Market overview
Saudi Arabia’s workshop-capex cycle for lifting systems is being pulled by a larger on-road fleet and higher annual vehicle throughput through service bays. Registered and roadworthy vehicles rose over the most recent two-year window, expanding the addressable base for periodic maintenance, tires, brakes, suspension, and underbody work that requires lifting.
Demand concentrates in Riyadh (Central), Jeddah/Makkah corridor (Western), and Dammam–Khobar–Dhahran (Eastern) because these regions combine the highest density of vehicles, dealerships, fleets, and multi-bay workshop clusters, plus strong logistics connectivity for parts and equipment installation. The rising national fleet—roadworthy vehicles—intensifies bay-capacity additions first in these metro corridors, where uptime matters most for dealer service lanes, ride-hailing vehicles, and commercial fleets operating continuous duty cycles.
Market segmentation
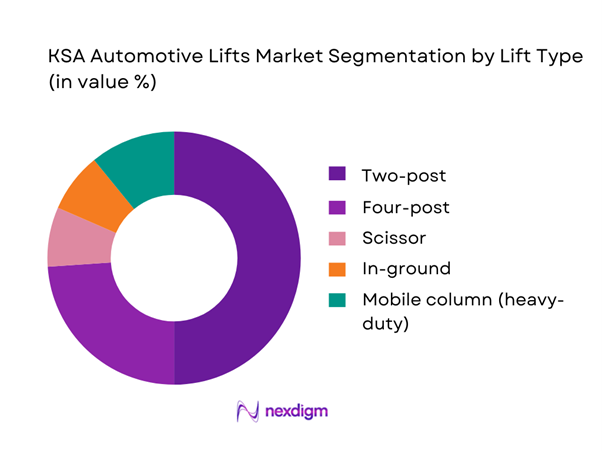
By Lift Type
KSA automotive lifts are segmented by lift type into two-post, four-post, scissor, in-ground, and mobile column lifts. Recently, two-post lifts typically dominate workshop installations because they maximize bay density per square meter, match mainstream passenger/SUV servicing needs, and offer the fastest “lift–work–lower” cycle for high-throughput mechanical jobs. As vehicle sales rose across the latest two years, dealerships and independents prioritize flexible bays that can handle repeated brake, suspension, oil, and underbody inspections without dedicating space to longer platforms. Two-post systems also minimize civil works versus in-ground lifts, which matters for rapid shop openings and retrofit projects across Riyadh/Jeddah/Dammam.
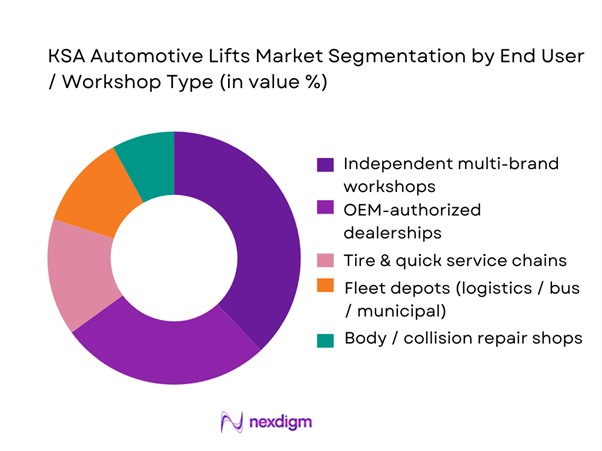
By End User / Workshop Type
KSA automotive lifts demand by end user segments into OEM-authorized dealerships, independent multi-brand workshops, tire & quick service chains, body/collision repair shops, and fleet depots. Recently, independent multi-brand workshops often account for the largest installed base additions because they scale fastest with the expanding vehicle parc and serve a broad mix of out-of-warranty vehicles. The roadworthy fleet increased vehicles, expanding the pool of vehicles that migrate from dealer-only service to cost-competitive independents, especially for wear-and-tear work. Independents also adopt standardized lift models for technician familiarity, faster training, and simpler spare-parts stocking—critical where downtime directly affects daily cash flow.
Competitive landscape
The KSA automotive lifts market is served by a mix of global lift manufacturers, workshop-equipment ecosystem players, and local distributors/installer-integrators. Competitive advantage is shaped less by the lift alone and more by installation quality, parts availability, and after-sales responsiveness across the main automotive hubs. In practice, buyers shortlist brands that can support warranty, preventive maintenance, and quick turnaround—because a lift being down can idle an entire service bay.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | Core lift portfolio fit for KSA | Typical capacity coverage | KSA route-to-market strength | Installation & civil-works support | After-sales model | Compliance / safety positioning |
| Bosch (Automotive Service Solutions) | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Snap-on (John Bean / Hofmann ecosystem) | 1920 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MAHA | 1889 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rotary / VSG | 1925 (Rotary) | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hunter Engineering | 1946 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Automotive Lifts Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
SUV-Dominant Service Mix
Saudi Arabia’s lift demand skews toward high-clearance, heavier passenger vehicles because workshop service volume is anchored in the country’s large private-vehicle stock and high annual “new issue” registrations. Registered and roadworthy vehicles rose from ~ to ~ units, and vehicles registered as a new issue reached ~ units (up from ~). These volumes feed routine suspension, brakes, steering, tires, and underbody inspections that benefit from higher lift reach, wider arm geometry, and higher capacity bands commonly selected for SUVs. Macro conditions enable sustained service activity: the economy is sized at USD ~ trillion and GDP per capita at USD ~, supporting both vehicle ownership and workshop spending on safety-critical equipment. Private vehicles are reported at ~ units within the overall parc, reinforcing a passenger/SUV-heavy service pipeline where two-post and scissor lifts typically cycle the most jobs per bay per day.
Dealership Throughput Mandates
Dealer service lanes expand lift purchases when annual new vehicle inflows and renewals keep bays at high utilization, forcing standardization and redundancy (more lifts per site, faster turn times, higher uptime). Administrative indicators show registered and roadworthy vehicles increasing, while newly issued vehicle registrations climbed. That “new issue” pipeline typically translates into higher first-years service events (PDI checks, warranty work, alignment/suspension checks after tire changes), pushing dealerships toward certified lift models with predictable service intervals and quick parts replenishment. Riyadh accounts for ~ of first-time driving licenses issued, signaling continued new-driver onboarding and vehicle usage intensity in the largest metro—conditions that keep dealer bays busy and drive lift refresh cycles. On the macro side, Saudi Arabia’s USD ~ trillion economy and USD ~ GDP per capita support higher dealer CAPEX capacity and multi-bay buildouts in primary metros.
Challenges
Importer Dependence
Automotive lifts in KSA are largely imported as equipment systems, making supply continuity sensitive to trade flows, logistics performance, and documentation compliance. Government transport indicators show road freight imports through land ports rose, highlighting how equipment inflows depend on cross-border freight capacity and clearance performance. When supply chains tighten (port congestion, documentation delays, backlogs), workshops face slower project completion and longer replacement cycles for worn components (hydraulic seals, lock assemblies, cables, power units). Macro dependence is reinforced by the scale of the economy: GDP is USD ~ trillion, and the country’s vehicle parc increased registered roadworthy vehicles—meaning demand is growing while supply remains exposed to import lead-time variability. For installers and distributors, importer dependence can also raise working-capital pressure in spares stocking because workshops expect near-immediate availability to protect bay uptime.
Installer Skill Variance
Lift performance in KSA is highly sensitive to installer quality because anchoring, leveling, power supply, hydraulic routing, and commissioning determine safety and uptime. Training pipeline expansion is underway, but variance remains: TVTC reported ~ trainees enrolled in international academies in technical colleges during the year, and ~ graduates from technical colleges and secondary industrial/architecture institutes—large numbers that still require consistent specialization, certification, and field supervision to translate into uniform installation quality nationwide. This matters because the vehicle base is large and rising, so a growing workshop universe creates more installation projects and more dispersion of installer capability across regions. Macro conditions—GDP at USD ~ trillion—support rapid workshop growth, but that speed can outpace standardized training and QA processes unless distributors invest in installer certification and audits.
Opportunities
Turnkey Workshop Projects
Turnkey projects (civil works + lifts + alignment + commissioning + training + after-sales) are positioned for growth because KSA’s service ecosystem is scaling in both vehicle stock and business formation, creating demand for fast, standardized, multi-bay rollouts. Registered and roadworthy vehicles increased, while vehicles registered as a new issue reached ~ units—volumes that keep workshop utilization high and justify new greenfield builds and retrofits. Business formation is also elevated, with ~ commercial registrations issued, expanding the pool of potential workshop operators, equipment integrators, and service contractors who can execute turnkey deployments across regions. From a macro base, GDP at USD ~ trillion supports private-sector expansion and capex cycles in automotive services. Turnkey providers can win by packaging compliance documentation, installer certification, commissioning logs, and preventive maintenance schedules—reducing downtime risk and warranty disputes for buyers.
Heavy-Duty Fleet Depot Lift Sets
Heavy-duty lift sets (mobile columns, in-ground, high-capacity four-post) are a strong opportunity because freight and fleet activity indicators point to persistent road-transport utilization that raises maintenance intensity, especially in depots that require uptime and standardized safety processes. Road freight imports through land ports increased, supporting the case for more structured depot maintenance and higher-capacity lifting infrastructure in logistics corridors and industrial clusters. Traffic injuries and serious accidents also sustain repair and inspection workloads where fleets push for controlled, in-house standards to reduce incident recurrence and downtime. Macro scale (GDP USD ~ trillion) and population (~ million) support ongoing domestic distribution demand that relies on road fleets.
Future outlook
Over the next five years, KSA lift demand is expected to rise with continued expansion in the vehicle parc, higher annual sales throughput, and ongoing professionalization of workshop chains across the main metros. Roadworthy vehicles already increased in the most recent two-year period, which mechanically raises service events that require lifting—tires, brakes, suspension, steering, underbody, and compliance checks. Growth is likely to be strongest where new service bays are added fastest: dealership expansions, independent chain rollouts, and fleet maintenance hubs along major logistics corridors.
Major players
- Rotary / Vehicle Service Group
- BendPak / Ranger
- Hunter Engineering
- MAHA Maschinenbau Haldenwang
- Nussbaum Automotive Solutions
- Stertil-Koni
- Ravaglioli
- Corghi
- Snap-on
- Bosch Automotive Service Solutions
- Beissbarth
- Launch Tech
- Guangzhou Jingjia Auto Equipment
- Qingdao Risense Mechatronics
Key target audience
- OEM dealership groups and dealer principals
- Independent workshop chain owners and operators
- Tire & quick service chain procurement heads
- Fleet operators & fleet maintenance heads
- Collision repair / body shop groups
- Workshop equipment distributors, installer-integrators, and service contractors
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build a KSA workshop ecosystem map covering OEM dealers, independents, tire chains, body shops, fleet depots, and inspection-lane operators. Desk research is combined with channel discovery to define variables such as bay counts, lift density, average replacement cycle, and the lift-type mix used by each workshop archetype.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We compile historical indicators for vehicle parc and vehicle sales to establish the serviceable base and workshop throughput context. We then construct a demand model using service-bay capacity additions, replacement demand, and new workshop openings, triangulating with distributor shipment patterns and installer activity.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate hypotheses through structured interviews (CATI) with distributors, installers, workshop chain operators, and dealership service heads. These inputs confirm price bands, lead times, failure modes, spares usage, and the real-world lift mix by vehicle type and workshop format.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize findings into segment-level insights and competitive benchmarking, verifying narratives against documented KSA vehicle parc and sales indicators. Final checks include consistency tests between top-down demand signals and bottom-up channel confirmations.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Scope Boundary, Lift Taxonomy & Configuration Rules, Unit–Value Conversion Logic, ASP Waterfall & Discounting Logic, Installed-Base & Replacement-Cycle Modeling, Workshop Bay Count & Utilization Proxies, Channel Mapping & Margin Stack, Primary Interview Coverage by Buyer Type, Distributor and Installer Validation, Data Triangulation and Error Bars, Limitations and Assumptions Register)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution in KSA
- Workshop Modernization Timeline and Inflection Points
- Operating Context Service-Center Formats and Bay Economics
- Value Chain and Ecosystem Map Brand Distributor Installer Workshop
- Growth Drivers
SUV-Dominant Service Mix
Dealership Throughput Mandates
Fleet Maintenance Professionalization
Multi-Bay Workshop Expansion
Alignment and ADAS Service Uplift
Safety and Ergonomics Push - Challenges
Importer Dependence
Installer Skill Variance
Civil Works and Concrete Constraints
Uptime and Spare-Parts Availability
Quality and Counterfeit Risk
Warranty Enforcement Friction - Opportunities
Turnkey Workshop Projects
Heavy-Duty Fleet Depot Lift Sets
Preventive Maintenance Contracts
Retrofits and Modernization Upgrades
Smart-Safety and IoT-Ready Lifts
Financing and Lease-to-Own Models - Trends
Rising Alignment Rack Penetration
Lift and Wheel-Service Bundling
Low-Footprint Bay Designs
Energy-Efficient Power Units
Faster Cycle-Time SKUs
Standardization on Certified Safety Systems - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- Technology and Product Architecture Deep-Dive
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- Installed Base Operating Units, 2019–2024
- Aftermarket Services Value Installation AMCs Parts, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
SUVs and Light Trucks
Light Commercial Vehicles
Heavy Commercial Vehicles
Buses and Coaches - By Application (in Value %)
General Mechanical Service
Wheel Alignment and Tire Service
Body and Collision Repair
Quick Service and Lubrication
Fleet and Depot Maintenance - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Electro-Hydraulic Lifts
Electro-Mechanical Lifts
Pneumatic-Hydraulic Assisted Lifts - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Non-Connected Conventional Lifts
Safety-Sensor Enabled Lifts
Diagnostics-Ready and Smart Lifts - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
OEM Dealership Workshops
Independent Multi-Brand Workshops
Tire and Quick-Service Chains
Fleet Operators and Logistics
Municipal and Government Depots - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Northern Region
Southern Region
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Lift Type Breadth and Capacity Range, Safety Certification and Locking Architecture, Installation Footprint and Bay Density Requirements, Lift Cycle Time and Duty-Cycle Robustness, After-Sales Coverage and SLA Commitments, Local Parts Stocking Depth and Lead-Time, Total Cost of Ownership Levers, Key-Account Delivery Capability)
- Market Share Assessment Framework
- SWOT of Major Players
- Pricing and Offer Benchmarking
- Company Profiles
Rotary Lift Vehicle Service Group
BendPak Ranger
Stertil-Koni
Nussbaum
MAHA
Ravaglioli
Hunter Engineering
Challenger Lifts
Forward Lift
ARI-HETRA
LAUNCH
Sugiyasu Bishamon
PEAK Corporation
EAE Workshop Equipment
- OEM Dealerships
- Independent Workshops
- Tire and Quick-Service Chains
- Collision Centers
- Fleet Depots
- Procurement Criteria Stack
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025–2030
- Installed Base Operating Units, 2025–2030
- Aftermarket Services Value, 2025–2030


