Market Overview
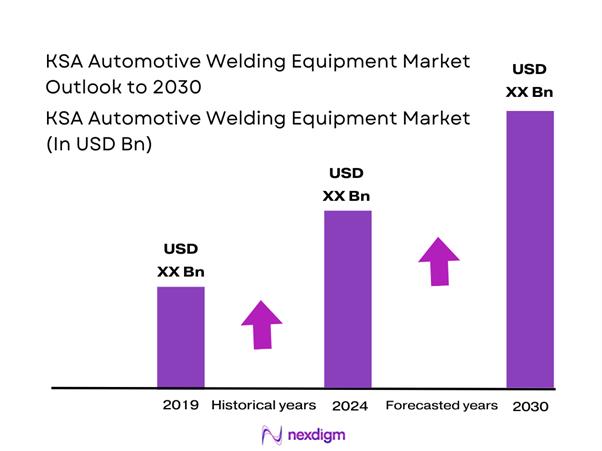
The KSA Automotive Welding Equipment market is valued at approximately USD ~ million, based on a consolidated analysis of import statistics, industrial equipment sales disclosures, and manufacturing investment data published by government bodies and OEM localization announcements. The market expanded from nearly USD ~ million in the previous period, driven by vehicle assembly localization initiatives, rising collision repair volumes, and higher capital expenditure by Tier suppliers. Growth is further supported by the expansion of automated welding lines and increased adoption of inverter-based MIG, TIG, and resistance welding systems across automotive production and service facilities.
The market is dominated by Riyadh, Jeddah, Dammam, and Jubail, supported by their concentration of automotive assembly units, Tier suppliers, and industrial clusters. Riyadh leads due to the presence of OEM-linked manufacturing zones, fleet maintenance hubs, and government-backed industrial parks. Jeddah dominates aftermarket welding demand owing to high vehicle density and collision repair activity. The Eastern Province benefits from proximity to industrial cities, logistics ports, and metal fabrication clusters, enabling faster deployment of high-capacity and robotic welding systems across automotive and industrial applications.
Market Segmentation
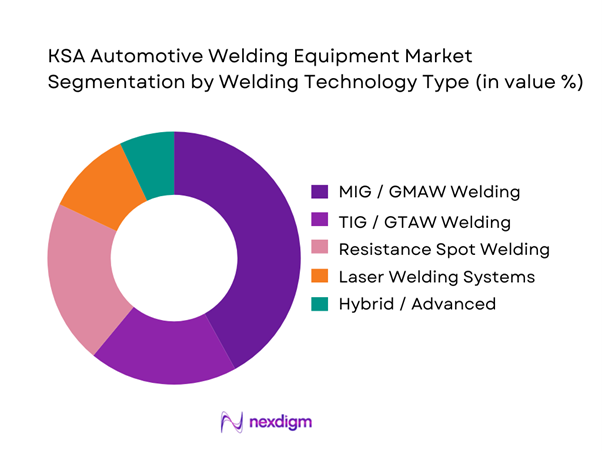
By Welding Technology Type
The KSA Automotive Welding Equipment market is segmented by welding technology type into MIG/GMAW welding equipment, TIG/GTAW welding equipment, resistance spot welding equipment, laser welding systems, and hybrid advanced welding systems. MIG/GMAW welding equipment dominates this segmentation, accounting for the largest market share in the automotive welding equipment landscape. Its dominance is driven by versatility across body-in-white operations, chassis welding, and aftermarket repair. MIG systems support high deposition rates, consistent arc stability, and compatibility with steel and aluminum, which are widely used in vehicle structures. Additionally, MIG welding requires comparatively lower operator skill levels than TIG, making it suitable for large-scale workshops and service centers. OEMs and Tier suppliers also favor MIG systems due to easier robotic integration and lower lifecycle operating costs.
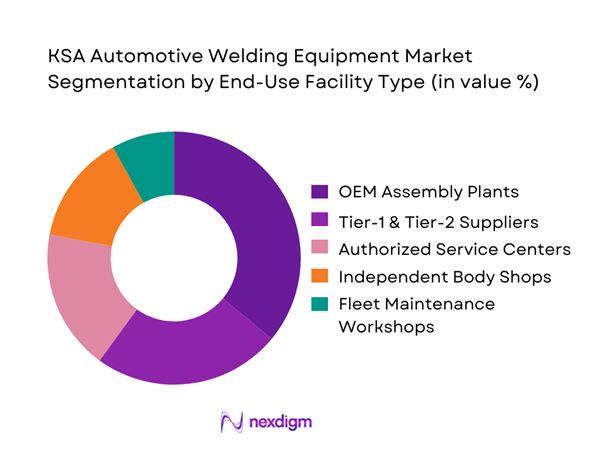
By End-Use Facility Type
The market is segmented into OEM assembly plants, Tier suppliers, authorized service centers, independent body shops, and fleet maintenance workshops. OEM assembly plants represent the dominant sub-segment, driven by sustained investments in localized vehicle production and CKD/SKD assembly lines. These facilities deploy high-capacity resistance spot welding systems, robotic MIG welding cells, and increasingly laser welding equipment for precision body joining. OEM plants prioritize throughput, repeatability, and compliance with global manufacturing standards, leading to higher capital spending per installation. The presence of long-term production contracts and government-supported localization policies further reinforces the dominance of this segment, making it the primary revenue contributor in the automotive welding equipment market.
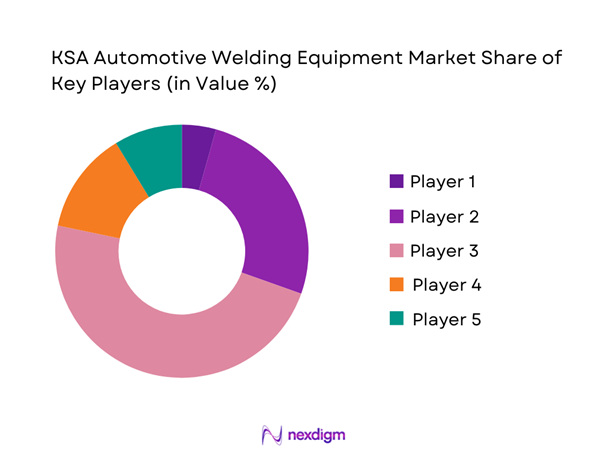
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Automotive Welding Equipment market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of global welding technology leaders and strong regional distributors. International manufacturers dominate high-end automated and robotic welding systems, while regional players and distributors lead mid-range and aftermarket equipment sales. Competition is driven by technology reliability, service response time, OEM approvals, and localized spare-parts availability. Long-term service contracts and training capabilities increasingly differentiate suppliers in the Saudi market.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Welding Technology Range | Automation Capability | Local Service Presence | Automotive OEM Approvals | Training & Certification | Pricing Position |
| Lincoln Electric | 1895 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ESAB | 1904 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Fronius | 1945 | Austria | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Panasonic Welding | 1955 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Miller Electric | 1929 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Automotive Welding Equipment Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Local manufacturing push
Saudi Arabia’s manufacturing-scale-up is a direct demand catalyst for automotive welding equipment because localized assembly and component fabrication require repeatable joining processes and qualified weld procedure controls. The macro backdrop supports sustained industrial capex, with the economy producing output at scale and income levels supporting domestic vehicle demand that anchors localization programs. At the workforce pipeline layer, the national vocational training system reported a large base of trainees and graduates in the same period, which is important because welding equipment adoption in plants is constrained by operator, technician, and maintenance staff availability for setup, calibration, and preventive maintenance. In road- transport logistics that supply automotive plants and service networks, cross-border land-port passenger flows reached high levels, indicating a large mobility ecosystem and transport utilization intensity that supports downstream automotive services and parts movement. Collectively, these indicators point to expanding industrial activity and workforce throughput, which typically increases installation of arc-welding power sources, resistance welding systems, fume extraction, jigs, fixtures, and automated welding cells in localized automotive manufacturing lines.
Vehicle parc growth
Vehicle parc expansion directly increases welding equipment usage through collision repair, fleet maintenance, and fabrication and rework in workshops. Saudi road transport data shows registered and roadworthy vehicles reached ~ vehicles while newly issued registrations during the year reached ~ vehicles, acting as a leading indicator for sustained demand in body shops, dealership workshops, and fleet depots that rely on MIG and TIG welding, spot welders, dent-pull systems, and structural repair tooling. The same data shows driving licenses issued for the first time increased compared with the previous period, which matters because first-time driver growth tends to increase vehicle utilization and workshop traffic, raising welding consumable pull-through and machine utilization in service ecosystems. On the macro side, the labor market remains comparatively tight, supporting higher household mobility and vehicle usage intensity that feeds repair and maintenance cycles. In practical market terms, a larger parc increases demand for welding equipment across chassis crack repair, exhaust and bracket repairs, frame pulling and re-welding, panel replacement, and accessory fabrication in commercial fleets, raising replacement purchases and service contracts for welding systems.
Challenges
Capex intensity
Automotive welding equipment demand in Saudi Arabia is highly sensitive to capex cycles because OEM welding cells, resistance welding systems, and robotic integration require upfront capital, commissioning, and long payback periods. The macro environment indicates investment is significant but financing conditions matter, as policy rates raise hurdle rates for private-sector borrowing and can delay automation upgrades in Tier suppliers and larger body shop chains. At the same time, macro stability supports long-term industrial confidence but does not remove the short-term challenge of high capex tickets for welding automation such as robotic arms, positioners, jigs, safety cells, and quality monitoring systems. The road-transport system shows a large registered vehicle base, which expands repair demand, yet many repair operators remain cashflow-driven. As a result, capex-heavy upgrades are often staggered or deferred when borrowing costs rise. Therefore, capex intensity is a concrete market constraint that slows technology refresh cycles, increases reliance on distributor financing and leasing, and pushes buyers toward modular upgrades rather than full-line automation, especially outside OEM plants and Tier suppliers.
Skilled welder availability
Even when demand exists, welding equipment adoption is constrained by skills availability, especially for advanced processes used in automotive applications such as pulse-MIG tuning, aluminum welding, resistance spot weld replication, robotic cell programming, and quality documentation. The labor pipeline is expanding, with the national training system reporting a large number of trainees and graduates in the same period, indicating meaningful throughput. However, the market still faces skill-matching challenges because automotive welding requires specific competencies beyond generic fabrication. Demand pressure is visible in the scale of the vehicle ecosystem, with a large registered vehicle base and substantial new registrations creating a heavy service workload, while collision intensity increases demand for structurally competent repairs that must meet insurer and safety expectations. From a macro labor perspective, relatively low unemployment suggests a tight market, making it harder for body shop chains and suppliers to recruit and retain certified welders and maintenance technicians at scale. Practically, this skill constraint pushes buyers toward suppliers with embedded training, quick commissioning support, localization, and after-sales maintenance, otherwise utilization remains low and equipment return on investment suffers.
Opportunities
Robotic welding adoption
Robotic welding adoption is a forward-growth opportunity in Saudi Arabia because it directly addresses current constraints visible in today’s data, including high throughput requirements driven by a large vehicle parc and accident volumes, and skills bottlenecks requiring consistent quality with limited specialist availability. The scale of the vehicle ecosystem creates sustained workshop and supplier workloads that favor automation where repeatability, cycle time, and rework reduction matter. Collision intensity supports a high volume of structural repairs and parts replacement, increasing the value of automation in component suppliers and in high-throughput repair chains through standardized procedures, quality documentation, and reduced variability. On the skills pipeline side, the number of vocational graduates is encouraging, but robotics reduces dependence on highly specialized manual welders by shifting skill needs toward programming, fixturing, and maintenance, which can be built through structured training and supplier-led certification. The macro base supports industrial expansion and plant modernization budgets, while low inflation supports planning stability for multi-year automation rollouts. This makes robotic welding a practical opportunity justified by current workload and workforce realities.
EV battery pack welding
EV battery pack welding is an opportunity that expands the complexity-weighted demand for welding equipment because battery packs and their enclosures require controlled joining of thin-to-medium gauge materials, consistent sealing integrity, and repeatability. This raises the need for advanced MIG and TIG variants, resistance welding, and precision joining systems. The enabling macro base is strong, with large economic output and high income levels supporting adoption of higher-spec vehicle technologies and the supplier ecosystem that follows. The operational pull-through comes from the sheer size and renewal of the vehicle ecosystem, with a large registered vehicle base and continuous new registrations creating a natural channel for new powertrain diffusion and the need for equipped service networks over time. Battery pack and enclosure-related fabrication also intersects with the broader import ecosystem for welding systems, showing that sophisticated welding platforms already enter the country and can be directed toward EV component production and specialized repair ecosystems. With a sizable vocational graduate pipeline, the workforce can be targeted toward EV-safe workshop operations, making this a scalable opportunity supported by current numbers.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the KSA Automotive Welding Equipment market is expected to witness steady and structurally strong growth, driven by vehicle manufacturing localization, expansion of EV-related welding applications, and increasing automation adoption. Investments in robotic welding, inverter-based power sources, and digitally monitored systems are expected to accelerate. Additionally, higher collision repair demand and fleet expansion will sustain aftermarket equipment purchases. The market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of ~ during the forecast period, supported by policy-driven industrialization and sustained automotive sector development.
Major Players
- Lincoln Electric
- ESAB
- Fronius International
- Panasonic Welding Systems
- Miller Electric
- ABB Robotics
- KUKA
- Yaskawa Motoman
- OTC Daihen
- CLOOS
- Hyundai Welding
- Kemppi
- Böhler Welding
- Ador Welding
Key Target Audience
- Automotive OEMs and Vehicle Assembly Plants
- Tier Automotive Component Manufacturers
- Authorized Automotive Service Center Networks
- Independent Body Shop Chains and Collision Repair Operators
- Fleet Operators and Fleet Maintenance Providers
- Industrial EPC Contractors and Automation Integrators
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study begins with mapping the automotive welding ecosystem in Saudi Arabia, identifying OEMs, suppliers, distributors, and service providers. Secondary research from government publications, trade data, and industrial databases is used to define critical market variables influencing demand and pricing.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data on equipment shipments, installed base, and replacement cycles is analyzed to construct market size estimates. Vehicle production data, repair volumes, and industrial investment flows are evaluated to validate demand patterns.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions are validated through structured interviews with equipment distributors, workshop operators, and plant managers. These discussions provide insights into purchasing behavior, technology adoption, and pricing dynamics.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights from primary and secondary sources are triangulated using bottom-up and top-down approaches to finalize market sizing, segmentation, and competitive analysis, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope validation, automotive welding equipment taxonomy, OEM vs aftermarket boundary assumptions, unit economics framework, value–volume triangulation, import–local assembly normalization, primary interviews with OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, body shop chains, EPC contractors, dealer validation, limitations and inference logic)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Industrial Evolution
- Automotive Manufacturing and Repair Ecosystem in KSA
- Role of Localization, Vision 2030, and IKTVA
- Automotive Welding Equipment Value Chain and Supply Chain Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Local manufacturing push
Vehicle parc growth
Body repair demand
EV structural welding - Challenges
Capex intensity
Skilled welder availability
Import dependence
Price sensitivity - Opportunities
Robotic welding adoption
EV battery pack welding
Aluminum body repair
Localized assembly - Trends
Pulse welding
Inverter-based systems
Smart welding
IoT-enabled machines - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Welding Technology Type (in Value %)
MIG / GMAW Welding Equipment
TIG / GTAW Welding Equipment
Resistance Spot Welding Equipment
Laser Welding Systems - By Automation Level (in Value %)
Manual / Semi-Automatic Welding Equipment
Robotic Welding Cells
Fully Automated Welding Lines - By Vehicle Type Served (in Value %)
Passenger Vehicles
Commercial Vehicles
Electric Vehicles
Special Purpose & Industrial Vehicles - By End-Use Facility Type (in Value %)
OEM Assembly Plants
Tier-1 & Tier-2 Component Suppliers
Authorized Service Centers & Dealership Workshops
Independent Body Shops & Collision Repair Centers
Fleet Maintenance & Industrial Workshops - By Power Source & Output Capacity (in Value %)
Low Output Welding Equipment
Medium Output Welding Equipment
High Output / Heavy-Duty Welding Equipment - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern & Northern Regions
- Market Share Analysis by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Welding technology portfolio depth, automation and robotic integration capability, output capacity range and duty cycle performance, automotive OEM approval and certification presence, local service network and response time, spare parts availability and localization, total cost of ownership positioning, training certification and after-sales support model)
- Competitive Benchmarking Matrix
- Pricing Analysis by Equipment Type and Capacity
- Business Strategy and Go-to-Market Models
- Detailed Company Profiles
Lincoln Electric
ESAB
Fronius International
Panasonic Welding Systems
Miller Electric
KUKA
ABB
Yaskawa Motoman
OTC Daihen
CLOOS
Hyundai Welding
Kemppi
Ador Welding
Voestalpine Böhler Welding
- Demand Drivers by End-User Category
- Purchasing Behavior and Budget Allocation Patterns
- Decision-Making Unit Analysis
- Productivity, Downtime, and Lifecycle Cost Expectations
- Pain Points and Unmet Needs
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Volume, 2025–2030
- By Average Price, 2025–2030


