Market Overview
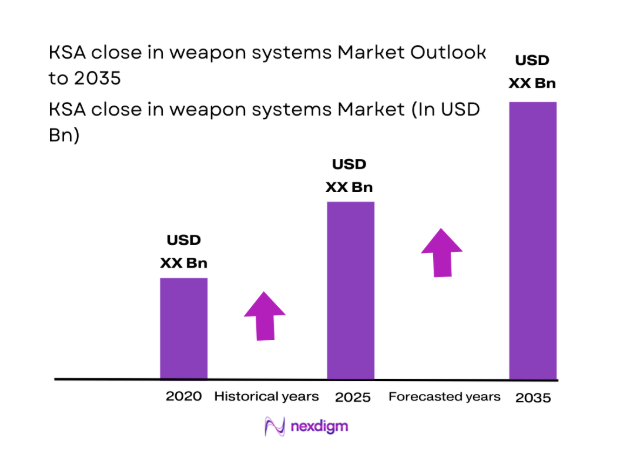
The KSA close in weapon systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting procurement cycles and platform modernization across multiple defense domains. Current procurement activity aligns with defense readiness objectives and fleet recapitalization programs across maritime and base protection missions. Capability enhancement initiatives focus on improving point-defense coverage, sensor integration, and response coordination across operational units. Ongoing modernization programs emphasize sustainment readiness, interoperability alignment, and phased upgrades supporting mission continuity.
Eastern Province concentrates demand around energy corridors and coastal terminals, supported by mature logistics nodes and defense-industrial clusters. Jeddah anchors maritime operations with shipyards, training ranges, and fleet sustainment infrastructure. Riyadh hosts command integration, acquisition oversight, and program governance centers. Yanbu and Jubail support maintenance ecosystems, depot-level services, and testing facilities. Policy alignment and localization frameworks reinforce regional clustering, accelerating capability absorption and operational coordination.
Market Segmentation
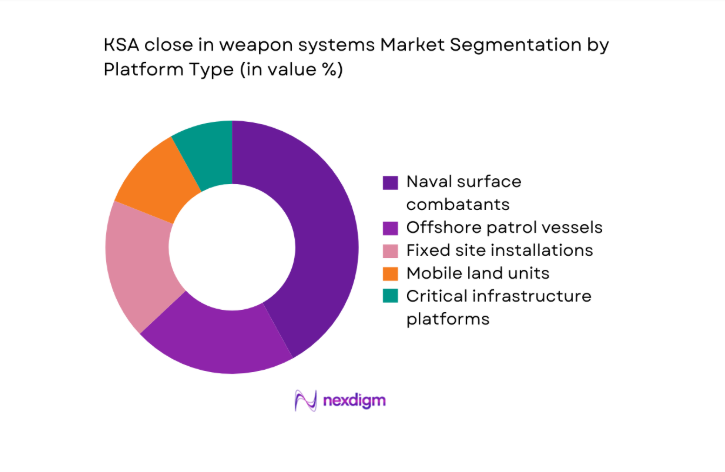
By Platform Type
Naval surface combatants dominate procurement prioritization because maritime threats demand layered terminal defense across congested sea lanes. Integration pathways favor shipborne architectures with radar cueing, automated tracking, and tight fire control loops. Coastal patrol fleets increasingly adopt compact point-defense suites to counter small aerial threats during escort missions. Fixed-site deployments complement naval coverage for ports and terminals, enabling persistent protection. Mobile land configurations remain selective, supporting expeditionary base protection during heightened alert cycles. Standardization initiatives reduce integration friction across hull classes and sensor suites. Sustainment readiness improves through common spares, training pipelines, and doctrine harmonization. Platform-centric acquisition aligns with fleet recapitalization schedules and lifecycle refresh programs. Interoperability mandates reinforce cross-platform compatibility. Capability roadmaps prioritize modular upgrades and software-defined fire control.
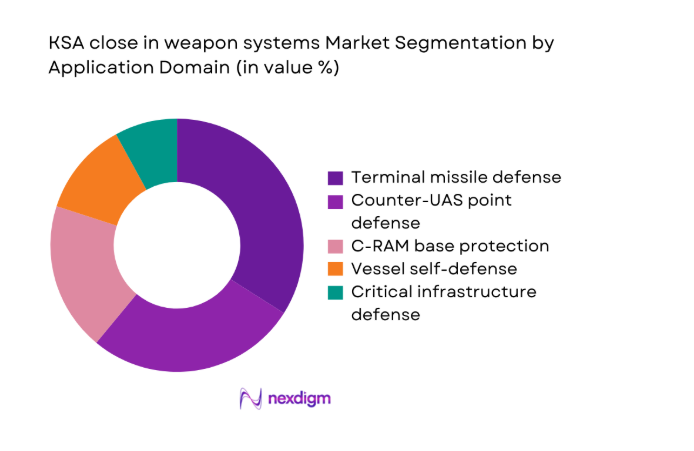
By Application Domain
Point defense against terminal missile threats anchors operational planning across maritime corridors and port approaches. Counter-UAS missions expand rapidly around bases, energy facilities, and logistics hubs. C-RAM protection addresses indirect fire risks near forward operating sites. Vessel self-defense integrates into layered IAMD constructs for escort and patrol missions. Critical infrastructure defense aligns with national resilience objectives across ports and terminals. Application-driven procurement emphasizes sensor fusion, rapid engagement timelines, and autonomous tracking performance. Training syllabi adapt to multi-threat scenarios and saturation attack profiles. Doctrine refinement aligns engagement authority with joint command structures. Application maturity shapes upgrade prioritization cycles. Interoperability across application domains enhances response coherence.
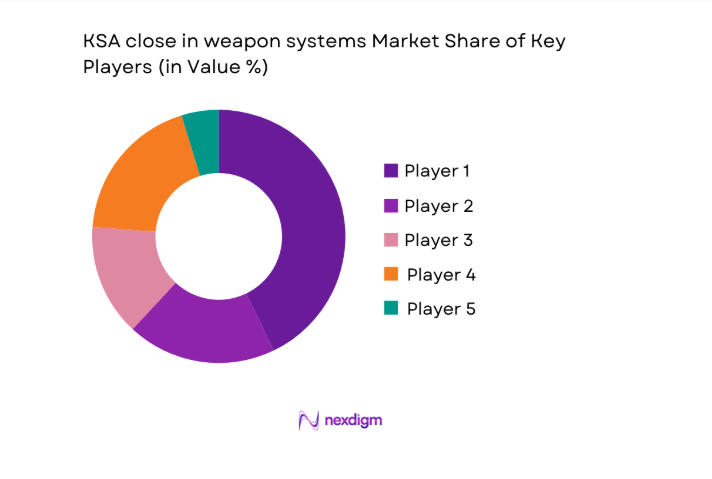
Competitive Landscape
Vendors compete on integration depth, localization commitments, and sustainment readiness aligned with national defense priorities. Partnerships emphasize technology transfer, depot establishment, and lifecycle support frameworks supporting operational availability.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| RTX | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA close in weapon systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising anti-ship missile and UAV threat environment
Regional security dynamics increase terminal threat exposure across maritime corridors and critical coastal infrastructure assets. Operational exercises recorded 24 complex threat profiles during joint drills validating layered point defense effectiveness. Adversary capabilities demonstrated higher maneuverability and electronic countermeasures across 2024 training environments. Fleet commanders prioritized rapid reaction timelines and autonomous tracking improvements to counter saturation scenarios. Sensor fusion programs expanded integration across 5 command centers to accelerate engagement decisions. Increased aerial incursions prompted base protection enhancements across 12 installations supporting logistics operations. Doctrine revisions emphasized coordinated cueing between shipborne radars and coastal surveillance networks. Interoperability testing validated engagement sequences across 9 joint task force exercises. Training syllabi incorporated 18 scenario variants simulating low observable aerial threats. Readiness audits reported improved response coordination following iterative digital fire control updates.
Expansion of naval and coastal security programs
Naval modernization programs expanded patrol coverage across congested sea lanes supporting maritime security operations. Fleet availability improved with 14 platform refits integrating modern point defense interfaces. Coastal surveillance nodes increased to 22 sites enhancing cueing fidelity for terminal defenses. Joint command exercises harmonized engagement authority across maritime and coastal commands. Platform lifecycle programs aligned with doctrine modernization and operator certification pathways. Shipyard modernization improved integration timelines across multi-vendor sensor and effector suites. Training throughput reached 36 certified operators across gunnery and missile control specialties. Digital integration milestones strengthened connectivity with joint battle management systems. Logistics nodes standardized spares catalogs to reduce downtime across deployed platforms. Operational tempo increased with coordinated patrol cycles across 5 coastal sectors.
Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle costs
Budget prioritization pressures constrain procurement pacing amid competing modernization programs across domains. Program governance emphasizes phasing to balance readiness objectives with resource stewardship requirements. Sustainment planning requires predictable funding cycles to maintain availability targets across fleets. Training pipelines demand recurring allocations to preserve operator proficiency and safety standards. Depot capacity expansion competes with parallel industrial localization initiatives across sectors. Technology refresh cycles introduce planning complexity for software-defined fire control architectures. Multi-year contracting frameworks mitigate volatility while preserving upgrade optionality. Readiness reporting requires transparent metrics to justify sustainment prioritization. Asset utilization tracking informs refurbishment sequencing and spares provisioning strategies. Governance oversight strengthens accountability for long-term availability commitments.
Integration complexity with existing C2 and sensors
Legacy command architectures complicate seamless integration with modern sensor-fused fire control solutions. Data standards divergence impedes rapid cueing across joint networks and platform interfaces. Software certification cycles lengthen deployment timelines for updated engagement algorithms. Cyber hardening requirements add validation steps before operational acceptance. Interoperability testing across 9 exercises revealed latency challenges under high traffic conditions. Interface harmonization demands coordinated vendor collaboration and standardized middleware frameworks. Operator retraining addresses workflow changes introduced by integrated battle management tools. Configuration management governs version control across distributed nodes and platforms. Validation protocols ensure safety envelopes remain intact during rapid upgrades. Governance committees align stakeholders on integration roadmaps and acceptance criteria.
Opportunities
Fleet recapitalization and new surface combatant programs
Planned surface combatant programs open integration windows for modern point defense architectures. New hull designs enable optimized sensor placement and engagement geometry improvements. Modular combat systems facilitate incremental upgrades without extensive structural modifications. Program milestones align with operator training pipelines and certification schedules. Shipyard digitization improves integration throughput across multi-vendor combat system suites. Common architecture standards streamline lifecycle upgrades across future fleet variants. Joint trials validate engagement performance during acceptance testing phases. Fleet doctrine updates incorporate layered defense concepts from inception stages. Sustainment frameworks embed availability metrics into platform service agreements. Early design involvement reduces integration friction and commissioning delays.
C-RAM deployment for base and infrastructure protection
Base protection programs prioritize terminal defense against indirect fire near logistics corridors. Infrastructure hardening initiatives integrate point defense with perimeter sensing networks. Mobile batteries enable rapid repositioning during heightened alert postures. Training curricula emphasize coordinated engagement across security forces and air defense units. Sensor fusion enhances detection fidelity across cluttered environments near critical facilities. Doctrine development aligns rules of engagement with civil protection mandates. Interagency coordination improves response timelines for facility protection scenarios. Readiness drills validate coverage envelopes across 12 protected sites. Maintenance planning standardizes uptime targets for fixed installations. Program governance supports phased expansion aligned with threat assessments.
Future Outlook
The outlook reflects continued emphasis on layered defense integration across naval, coastal, and critical infrastructure protection missions. Localization frameworks will deepen sustainment capacity and software-defined upgrades. Interoperability with joint battle management will mature through phased integration milestones. Capability roadmaps emphasize counter-UAS resilience and saturation defense readiness through 2035.
Major Players
- RTX
- Northrop Grumman
- BAE Systems
- Leonardo
- Thales
- Rheinmetall
- Saab
- ASELSAN
- Hanwha Defense
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Elbit Systems
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- MBDA
- Lockheed Martin
- L3Harris Technologies
Key Target Audience
- Royal Saudi Naval Forces procurement directorates
- Saudi Ministry of Defense acquisition agencies
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries program offices
- Critical infrastructure security operators
- Port and coastal authority defense units
- Systems integrators and MRO providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables were defined around platform integration depth, operational readiness indicators, interoperability maturity, and localization commitments. Threat profiles, deployment patterns, and training throughput informed scope boundaries. Taxonomy aligned platforms, applications, and connectivity architectures for consistent analysis.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Analytical models mapped procurement cycles to fleet modernization timelines and doctrine updates. Deployment footprints and readiness metrics structured demand assessment. Integration pathways informed capability clustering across naval, coastal, and fixed-site domains.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on adoption drivers and integration barriers were validated through expert workshops and operational scenario reviews. Feedback refined assumptions on interoperability readiness and training capacity. Iterative validation strengthened scenario robustness.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into coherent narratives linking threat evolution, platform roadmaps, and ecosystem readiness. Cross-domain insights informed segmentation logic and competitive positioning. Outputs prioritized operational relevance and policy alignment.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope for KSA CIWS Programs, Platform taxonomy mapping across naval and land assets, Bottom-up shipment and active system modeling from awarded contracts, Program-level revenue attribution and ASP normalization, Interviews with Saudi MoD, RSNF and prime contractors, Triangulation with defense budgets, SIPRI/Janes and trade data, Assumptions on localization, offsets and upgrade cycles)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Operational use cases and threat environment
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and local content framework
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising anti-ship missile and UAV threat environment
Expansion of naval and coastal security programs
Protection requirements for critical energy infrastructure
Modernization of integrated air and missile defense architecture
Localization and industrial participation mandates
Increased defense budget allocation for point defense - Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle costs
Integration complexity with existing C2 and sensors
Export control and technology transfer constraints
Sustainment and MRO capacity localization gaps
Training and doctrine adaptation requirements
Interoperability across multi-vendor systems - Opportunities
Fleet recapitalization and new surface combatant programs
C-RAM deployment for base and infrastructure protection
Upgrades and life-extension of legacy CIWS
Local assembly, MRO and component manufacturing
Directed energy point defense pilots
Joint IAMD networking and sensor fusion programs - Trends
Shift toward networked and layered point defense
Growing emphasis on counter-UAS and asymmetric threats
Hybrid gun-missile and multi-effectors adoption
Increased localization and offset-driven partnerships
Digital fire control, AI-assisted tracking and cueing
Lifecycle service contracts and performance-based logistics - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Naval surface combatant fleet
Offshore patrol and coastal security fleet
Fixed site air defense assets
Mobile land defense units
Critical infrastructure protection assets - By Application (in Value %)
Anti-ship missile terminal defense
Anti-aircraft and counter-UAS point defense
C-RAM base protection
Vessel self-defense and layered IAMD
Critical energy and port facility defense - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Gun-based CIWS
Missile-based CIWS
Hybrid gun-missile systems
Directed energy point defense
Sensor-fused fire control architectures - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Navy and maritime security forces
Air force and air defense forces
Army and ground forces
Oil and gas infrastructure operators
Port and coastal authorities - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone platform-integrated systems
Network-centric IAMD integrated systems
C2-integrated battery-level systems
Remote sensor-fused architectures
Joint fires and battle management integrated systems - By Region (in Value %)
Eastern Province
Western Region
Central Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (System performance envelopes, Integration with IAMD networks, Local content and offset commitments, Lifecycle cost and MRO footprint, Delivery timelines and program risk, Technology transfer depth, Upgrade roadmap and scalability, Pricing and financing models)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
RTX (Raytheon)
Northrop Grumman
BAE Systems
Leonardo
Thales
Rheinmetall
Saab
ASELSAN
Hanwha Defense
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Elbit Systems
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
MBDA
Lockheed Martin
L3Harris Technologies
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service and availability expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


