the next ~, the KSA Automatic Emergency Braking market is expected to transition from feature-led adoption to architecture-level standardization. Regulatory enforcement, insurer-driven incentives, and rising consumer safety awareness will push AEB from optional to default fitment across vehicle categories. Technological evolution toward domain controllers and centralized compute platforms will reduce per-vehicle integration cost, further accelerating adoption. Additionally, increased government fleet safety mandates and logistics sector compliance requirements will reinforce sustained market growth.
Major Players
- Bosch
- Continental
- ZF Friedrichshafen
- Valeo
- Denso
- Hyundai Mobis
- Aptiv
- Magna International
- Mobileye
- FORVIA Hella
- Aisin
- NVIDIA (Automotive)
- NXP Semiconductors
- Texas Instruments
Key Target Audience
- Passenger Vehicle OEMs and Importers
- Commercial Vehicle Manufacturers and Fleet OEMs
- Tier-1 ADAS and Brake System Suppliers
- Automotive Dealership Groups and Distributor Networks
- Insurance Companies and Vehicle Risk Underwriters
- Logistics and Ride-Hailing Fleet Operators
- Investment and Venture Capital Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with ecosystem mapping across OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, regulators, and fleet operators. Secondary sources and proprietary automotive databases are used to identify safety mandates, platform penetration, and system architectures influencing the AEB market.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical shipment data, vehicle registration volumes, and OEM ADAS package pricing are analyzed using a bottom-up approach. Factory-fit and fleet installations are mapped to revenue generation patterns to ensure accuracy.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses are validated through CATI interviews with ADAS engineers, fleet procurement heads, insurers, and dealership executives. These insights refine system pricing, penetration assumptions, and adoption timelines.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Primary insights are triangulated with supplier shipment disclosures and regulatory data to finalize market sizing, segmentation, and competitive positioning with high confidence.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Boundaries, KSA Homologation and Type-Approval Context, Assumptions and Exclusions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Logic for Factory-Fit vs Retrofit, Installed Base Modeling Approach, Teardown-Based BOM Validation, Channel Checks with Dealers and Importers, Fleet Procurement Interviews, Scenario Building, Data Triangulation, Limitations and Confidence Scoring)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Adoption Inflection Points
- KSA Mobility Context
- Demand-Stack Evolution Across End Users
- Ecosystem Timeline
- Growth Drivers
Road Safety Policy Push
OEM Standardization of ADAS
Fleet Safety KPIs and Insurance Influence
Consumer Safety Feature Awareness
Urban Expressway Driving Profiles - Challenges
Sensor Performance in Harsh Environmental Conditions
Software Validation Complexity
OEM Cost-Down Pressures
Aftermarket Counterfeit Risk
Calibration and Service Capability Gaps - Opportunities
VRU and Junction AEB Expansion
Brake-by-Wire Integration
Localization of Validation and Calibration Services
Fleet-First Safety Bundles
Software Monetization and OTA Enablement - Trends
Shift Toward Sensor Fusion
Migration to Centralized Vehicle Compute
Increased Use of Virtual Validation
ADAS Feature Bundling
Regulatory Convergence with Global Safety Protocols - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Unit Shipments, 2019–2024
- By Feature Mix, 2019–2024
- By Factory-Fit vs Retrofit, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
SUVs and MPVs
Light Commercial Vehicles
Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Buses and Coaches - By Application (in Value %)
City AEB
Inter-Urban AEB
VRU AEB
Junction AEB
Rear and Reverse AEB - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Camera-Based Systems
Radar-Based Systems
Camera and Radar Fusion
Multi-Radar Fusion
Advanced Sensor Fusion with Central Compute - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone ADAS Systems
Domain Controller-Based Systems
Centralized Vehicle Compute Systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Private Vehicle Owners
Corporate Fleets
Government Fleets
Ride-Hailing and Delivery Platforms
Logistics and Industrial Fleets - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Northern Region
Southern Region
- Competitive Intensity Mapping
- Market Share Assessment Framework
- Cross Comparison Parameters (KSA OEM Program Wins and Homologation Readiness, Sensor Suite Strategy and Roadmap, AEB Feature Coverage and ODD Limits, Compute Architecture and OTA Capability, Actuation Integration Depth and Redundancy, Validation Assets and Release Velocity, Field Reliability KPIs and Serviceability, Local Support Footprint and Partner Ecosystem)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Partnership and Alliance Mapping
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Robert Bosch GmbH
Continental AG
ZF Friedrichshafen AG
Valeo
DENSO Corporation
Aisin Corporation
Hyundai Mobis
Aptiv PLC
Magna International
FORVIA HELLA
Mobileye
NVIDIA
NXP Semiconductors
Texas Instruments
Ambarella
- Private Passenger Vehicle Buyers
- Government and Public Sector Fleets
- Corporate and Logistics Fleet Operators
- Ride-Hailing and Mobility Platform Operators
- Insurance Providers and Risk Underwriters
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Unit Shipments, 2025–2030
- By Feature Mix Evolution, 2025–2030
- By Factory-Fit vs Retrofit Trajectory, 2025–2030


