Market Overview
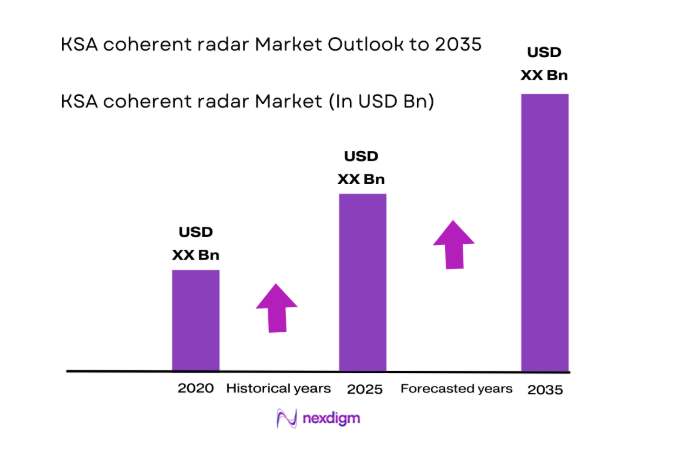
The KSA coherent radar market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained defense modernization priorities and ongoing capability enhancement programs. This level indicates steady procurement activity aligned with national security objectives and layered airspace protection needs. The market is characterized by a growing installed footprint across strategic locations supporting surveillance and early warning missions. Investment emphasis continues to favor advanced coherent architectures integrated within networked command environments. Deployment momentum is supported by long-term modernization roadmaps and phased capability upgrades.
Demand concentrates around Riyadh, Jeddah, and Eastern Province installations due to command infrastructure density and airspace protection priorities. Coastal corridors exhibit elevated deployment density driven by maritime surveillance requirements and border monitoring. Industrial hubs host integrated nodes supporting critical infrastructure protection and airfield security mandates. Ecosystem maturity reflects co-location of integrators, service providers, and logistics bases near operational commands. Policy frameworks emphasize localization, offset participation, and interoperability standards, shaping procurement preferences and deployment architectures.
Market Segmentation
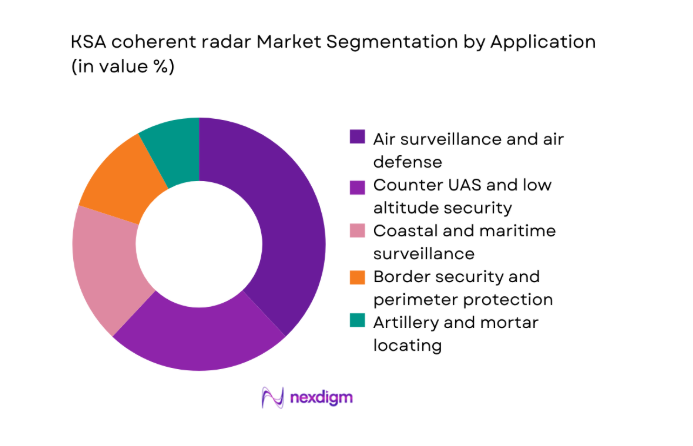
By Application
Air surveillance and air defense systems dominate deployments because layered defense mandates prioritize persistent, coherent detection capabilities. Operational planners emphasize low altitude coverage for countering small aerial threats across urban and critical infrastructure zones. Coastal surveillance applications remain prominent due to maritime domain awareness requirements supporting port security and shipping lanes. Border security applications leverage coherent radars for terrain clutter rejection and persistent monitoring across remote corridors. Artillery and mortar locating capabilities are increasingly embedded within multi mission architectures to consolidate command integration. Interoperability requirements favor applications compatible with networked command environments supporting coordinated responses.
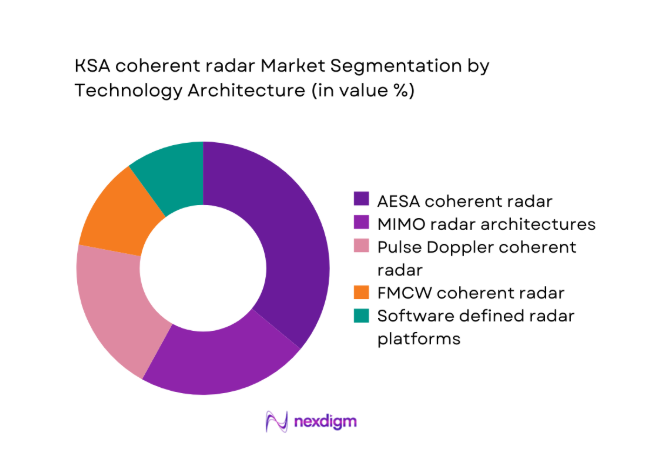
By Technology Architecture
AESA coherent architectures dominate adoption because beam agility and resilience support contested electromagnetic environments. MIMO configurations gain traction where distributed sensing improves target discrimination across complex terrain profiles. Pulse Doppler coherent systems remain prevalent within legacy upgrades supporting incremental modernization pathways. FMCW coherent platforms serve perimeter security and counter UAS missions requiring continuous wave performance. Software defined radar architectures expand rapidly due to modular upgrades and rapid waveform reconfiguration. Buyers prioritize architectures aligned with secure networking, electronic protection, and lifecycle upgradeability mandates.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment features diversified portfolios spanning sensors, integration services, and sustainment frameworks. Positioning emphasizes localization readiness, interoperability compliance, and lifecycle support capabilities. Buyers favor vendors demonstrating resilient supply chains and robust electronic protection competencies.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Thales | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA coherent radar Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of air defense and surveillance networks
Modernization programs accelerated across 2024 with expanded command integration nodes enabling coherent sensor coordination nationwide. Procurement roadmaps emphasized multi mission coverage supporting air defense, counter intrusion, and maritime surveillance missions. Platform refresh cycles prioritized digital beamforming upgrades to enhance detection accuracy across cluttered environments. Operational doctrines incorporated distributed sensing concepts supporting resilient coverage during contested electromagnetic conditions. Training pipelines expanded during 2025 to support sustainment of modernized coherent radar fleets. Lifecycle management frameworks strengthened availability through contracted support and performance based sustainment arrangements. Interoperability requirements encouraged standardized interfaces across command systems supporting coordinated responses. Deployment planning increasingly considered terrain adaptive siting to maximize coherent detection envelopes. Modernization alignment improved readiness metrics across installations through standardized maintenance and spares frameworks. Governance oversight reinforced configuration control and cybersecurity compliance across networked radar architectures.
Rising counter UAS and low altitude threat environment
Low altitude threat prevalence increased during 2024 across critical infrastructure protection zones nationwide. Security planners emphasized persistent surveillance for small targets with challenging signatures and clutter profiles. Coherent radars provided discrimination improvements supporting early warning against unconventional aerial intrusions. Integration with electro optical systems enhanced cueing and tracking continuity across operational environments. Exercises conducted during 2025 validated coordinated response protocols integrating detection with command workflows. Border and perimeter deployments expanded to address emerging drone utilization patterns. Interagency coordination strengthened shared situational awareness across civil aviation and security stakeholders. Networked sensor fusion reduced false alarms and improved classification confidence for operators. Operational readiness benefited from refined detection algorithms and waveform adaptability improvements. Training curricula incorporated counter UAS tactics and coherent radar operational best practices.
Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle support costs
Capital intensive procurement constrained program pacing across multi site deployments during 2024 planning cycles. Sustainment frameworks required specialized spares, calibration equipment, and certified maintenance competencies. Budget prioritization created tradeoffs between capability breadth and deployment density across regions. Lifecycle management complexity increased with networked architectures requiring cybersecurity hardening. Training investments expanded to address specialized operator and maintainer skill requirements. Logistics planning faced lead time variability for sensitive components and secure replacements. Configuration management overhead increased due to frequent software updates and waveform tuning requirements. Contracting cycles lengthened due to compliance reviews and localization mandates. Readiness risks emerged when spares provisioning lagged deployment tempos across remote sites. Financial governance emphasized phased rollouts to manage affordability constraints responsibly.
Technology transfer and localization constraints
Localization policies required structured knowledge transfer frameworks aligned with national industrial objectives. Sensitive technologies faced export control considerations affecting integration timelines and scope. Certification pathways demanded rigorous testing before local assembly authorization approvals. Workforce readiness required sustained training pipelines to achieve independent sustainment capabilities. Supplier onboarding cycles extended due to compliance verification and security vetting requirements. Intellectual property governance frameworks necessitated careful delineation across joint development activities. Quality assurance processes matured gradually across newly accredited local facilities. Program schedules adjusted to accommodate localization milestones and capability ramp up timelines. Tooling and test infrastructure investments required coordination with regulatory approvals processes. Stakeholder alignment improved through phased capability transfer and supervised sustainment operations.
Opportunities
New layered air defense and early warning projects
Planned layered defense initiatives expand coherent radar roles across detection, tracking, and cueing functions. Early warning architectures benefit from distributed sensing integrated with resilient command networks. Program scoping in 2024 emphasized multi mission configurations to maximize operational flexibility. Field trials during 2025 validated performance gains across complex terrain and maritime corridors. Interoperable interfaces enable scalable expansion across future nodes and platforms. Procurement frameworks encourage modular growth supporting incremental coverage densification. Collaborative exercises strengthen operational integration with intercept and response elements. Systems engineering approaches prioritize open architectures enabling technology refresh cycles. Data fusion improvements enhance early warning accuracy across multi sensor environments. Program governance frameworks support staged deployments aligned with readiness milestones.
Expansion of coastal and critical infrastructure surveillance
Coastal surveillance expansion supports port security, shipping lane monitoring, and offshore asset protection. Critical infrastructure protection programs prioritize persistent detection across energy and transport nodes. Coherent radars provide clutter resilient coverage supporting maritime and littoral environments. Integration with maritime command centers enhances coordinated responses to emerging threats. Deployment planning during 2024 prioritized high traffic corridors and sensitive facilities. Networked architectures enable shared situational awareness across security stakeholders. Environmental hardening improvements extend operational availability across harsh coastal conditions. Sustainment partnerships strengthen uptime through regionally distributed service hubs. Training initiatives focus on maritime operating profiles and target classification competencies. Expansion programs create pathways for localized assembly and lifecycle support growth.
Future Outlook
The outlook anticipates continued modernization aligned with layered defense priorities and networked sensing architectures. Policy emphasis on localization will shape supplier strategies and partnership models. Interoperability with multi domain command environments will guide architecture choices. Adoption of software defined capabilities is expected to accelerate upgrade cycles. Demand will remain anchored to airspace security, coastal surveillance, and counter UAS missions.
Major Players
- Thales
- Raytheon
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Leonardo
- Saab
- Hensoldt
- Indra
- Elbit Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Aselsan
- BAE Systems
- Rohde and Schwarz
- Terma
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
Key Target Audience
- Defense procurement authorities and program offices
- Ministry of Defense operational commands
- General Authority for Military Industries regulatory units
- Border Guard and coastal security agencies
- Civil aviation authorities overseeing airspace protection
- Critical infrastructure operators in energy and transport
- Systems integrators and local manufacturing partners
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study defines platform classes, mission profiles, and deployment contexts across airspace, coastal, and border environments. Capability attributes include coherence techniques, network integration, and electronic protection features. Variables incorporate sustainment readiness, localization readiness, and interoperability requirements.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Program pipelines, procurement frameworks, and deployment patterns are mapped across operational theaters. Architecture adoption pathways are analyzed alongside upgrade and modernization cycles. Integration dependencies with command systems and service ecosystems are incorporated.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Operational assumptions are validated through structured consultations with domain practitioners and integrators. Scenario testing examines performance across cluttered environments and contested electromagnetic conditions. Feedback loops refine architecture prioritization and sustainment models.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are synthesized into coherent narratives linking drivers, challenges, and opportunities. Segmentation insights inform deployment and architecture preferences. Outputs align with policy, localization, and interoperability considerations guiding strategic decisions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Delimitation for KSA Coherent Radar Systems, Platform taxonomy by fleet and application, Bottom-up shipment and active-system build, ASP normalization and contract value allocation, Primary interviews with KSA MoD and local integrators, Tender database and offset program analysis, Data triangulation with import data and program milestones)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Operational usage pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and local content framework
- Regulatory and procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of air defense and surveillance networks
Rising counter-UAS and low-altitude threat environment
Border and coastal security reinforcement programs
Localization and military industrialization initiatives
Integration with network-centric warfare architectures - Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle support costs
Technology transfer and localization constraints
Complex integration with legacy C2 systems
Skilled workforce and sustainment capability gaps
Lengthy procurement and qualification cycles - Opportunities
New layered air defense and early warning projects
Expansion of coastal and critical infrastructure surveillance
Local assembly and MRO partnerships under offset programs
Adoption of software-defined and MIMO architectures
Upgrades and mid-life modernization of existing fleets - Trends
Shift toward AESA and digital beamforming
Increased emphasis on networked and distributed sensors
Growing use of counter-UAS optimized radars
Focus on modular and software-upgradable platforms
Higher demand for electronic protection and ECCM features - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Stationary ground-based
Transportable ground-based
Shipborne
Airborne - By Application (in Value %)
Air surveillance and air defense
Counter-UAS and low-altitude security
Coastal and maritime surveillance
Border security and perimeter protection
Artillery and mortar locating - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Pulse-Doppler coherent radar
FMCW coherent radar
AESA coherent radar
MIMO radar architectures
Software-defined radar platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense forces
Homeland security and border guard
Civil aviation authorities
Maritime security agencies
Critical infrastructure protection - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone systems
Networked C2-integrated systems
SATCOM-enabled nodes
Secure IP and fiber-linked systems
Tactical data link enabled systems - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Northern Region
Southern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
Cross Comparison Parameters (Frequency bands, Detection range, Multi-target tracking capacity, Network integration, AESA and MIMO capability, Mobility and deployment time, Lifecycle support footprint, Price per system) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Thales
Raytheon
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
Leonardo
Saab
Hensoldt
Indra
Elbit Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
Aselsan
BAE Systems
Rohde & Schwarz
Terma
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service and sustainment expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


