Market Overview
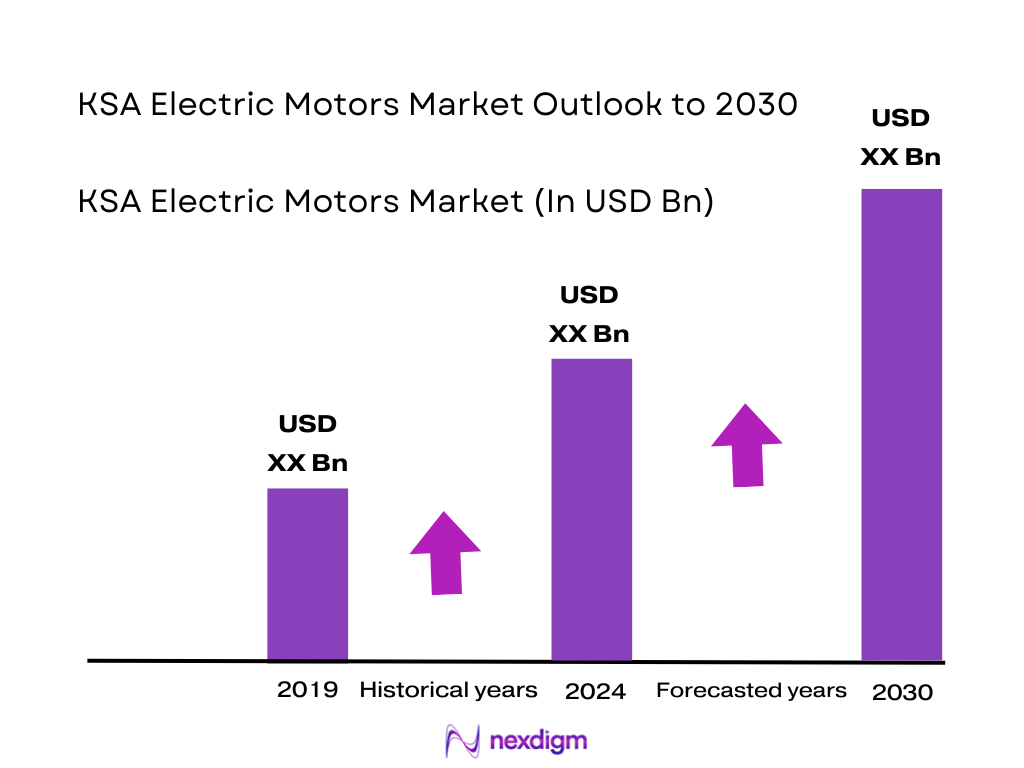
The KSA electric motor market is valued at about USD ~ million, up from roughly USD ~ million in the preceding cycle. The uplift is driven by the expansion of non-oil manufacturing, power, water and HVAC infrastructure under Vision 2030, where non-oil real GDP has been growing faster than the overall economy, supported by private investment in construction, logistics and industrial capacity.
Within the Middle East, Saudi Arabia is the largest national market for electric motors, ahead of the UAE and Qatar, due to its scale in petrochemicals, power generation, water desalination and heavy industry. Demand is concentrated around Riyadh as the administrative and commercial hub, the Eastern Province (Dammam, Jubail, Khobar) as the core oil and gas and petrochemical cluster, and the western corridor (Jeddah, Yanbu, Mecca/Medina) linked to ports, refineries and large infrastructure programs.
Market Segmentation
By Motor Type
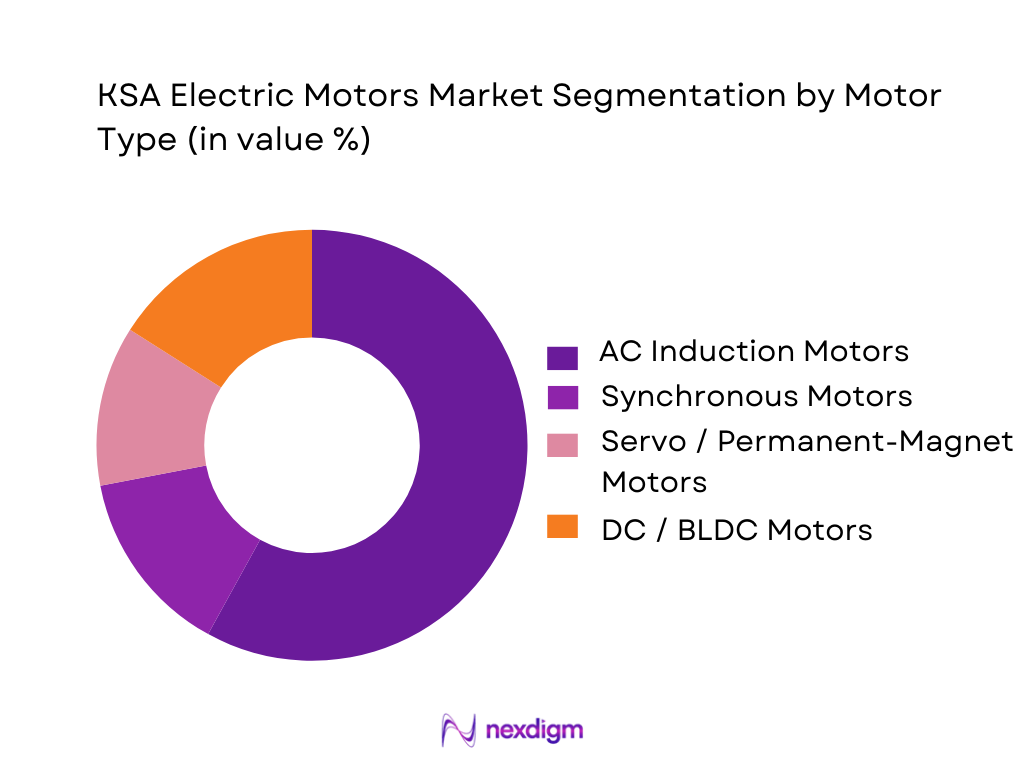
The KSA Electric Motors Market is segmented into AC Induction Motors, Synchronous Motors, Servo/Permanent-Magnet Motors and DC/BLDC Motors. AC Induction Motors currently dominate the motor type mix in KSA, underpinned by their entrenched use across pumps, compressors, fans and general-purpose drives in industrial machinery, oil and gas, and water & utilities applications. Regional analysis indicates that industrial machinery and HVAC are the leading applications for electric motors in the Middle East, patterns that closely mirror Saudi Arabia’s use case structure. Standard frame IE2–IE3 induction machines are also widely available through local distributors, making them the default choice for retrofit and brownfield projects where reliability, ruggedness and compatibility with existing switchgear matter more than high-end control features.
 By End-Use Industry
By End-Use Industry
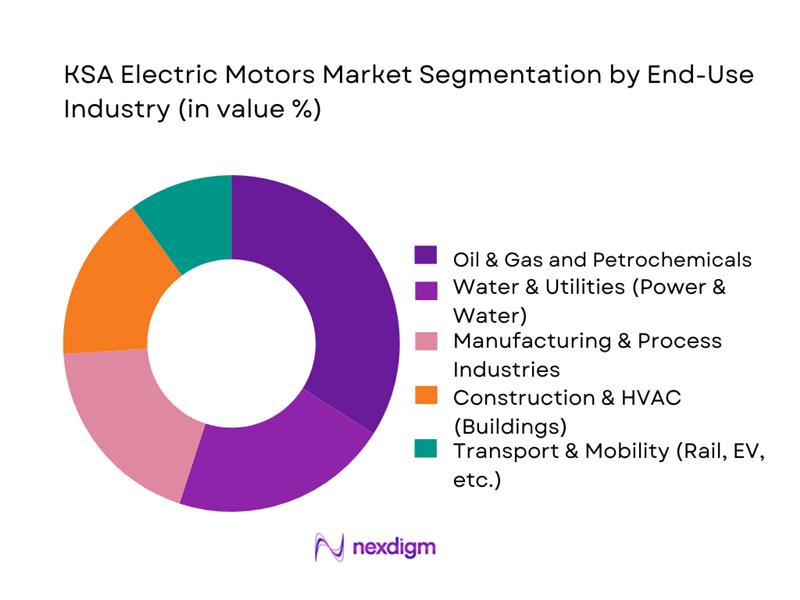
By End-Use Industry, the KSA Electric Motors Market is segmented into Oil & Gas and Petrochemicals, Water & Utilities, Manufacturing & Process Industries, Construction & HVAC, and Transport & Mobility. Oil & Gas and Petrochemicals hold the leading share, reflecting the presence of world-scale complexes in Jubail and Yanbu and integrated value chains anchored by SABIC and Aramco. Jubail alone hosts more than 170 industrial enterprises and is positioned as one of the world’s largest petrochemical hubs, driving intense demand for motors in rotating equipment (pumps, compressors, extruders). High-duty motors are also embedded in crude handling, gas processing, LNG, and refinery utilities, while petrochemicals export growth and expansions under the National Industrial Development and Logistics Program (NIDLP) sustain a steady replacement cycle and upgrades to higher-efficiency IE3/IE4 platforms.
Competitive Landscape
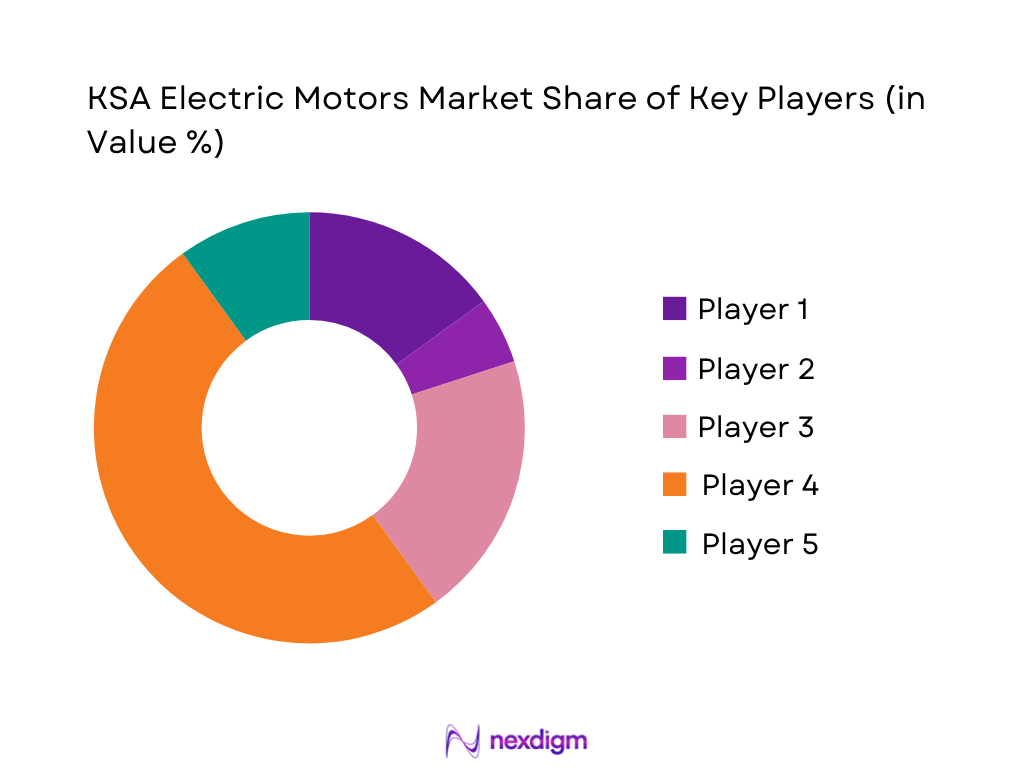
The KSA Electric Motors Market is characterized by a hybrid structure: global OEMs dominate the high-value medium- and high-voltage segment, while regional specialists and distributors serve low-voltage and replacement demand. ABB, Siemens, WEG, TECO Middle East and Nidec (via Leroy-Somer) maintain strong visibility through regional offices, local assembly/repair centers and distribution networks. ABB operates a manufacturing facility in Dammam producing motors among other equipment, WEG opened an office in Riyadh in 2024 to deepen its Saudi presence, TECO Middle East runs the region’s first medium- and high-voltage induction motor plant, while Siemens and Nidec are embedded across power, industrial and backup-power projects through partners and EPCs.
| Company | Establishment Year (Global) | Global HQ City/Country | KSA Presence Model (Channel & Footprint) | Key Motor Portfolio in KSA | Core End-Use Focus in KSA | Local Service / Manufacturing Footprint | Differentiating Edge in KSA Electric Motors Space |
| ABB | 1988 | Zurich, Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Siemens | 1847 | Munich, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| WEG | 1961 | Jaraguá do Sul, Brazil | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| TECO Middle East | 1956 | Taipei, Taiwan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Nidec (Leroy-Somer) | 1973 | Kyoto, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Electric Motors Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Industrial Electrification
Saudi Arabia’s push to grow its non-oil economy is intensifying electric-motor demand across factories and process plants. Manufacturing value added reached about USD ~ billion in one recent year and USD ~ billion the following year, based on World Bank-derived estimates for the Kingdom’s manufacturing value added. Total non-oil output at constant prices has been quoted at around USD ~ billion, with non-government investment in non-oil sectors at roughly USD ~ billion, underscoring a rapidly expanding industrial base that depends on LV/MV motors, pumps and fans for process automation, utilities and material handling. Concurrently, electricity consumption climbed to around 327,000 GWh, up from about 309,500 GWh a year earlier, highlighting growing electrical load in industry and infrastructure that structurally pulls in high-efficiency motors and drive packages.
Desalination Capacity Build-Out
Saudi Arabia is now the world’s largest producer of desalinated water, and each plant is an intensive user of large pumps and MV motors for intake, high-pressure RO trains and distribution. The Saline Water Conversion Corporation (SWCC) reports daily desalinated water production capacity of over 11.5 million m³, up from around 5.9–6.6 million m³ per day earlier in the decade, reflecting a steep ramp-up in electrically driven desalination assets.A US government commercial brief notes that SWCC operates about 30 desalination plants, with plans to add 5 more and an approved desalination budget of roughly USD ~ billion, while the National Water Company earmarked over USD ~ billion for water and wastewater projects in a single budget cycle. This expanding, motor-heavy desalination and water-treatment backbone structurally increases installed bases of corrosion-resistant, high-efficiency motors across coastal and inland sites.
Challenges
IE3+ Compliance Cost
While efficiency mandates support long-term savings, the upfront burden of moving entire installed bases to IE3+ motors and drive-based systems is significant for Saudi industrial users. With industrial energy intensity measured at 228 BoE per million SAR compared to 153 in buildings, regulators logically focus on factories as priority decarbonization targets, but this also concentrates compliance costs in the very sectors driving diversification. Small and mid-sized factories—among the 7,741 plants employing over 1 million workers—must plan for large-scale replacement of legacy IE1/IE2 motors across pumps, compressors and conveyors. IMF Article IV assessments note that Saudi Arabia has been front-loading capital spending to support non-oil growth, which, while positive macro-economically, tightens internal capex envelopes at plant level and makes timing of IE3+ upgrades more complex when firms are already investing in new lines and giga-project orders.
Skilled Technician Gap
The KSA electric-motor ecosystem depends heavily on well-trained technicians for installation, commissioning and condition-based maintenance, yet technical human capital is still catching up with industrial expansion. The Technical and Vocational Training Corporation (TVTC) reports 53,810 trainees in habilitation and diploma programs and about 246,883 enrolled in broader training streams, illustrating a scaling system but one that must serve an industrial workforce above 1 million across 7,741 factories plus over 39,000 new workers hired in just one recent year of factory start-ups. World Bank data show youth unemployment in Saudi Arabia remains in double digits, while IMF Article IV documents stress that labor-market reform is ongoing despite unemployment reaching historic lows overall. This combination of a fast-growing industrial base, a still-maturing vocational pipeline and pockets of youth unemployment underlines structural shortages of experienced motor, drives and automation technicians, especially outside Riyadh and the Eastern Province.
Opportunities
Vision-Aligned Localization
Vision 2030 explicitly positions industry, mining, and advanced manufacturing as growth pillars, creating a policy tailwind for localization of electric-motor manufacturing, assembly and repair. Official national accounts show nominal GDP at around SAR ~ billion in one year and SAR ~ billion the next, with real GDP growth of 2.7% in the latter period driven primarily by 6.0% growth in non-oil activities and 3.3% in government activities. IMF Article IV reports and Saudi government communiqués highlight robust non-oil growth—non-oil GDP expanding by 3.8–4.5% in recent years—supported by accelerated project implementation and private investment. PIF, with assets of approximately SAR 2.81 trillion, continues to steer capital into strategic sectors, while private-sector industrial city investments have reached roughly SAR 1.9 trillion alongside 1.09 million licensed industrial workers and 1,346 new licenses in a single year. These macro numbers signal substantial scope for domestic motor production, local content programs and joint ventures that substitute imports in key motor ranges and build regional export capacity.
Retrofitting Drives & Motors
The scale of existing electrically driven loads in Saudi Arabia makes retrofits a major structural opportunity for the electric-motors market, even without relying on future forecasts. GASTAT data show total electricity consumption of about 327,000 GWh, up from 309,500 GWh a year earlier, while electricity transmitted to the grid reached nearly 380,900 GWh. Industrial energy consumption intensity sits at 228 BoE per million SAR, significantly higher than buildings and transport, confirming that industrial motors, pumps and compressors are prime candidates for efficiency upgrades.Desalination capacity exceeding 11.5 million m³/day, operated through dozens of plants, adds a further layer of large-frame pump motors that can benefit from high-efficiency replacements and VFD retrofits. At the same time, non-oil economic activity worth around USD ~ billion and non-government investments near USD ~ billion in a recent year suggest a vast, financed asset base where retrofits can be integrated into planned shutdowns, improving load-factor profiles without requiring new-build projects. Together, these current-day load and investment figures strongly support a long runway for retrofit-driven growth in the KSA electric-motors space.
Future Outlook
Over the next six years, the KSA Electric Motors Market is expected to grow steadily as Vision 2030 moves into its implementation-heavy phase, with industrial diversification, power system reinforcement and water/security infrastructure at the core. Non-oil real GDP expansion above headline growth, combined with sustained capex in manufacturing, logistics, tourism, data centers and EV-adjacent ecosystems, will keep underlying demand for electric motors on an upward trajectory. At the same time, policy pressure on energy efficiency and localization will gradually shift the mix toward IE3/IE4 motors and locally assembled medium-voltage machines, strengthening the role of regional hubs like Dammam, Jubail and Riyadh in supply and service.
Given 4% long-term annual growth outlook for Saudi electric motors and the broader regional push toward electrification, a working planning assumption of around 3.8% CAGR between 2024 and 2030 appears reasonable for base-case scenarios, with upside in years of faster project awards or major new industrial clusters reaching commissioning.
Major Players
- ABB
- Siemens
- WEG
- TECO Middle East
- Nidec
- Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
- Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems
- Regal Rexnord
- Emerson Electric
- CG Power & Industrial Solutions
- Brook Crompton
- Lafert Group
- VEM Motors
- Siemens Energy
Key Target Audience
- Industrial project developers and EPC contractors
- Oil & gas and petrochemical operators
- Power generation and transmission utilities
- Water and wastewater utilities and authorities
- OEMs and system integrators for pumps, compressors, HVAC and process equipment packages
- Large industrial end-users in mining, steel, cement and manufacturing clusters
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map covering all major stakeholders in the KSA Electric Motors Market, including OEMs, distributors, EPCs, utilities and industrial end-users. Extensive desk research is conducted using secondary and proprietary databases, alongside national statistics (GASTAT, IMF, World Bank) and Vision 2030 documentation, to capture macro- and sector-level indicators. The objective is to define critical variables such as installed motor base, replacement cycles, efficiency-class penetration, and sectoral capex pipelines.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data for the KSA Electric Motors Market is compiled from multi-client reports and triangulated with import/export data and OEM disclosures. We analyze penetration by motor type, voltage class and end-use industry, cross-referenced with indicators such as industrial output, power generation capacity additions and desalination capacity. A bottom-up estimation of revenues is built by mapping installed capacities, average motor prices and replacement/expansion demand per sector.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses on growth rates, mix shifts (e.g., IE2 to IE3/IE4), localization and sectoral demand are validated through structured interviews and CATI discussions with stakeholders across the value chain. This includes regional heads of motor OEMs, channel partners, EPC project directors, maintenance managers at large plants, and sourcing leaders at utilities. Their feedback on order pipelines, technology preferences (e.g., VFD integration, high-efficiency motors), and pain points (lead times, after-sales support) is used to refine model assumptions and validate both top-down and bottom-up estimates.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase combines quantitative models with qualitative insights to produce a cohesive view of the KSA Electric Motors Market. Direct engagements with electric motor manufacturers and distributors help segment revenues by motor type, voltage range, and end-use clusters, and clarify margins and channel structures. These interactions also verify adoption patterns of premium-efficiency motors, digital monitoring solutions and localized assembly. The outcome is a validated dataset and narrative covering current size (including 2024 market value), forecast CAGR for 2024–2030, competitive positioning, and scenario-based outlook tailored to investors and industry decision-makers.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Assumptions, Electric Motor Classification Framework, Motor Power Ratings & Efficiency Class Definitions, Market Sizing & Forecasting Approach, VFD Penetration Assessment, Consolidated Research Approach, Supply-Side Validation through OEM/Distributor Interviews, Primary Respondent Mix, Limitations & Forward-Looking Constructs)
- Definition & Scope
- Industry Genesis & Technology Evolution
- Timeline of Major Global & Regional Entrants
- Electrical Equipment Investment Cycle
- Supply Chain & Value Chain Structure
- Growth Drivers
Industrial Electrification
Desalination Capacity Build-Out
Smart Factory Adoption
Mega-Project Construction Pipelines
Energy Efficiency Mandates - Market Challenges
IE3+ Compliance Cost
Skilled Technician Gap
Long Lead Times for MV Motors
Import Dependency for Core Materials
Post-Sales Service Deficit - Opportunities
Vision-Aligned Localization
Retrofitting Drives & Motors
Explosion-Proof O&G Motors
E-Mobility Motors
Predictive Maintenance Platforms - Trends
Shift to IE4–IE5 Motors
Servo & PM Motor Penetration
HV Motor Digital Twins
IIoT-Enabled Motor Condition Monitoring
Vertical Motor Demand for Desalination - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019-2024
- By Motor Type (in Value %)
AC Induction Motors
Synchronous Motors
Servo Motors
PM Motors
Brushed/Brushless DC Motors - By Power Rating (in Value %)
Fractional HP Motors
Low-Voltage Motors
Medium-Voltage Motors
High-Power >500 kW Motors - By Application (in Value %)
HVAC Systems
Industrial Pumps & Compressors
Oil & Gas Rotating Equipment
Water Desalination Plants
Elevators/Escalators
Automotive & EV Systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Oil & Gas, Petrochemicals
Utilities
Water & Wastewater
Construction
Manufacturing/Automation
Transportation & Mobility - By Efficiency Class (in Value %)
IE1 Standard
IE2 High Efficiency
IE3 Premium
IE4 Super Premium
IE5 Ultra-Premium - By Distribution Model (in Value %)
Direct OEM Sales
EPC Contractors
System Integrators
Industrial Distributors
Online Technical Channels - By Region (in Value %)
Central
Western
Eastern
Northern
Southern
- Market Share of Major Players
- Cross-Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Motor Portfolio Depth, Power Rating Breadth, Efficiency Class Coverage IE1–IE5, After-Sales Service Infrastructure, Localization/Assembly Capability, Installed Base in O&G/Utilities, Distributor Network Strength)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
ABB
Siemens
WEG
TECO Middle East
Nidec Leroy-Somer
Toshiba Gulf
Hyundai Electric
Regal Rexnord
Emerson
Brook Crompton
CG Power
Marathon Motors
Baldor Electric
Lafert Motors
- Industrial User Demand Behaviors
- Budget Allocation Patterns
- Compliance & Certification Requirements
- Pain Points & Motors Failure Modes
- Decision-Making Matrix
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025-2030