Market Overview
The KSA C4ISR market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained defense digitization initiatives and integrated command modernization programs. The market is shaped by rising deployment of networked surveillance platforms, multi-domain command systems, and secure communications infrastructure. Adoption intensity increased during 2024 and 2025 as operational readiness priorities expanded. Platform refresh cycles, interoperability upgrades, and data-centric architectures supported consistent system integration demand across land, air, and maritime forces.
Demand concentration remains strongest across Riyadh, Eastern Province, and Western defense hubs due to command headquarters density and infrastructure maturity. These regions benefit from established military bases, satellite ground stations, and secure fiber backbones. Local industrial participation, policy-driven localization mandates, and proximity to defense decision centers further reinforce dominance. Southern operational zones also contribute through border security deployments, although ecosystem depth and integrator presence remain comparatively limited.
Market Segmentation
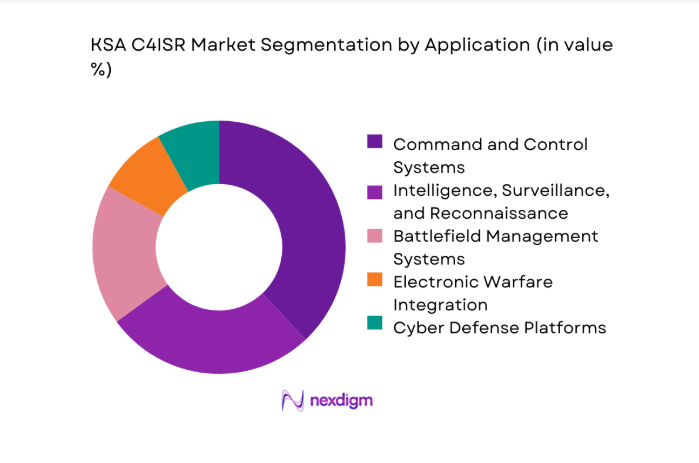
By Application
The application-based segmentation of the KSA C4ISR market highlights command and control systems as the dominant segment due to joint-force coordination priorities. Intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance platforms continue gaining traction as sensor fusion and real-time analytics mature. Battlefield management systems experience steady adoption supporting tactical visibility. Electronic warfare integration remains selective, while cyber defense platforms expand gradually with network-centric doctrines. The dominance is reinforced by multi-service integration requirements, centralized command architectures, and sustained modernization initiatives during 2024 and 2025.
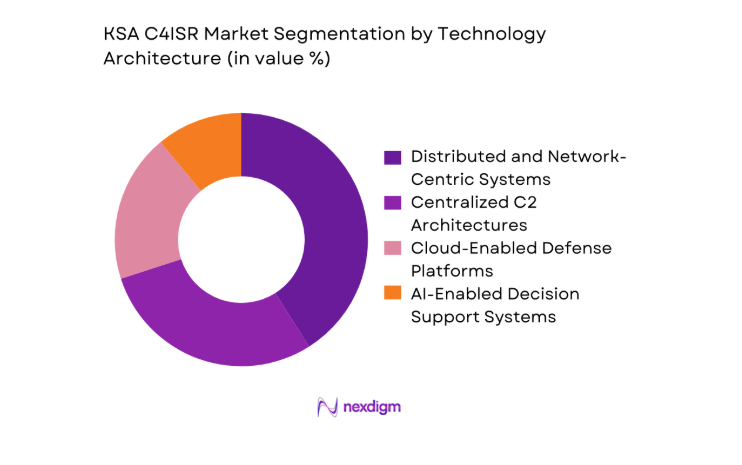
By Technology Architecture
Technology architecture segmentation shows distributed and network-centric systems leading adoption due to operational flexibility advantages. Centralized architectures remain relevant for strategic command environments but face gradual replacement. Cloud-enabled defense platforms gain importance as data volumes expand and secure virtualization matures. AI-enabled decision support systems represent an emerging segment, driven by analytics-driven operational planning. The dominance of distributed architectures reflects interoperability needs, real-time data exchange priorities, and evolving multi-domain operational doctrines observed during 2024 and 2025.
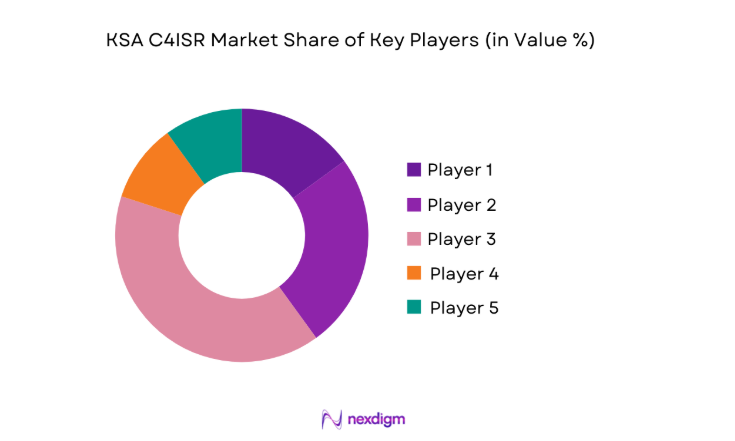
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the KSA C4ISR market is characterized by a mix of global defense primes and strong domestic integrators. Market positioning is influenced by localization depth, system integration capability, and long-term sustainment support alignment with national defense priorities.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon Technologies | 2020 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Group | 2000 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saudi Arabian Military Industries | 2017 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA C4ISR Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of Saudi Armed Forces
Modernization of Saudi Armed Forces continues driving the KSA C4ISR market through accelerated replacement of legacy command systems. Defense authorities emphasized integrated situational awareness platforms during 2024 and 2025 to improve operational decision accuracy. Modernization programs prioritize multi-domain visibility, secure data exchange, and synchronized command structures across service branches. Upgrades include sensor fusion, real-time analytics, and hardened communications supporting complex operational environments. These initiatives align with evolving threat scenarios requiring faster command responsiveness and improved information reliability. Training alignment and doctrine updates further reinforce technology adoption across operational units. Domestic industrial participation increased as modernization projects emphasized localized system integration capabilities. Incremental deployment cycles sustained continuous demand for software-defined and modular architectures. Inter-service compatibility requirements strengthened reliance on standardized C4ISR frameworks. Overall modernization momentum remains a foundational catalyst shaping sustained market expansion.
Integration of joint-force operations
Integration of joint-force operations significantly influences C4ISR demand by requiring unified command visibility across land, air, and naval assets. Operational doctrines increasingly emphasize synchronized planning and execution across multiple domains simultaneously. During 2024 and 2025, joint exercises highlighted gaps in fragmented communication architectures. Addressing these gaps accelerated investments in interoperable command platforms and shared intelligence layers. Joint-force integration mandates common data standards and cross-domain information accessibility. Secure connectivity between tactical and strategic echelons became operationally critical. These requirements favor scalable architectures capable of aggregating diverse sensor inputs. Decision-makers increasingly rely on fused operational pictures for coordinated mission execution. Integration efforts also drive demand for centralized training and simulation environments. Consequently, joint-force operational integration remains a persistent growth driver.
Challenges
High system integration complexity
High system integration complexity presents a major challenge within the KSA C4ISR market due to heterogeneous platform environments. Multiple legacy systems coexist with modern digital architectures, complicating seamless interoperability efforts. Integration projects often require customized middleware and extensive validation cycles. During 2024 and 2025, program timelines extended due to interface incompatibilities. Complexity increases when incorporating multi-vendor hardware and software stacks. Security certification processes further lengthen integration schedules. Skilled system engineering resources remain constrained, adding execution risk. Complex integration elevates operational disruption risks during transition phases. These factors increase coordination burdens for defense authorities and integrators. Consequently, integration complexity restrains deployment speed despite strong strategic demand.
Interoperability across legacy platforms
Interoperability across legacy platforms remains a persistent challenge limiting operational efficiency within the KSA C4ISR market. Many deployed systems were designed using proprietary standards lacking modern data exchange compatibility. Retrofitting interoperability layers requires extensive customization and testing efforts. During 2024 and 2025, interoperability shortfalls surfaced during multi-service operational exercises. Data latency and inconsistent formats hinder real-time situational awareness. Addressing these gaps demands incremental upgrades rather than full replacements. Budget prioritization challenges further slow comprehensive interoperability initiatives. Legacy constraints also complicate cybersecurity hardening processes. Training personnel across mixed-technology environments adds operational strain. Overall, legacy interoperability remains a structural market constraint.
Opportunities
Localization of C4ISR manufacturing and software
Localization of C4ISR manufacturing and software presents a significant opportunity within the KSA C4ISR market ecosystem. National policies encourage domestic development of mission-critical defense technologies. During 2024 and 2025, localization requirements increased across major acquisition programs. Local software development enhances customization aligned with operational doctrines. Domestic manufacturing reduces dependency on external supply chains and geopolitical constraints. Technology transfer initiatives support capability building within local firms. Localization also strengthens lifecycle support and system sustainment responsiveness. Employment development further reinforces political and institutional backing. Integrated local ecosystems improve long-term cost efficiency without exposing monetary figures. Consequently, localization initiatives offer substantial strategic and commercial opportunities.
Expansion of space-based ISR capabilities
Expansion of space-based ISR capabilities creates new growth avenues within the KSA C4ISR market landscape. Satellite-enabled surveillance enhances border monitoring, maritime awareness, and strategic intelligence collection. During 2024 and 2025, increased emphasis on persistent wide-area coverage emerged. Space-based assets complement terrestrial and airborne sensors through layered intelligence architectures. Integration with ground command systems improves data continuity and resilience. Advances in small satellite deployment accelerate deployment flexibility. Secure downlink infrastructure strengthens real-time intelligence dissemination. Domestic participation in space programs further supports ecosystem growth. Space ISR expansion aligns with long-term national security objectives. Overall, this opportunity expands C4ISR capability depth significantly.
Future Outlook
The KSA C4ISR market outlook through 2035 reflects sustained emphasis on integrated defense digitization and multi-domain operational readiness. Continued localization, joint-force interoperability, and space-based intelligence expansion will shape procurement priorities. Technology convergence across cyber, electronic warfare, and AI-enabled analytics is expected to redefine system architectures. Long-term planning frameworks support gradual modernization cycles rather than abrupt replacements.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon Technologies
- Northrop Grumman
- BAE Systems
- Thales Group
- Leonardo
- Saab AB
- L3Harris Technologies
- Elbit Systems
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Boeing Defense
- Rheinmetall
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Advanced Electronics Company
- Alsalam Aerospace Industries
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defense procurement departments
- Saudi Armed Forces operational commands
- National Guard acquisition units
- Internal Security Forces technology divisions
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries program offices
- Defense-focused investments and venture capital firms
- Communications and satellite infrastructure agencies
- National cybersecurity and regulatory authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Involved defining C4ISR scope, operational domains, technology layers, and end-user structures relevant to national defense environments.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Applied segmentation logic, deployment mapping, and integration pathways to structure qualitative and quantitative assessment.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Engaged defense engineers, system integrators, and operational planners to validate assumptions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Consolidated insights into coherent market narratives aligned with strategic and operational realities.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and C4ISR capability scope alignment, KSA defense taxonomy and mission-layer segmentation logic, top-down and bottom-up platform-level market sizing, program-wise revenue attribution across acquisition and sustainment phases, primary validation with Saudi MoD and system integrators, multi-source triangulation with classified-budget proxies and export controls)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational usage across joint-force doctrines
- Defense ecosystem and integrator structure
- Supply chain and localization framework
- Regulatory and offset environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of Saudi Armed Forces
Integration of joint-force operations
Rising border security and threat surveillance needs
Vision 2030 defense localization mandates
Adoption of AI and data-centric warfare concepts - Challenges
High system integration complexity
Interoperability across legacy platforms
Dependence on foreign technology transfers
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities
Long procurement and approval cycles - Opportunities
Localization of C4ISR manufacturing and software
Expansion of space-based ISR capabilities
Public-private partnerships with Saudi firms
Upgrades and lifecycle support of legacy systems
Export-oriented regional defense collaboration - Trends
Shift toward network-centric warfare
Increased use of AI-driven analytics
Convergence of cyber and electronic warfare
Modular and open-architecture systems
Emphasis on real-time situational awareness - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Land Forces
Air Forces
Naval Forces
Joint and Strategic Commands - By Application (in Value %)
Command and Control Systems
Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance
Battlefield Management Systems
Electronic Warfare Integration
Cyber Defense and Network Security - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Centralized C2 Architectures
Distributed and Network-Centric Systems
Cloud-Enabled Defense Platforms
AI-Enabled Decision Support Systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Ministry of Defense
Saudi Armed Forces Branches
National Guard
Internal Security Forces - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Satellite Communications
Tactical Radio Networks
Fiber-Optic and Fixed Networks
Hybrid and Multi-Band Networks - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Border Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (platform coverage, technology maturity, localization capability, integration expertise, pricing competitiveness, cybersecurity strength, after-sales support, government relationships)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon Technologies
Northrop Grumman
BAE Systems
Thales Group
Leonardo
Saab AB
L3Harris Technologies
Elbit Systems
Airbus Defence and Space
Boeing Defense
Rheinmetall
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
Advanced Electronics Company
Alsalam Aerospace Industries
- Demand drivers linked to force readiness
- Defense procurement and tender mechanisms
- Vendor qualification and offset requirements
- Budget allocation and multi-year funding cycles
- System integration and operational risk factors
- After-sales support and training expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


