Market Overview
The KSA automotive hand tools market sits within the broader Saudi Arabia hand tools industry, which is valued at USD ~ million in the latest year, supported by sustained workshop maintenance demand and rising tool replacement cycles. The market’s momentum is reinforced by the scale of the national vehicle maintenance economy: Saudi Arabia’s automotive aftermarket generated USD ~ million in the previous year, underpinning steady throughput across independent garages, dealership service bays, tire/quick-service chains, and fleet workshops.
Demand is concentrated in the Kingdom’s main workshop and trade corridors—Riyadh (fleet and multi-branch garage networks), Jeddah/Makkah corridor (high vehicle density and quick-service clusters), and the Eastern Province (Dammam–Khobar–Jubail) where industrial fleets drive preventive maintenance and tool control. On the supply side, the market is dominated by import-led sourcing from global tool-manufacturing hubs (notably Germany, the United States, Japan, and China) because pro-grade automotive tools require consistent metallurgical quality, tight tolerances, and recognized brand warranties; Saudi Arabia also participates in hand-tool trade flows, including USD ~ million in exports of “sets of hand tools” in the previous year, highlighting active re-export and distribution activity.
Market Segmentation
By Tool Category
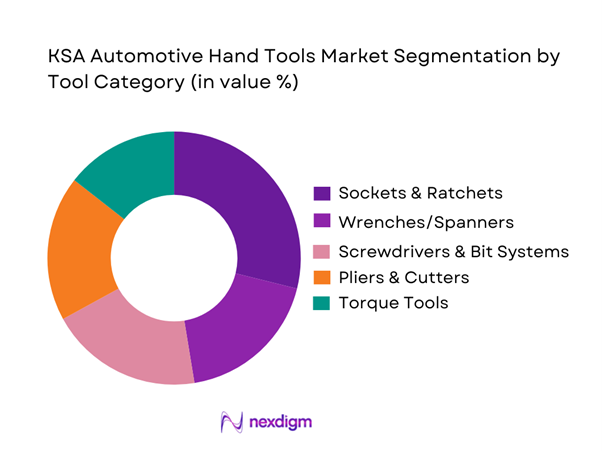
KSA automotive hand tools demand is segmented by tool category into sockets & ratchets, wrenches/spanners, screwdrivers & bit systems, pliers & cutters, torque tools (torque wrenches/angle tools), striking tools, pullers/extractors & specialty automotive tools, and tool storage & kits. Recently, sockets & ratchets hold a dominant market share because they are universal to high-frequency service jobs (brakes, suspension, underbody fasteners, routine removals), they are purchased in sets and replenished frequently (lost sockets, worn drives), and they are sensitive to rounding/fit—pushing workshops toward reliable assortments. In Saudi garages, the combination of fast service turnarounds and standardized metric fasteners increases the pull for complete socket ranges, deep sockets, extensions, and ratchet rebuildability, making this category the “core basket” for both independent workshops and fleet bays.
By End User
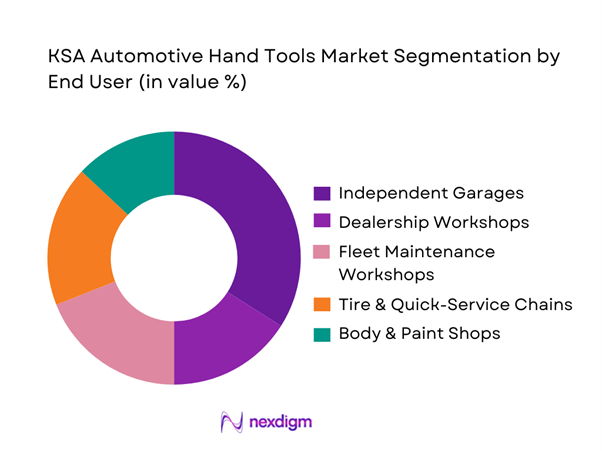
KSA automotive hand tools demand is segmented by end user into independent garages, dealership workshops, fleet maintenance (logistics, construction, utilities, rental fleets), tire & quick-service chains, body & paint shops, and DIY/enthusiast users. Recently, independent garages dominate the market because they represent the broadest installed base of service points and typically operate multi-brand repair models requiring wider tool coverage than single-OEM service bays. They also restock more often across mid-tier and pro-grade brands, balancing cost with durability. In addition, independents are more exposed to “tool loss economics” (technician turnover, misplacement, and uncontrolled tool issuance), which increases repeat purchases of core items like sockets, ratchets, combination spanners, and pliers. Fleet workshops, while high-intensity users, often buy via structured tenders and tool-control programs, which can reduce ad-hoc replacement compared with independents.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA automotive hand tools market is characterized by a layered competitive structure: premium professional brands serving dealership and fleet bays, value-to-mid brands serving high-volume independent workshops, and price-led imports competing aggressively in commodity tools. Brand trust, metallurgical consistency (Cr-V/Cr-Mo grades), fast availability through Saudi distributors, and warranty responsiveness matter as much as price—especially for sockets/ratchets and torque tools where failures directly slow workshop throughput.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Core Automotive Hand-Tool Strength | KSA Go-to-Market Model | Channel Strength in KSA | Warranty / Service Orientation | Typical Buyer Fit | Differentiation Lever |
| Snap-on | 1920 | Kenosha, Wisconsin, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Stanley Black & Decker (STANLEY / DEWALT) | 1843 | New Britain, Connecticut, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bosch | 1886 | Gerlingen, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| KNIPEX | 1882 | Wuppertal, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Wera | 1936 | Wuppertal, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Automotive Hand Tools Market Dynamics and Industry Analysis
Growth Drivers
Workshop throughput expansion
KSA’s workshop load is rising because the “serviceable vehicle base” and the operating intensity around it are expanding at the same time. Official road-transport statistics show registered and roadworthy vehicles increased to ~ million (from ~ million), and newly registered vehicles exceeded ~ million in the same period—both of which mechanically translate into more routine inspections, tyre/brake work, fastening jobs, and quick-turn bay activity that consumes sockets, wrenches, screwdrivers, pliers, cutters, clamps, and torque tools at scale. The same publication also records ~ newly issued driving licenses and ~ renewed licenses, which is a strong proxy for higher utilization and a broader maintenance population that feeds independent garages, dealership workshops, and fleet service hubs. At a macro capacity level, the economy’s scale matters: World Bank data shows GDP at USD ~ trillion and GDP per capita at USD ~, which supports continued vehicle purchases, aftermarket spend, and professionalization of workshop operations (tooling upgrades, bay productivity tools, and higher tool replacement rates). Riyadh, Jeddah, Dammam/Khobar, and industrial corridors (Jubail–Dammam–Riyadh) typically concentrate workshop clusters because they combine higher vehicle parc density, commercial fleets, and dealer networks—raising daily repair orders and accelerating tool wear/consumption (especially consumable hand tools, ratchets, bits, and torque-handling accessories).
Preventive maintenance adoption
Preventive maintenance is accelerating in KSA because the cost of unplanned downtime is rising across private mobility and commercial operations, while road-safety and roadworthiness attention is increasing. Government road-transport indicators show ~ serious traffic accidents alongside ~ traffic fatalities and ~ traffic-accident injuries in the same reporting period—statistics that keep roadworthiness, inspections, and component replacement (brakes, steering, suspension, tyres, battery/charging system, cooling) high on operator agendas. Preventive work is hand-tool intensive: torque checks, fastener integrity, leak checks, belt/hoses changes, wheel-end service, and battery maintenance all increase demand for torque tools, socket sets, hex/torx drivers, pliers, cutters, clamps, and specialty hand tools used by technicians. The vehicle base itself is expanding—~ million registered and roadworthy vehicles—which enlarges the preventive maintenance “denominator” even if driving patterns stay constant. On the macro side, World Bank data indicates a population of ~, which supports a large active driver pool and continual utilization of passenger vehicles, while GDP scale supports fleet expansion and workshop investment in standard operating procedures.
Challenges
Counterfeit and parallel imports
Counterfeit and grey-channel tools are a structural challenge because workshops often operate under time pressure and may accept “look-alike” tools if availability is immediate—yet failures (rounded fasteners, cracked sockets, torque drift) raise rework and safety risks. Enforcement data indicates the scale of the broader counterfeit problem: reporting states ~ infringing materials were seized and about ~ infringing websites were blocked/removed, achieved via ~ inspection tours across ~ cities—a signal that online and offline channels can carry high volumes of non-compliant goods that can include tools and tool accessories. Separately, the Ministry of Commerce’s enforcement environment is active; for example, it reported ~ violations referred to the Anti-Concealment Law Committee in a single quarter along with ~ suspected-breach reports and SAR ~ million in fines—conditions that often correlate with parallel trading behaviors and weak traceability in fragmented retail. For hand tools, the operational impact is direct: counterfeit torque wrenches and sockets can cause safety incidents and comebacks; counterfeit consumable bits and cutters raise job-cycle time and replacement frequency; and parallel imports complicate warranty, spare parts, and service claims. Macro demand conditions amplify the challenge: with ~ million registered and roadworthy vehicles, the workshop ecosystem is large and distributed, creating many points of sale where grey-market products can enter.
Warranty and calibration trust gaps
In professional workshops, trust increasingly depends on whether tools are authentic, supported, and (for torque tools) traceably calibrated. The challenge in KSA is uneven calibration access and inconsistent discipline across independent garages, quick-service outlets, and smaller fleet workshops. This matters because torque accuracy affects wheel fastening, brake assemblies, steering components, and other safety-critical work—comebacks and failures can be expensive in a high-throughput environment. The opportunity exists, but the current state is fragmented: the Saudi Accreditation Center maintains a national accreditation system and lists large numbers of accredited bodies; its site highlights ~ accredited bodies overall—evidence of growing conformity infrastructure, but not all workshops are connected to it operationally. At the workshop-demand level, the scale is huge: ~ million registered and roadworthy vehicles and over ~ million newly registered vehicles imply constant mechanical work where torque reliability matters. Also, road-safety indicators (~ serious accidents) intensify scrutiny on workshop quality and parts/fastener integrity. Practically, the trust gap shows up as: buyers preferring “known brands” despite higher upfront cost; fleets building internal tool lists and standard operating procedures; and more insistence on calibration certificates for torque wrenches used in safety-related tasks.
Opportunities
Tool-control systems for fleets
Fleet tool-control (shadow boards, RFID tagging, issue/return logs, and technician accountability systems) is a high-potential opportunity in KSA because fleet maintenance scale is large and expanding, and loss/downtime costs are meaningful. Demand is supported by multiple “current-state” indicators: the serviceable base is ~ million registered and roadworthy vehicles, and the system continues to add vehicles (newly registered vehicles exceeded ~ million). Logistics intensity supports fleet growth: ports handled ~ tons of cargo, and land-freight indicators show ~ tons of exports and ~ tons of imports through land ports—conditions that typically sustain large commercial fleets (trucks, LCVs, service vans) and multi-shift maintenance operations. Tool-control becomes valuable when fleets run multiple bays and rotating technicians: it reduces tool loss, shortens job time (technicians find the right tool instantly), and helps compliance (documented torque tool custody and calibration status). It also fits KSA’s formalization trend: Ministry of Commerce reporting shows ~ active commercial records, reflecting a broad base of formal businesses where SOP-driven operations and audited maintenance are more likely.
Torque and calibration service offerings
A high-value growth pocket in KSA is “tools-as-a-managed-service” around torque and calibration—because workshops increasingly need defensible quality, and fleets/dealer groups want repeatability and reduced comebacks. The demand base is already large: transport indicators show ~ million registered and roadworthy vehicles, over ~ million newly registered vehicles, and high road-safety relevance (~ serious accidents), all of which increase attention on correct fastening, wheel torque integrity, brake work, and safety-critical maintenance that benefits from calibrated torque tools. On the supply side, Saudi Accreditation Center data indicates a substantial conformity ecosystem, highlighting ~ accredited bodies, which supports the feasibility of building wider calibration access through accredited labs and structured service networks. The core commercial model is practical and immediate: workshops and fleets can subscribe to periodic torque tool verification, certificate issuance, and replacement/loaner tool continuity—reducing downtime. This also directly addresses a market pain point: “warranty and calibration trust gaps.” Importantly, this opportunity does not need “future market” numbers to be rational; it is backed by current operational scale and current compliance expectations.
Future Outlook
Over the next five to six years, the KSA automotive hand tools market is expected to expand steadily, supported by continued growth in vehicle maintenance intensity, higher service complexity (electronics-heavy vehicles, tighter fastener tolerances), and more structured fleet maintenance practices. Tool buying is also shifting from “single-item replenishment” to managed tool programs—kits, shadow boards, tool-control systems, and calibration-linked torque tool procurement. Forecast indicators for Saudi hand tools point to mid-single-digit growth for the Saudi hand tools market context.
Major Players
- Snap-on
- Stanley
- DeWalt
- Bosch
- Facom
- Bahco
- Gedore
- KNIPEX
- Wiha
- Wera
- SATA
- Irwin Tools
- King Tony
- INGCO
Key Target Audience
- Head of Procurement
- Head of After-Sales
- Head of Maintenance
- Head of Workshop Operations
- Head of MRO Procurement
- Category Manager
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build an ecosystem map covering tool manufacturers, Saudi distributors, workshop formats, and fleet maintenance operators. Desk research is combined with trade/channel mapping to identify variables such as professional vs DIY demand, replacement frequency by tool class, and premium vs value brand ladders.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical demand signals are constructed using triangulation across workshop density, automotive service activity proxies, distributor sell-through patterns, and import-led category movement. The model splits demand into core consumption baskets (sockets/ratchets, wrenches, pliers, torque tools) and maps them to end-user purchase behaviors.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on category dominance, channel behavior, and price-tier migration are validated through structured interviews with distributors, large garage operators, and fleet workshop managers. Insights focus on SKU velocity, warranty returns, counterfeit exposure, and calibration practices for torque tools.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are synthesized into a consolidated dataset, applying top-down and bottom-up reconciliation across channels and end users. The output is stress-tested against on-ground availability, procurement cycles, and service workflow realities to ensure the market narrative aligns with operational truth.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Primary Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Validation and Triangulation, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Automotive Aftermarket Linkages
- Business Cycle and Seasonality
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Workshop throughput expansion
Preventive maintenance adoption
Fleet servicing intensity
Giga-project logistics fleet demand
Productivity and quality focus - Challenges
Counterfeit and parallel imports
Warranty and calibration trust gaps
Price undercutting and margin pressure
Stock availability volatility - Opportunities
Tool-control systems for fleets
Torque and calibration service offerings
Insulated toolkits for EV and high-voltage servicing
Private-label brand expansion
B2B framework contracts - Trends
Tool storage modularity
Quick-change and time-saving tool designs
Premiumization in torque tools
Hybrid retail-to-online procurement
Arabic-first training and technical content - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Import vs Local Sourcing Mix, 2019–2024
- By Professional vs DIY Consumption Mix, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Sockets and ratchets
Spanners and wrenches
Screwdrivers
Pliers and cutters
Torque tools - By Application (in Value %)
Independent garages
Dealership workshops
Fleet maintenance centers
Tire and quick-service chains
Body shops - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Manual precision tools
Impact-rated hand tools
Insulated and VDE-certified tools
Non-sparking tools
Ergonomic and anti-slip designs - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Offline traditional procurement
Distributor-managed B2B programs
E-commerce marketplace procurement
Hybrid online-to-offline sourcing - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Passenger vehicle servicing
Commercial vehicle servicing
Logistics and fleet operations
Construction and industrial maintenance
Oil and gas field services - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Market Share Context of Major Players on the Basis of Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Tool portfolio coverage for automotive jobs, Torque accuracy and calibration support, Insulated and VDE safety-range depth, KSA distributor footprint and stock availability, E-commerce strength on Amazon.sa and Noon, Warranty terms and after-sales responsiveness, Anti-counterfeit controls and authenticity verification, B2B fleet and dealership program capability)
- Competitive Benchmarking Matrix
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Go-to-Market Strategy Comparison
- Distributor and Retailer Ecosystem Mapping
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Snap-on
Stanley Hand Tools
DeWalt Hand Tools
Bosch
Facom
Bahco
Knipex
Gedore
Wiha
Wera
SATA
Irwin Tools
Klein Tools
INGCO
- Market Demand and Utilization
- Purchasing Power and Budget Allocations
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision-Making Process
- Channel Preferences and Service Expectations
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025–2030
- By Import vs Local Sourcing Mix, 2025–2030
- By Professional vs DIY Consumption Mix, 2025–2030


