Market Overview
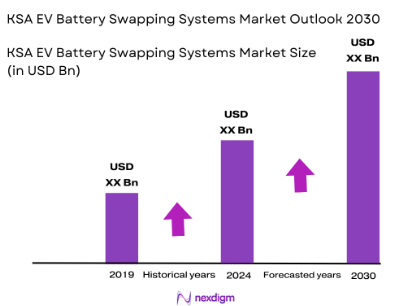
The EV battery swapping systems market in Saudi Arabia is valued at USD ~ million, driven by the growing push towards electrifying transportation as part of the nation’s Vision 2030. This initiative seeks to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable energy sources. The Saudi government is investing heavily in EV infrastructure, including battery swapping stations, to facilitate faster adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). The market is also supported by strategic collaborations between local government bodies and private stakeholders to build a robust charging infrastructure. The rapid growth of the Saudi EV market, which is expected to see over 1 million EVs on the roads by 2030, will significantly drive the demand for battery swapping systems.
Saudi Arabia’s major cities, particularly Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dammam, are driving the adoption of EV battery swapping systems. Riyadh, as the capital city, leads the country’s EV infrastructure development, supported by government-backed initiatives. The city’s urban planning and growing focus on reducing emissions through sustainable mobility contribute significantly to the market’s expansion. Jeddah, located on the Red Sea coast, is also a key player in the adoption of EVs, as the city is focusing on sustainability within its transportation systems. Dammam, being the industrial hub, also has increased investments in EV infrastructure, catering to the growing demand for commercial EVs and fleets.
Market Segmentation
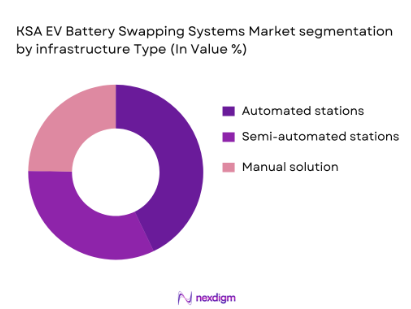
By Infrastructure Type
The KSA EV battery swapping market is segmented based on infrastructure type into automated, semi-automated, and manual battery swapping stations. The automated battery swapping stations currently dominate the market, accounting for the majority of the market share due to their higher efficiency, faster turnaround times, and scalability. These automated systems are designed to cater to both passenger and commercial EVs, providing quick battery replacement that reduces the waiting time compared to traditional charging stations. As more automated systems are deployed across major cities, their dominance is expected to grow, facilitating large-scale EV adoption.
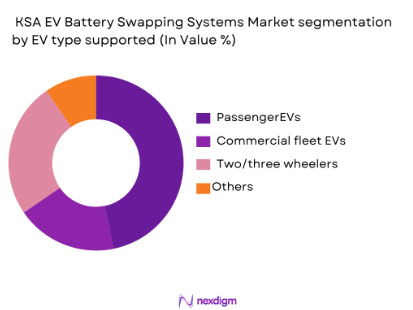
By EV Type Supported
The market is segmented by the type of EVs supported, including passenger EVs, commercial fleet EVs, two/three-wheelers, and others (buses and logistics vehicles). The passenger EV segment holds the dominant market share due to the increasing adoption of electric vehicles for private use, supported by government incentives, lower operational costs, and environmental benefits. As EVs become more mainstream in urban areas, the demand for battery swapping stations tailored to passenger vehicles is expected to rise significantly.
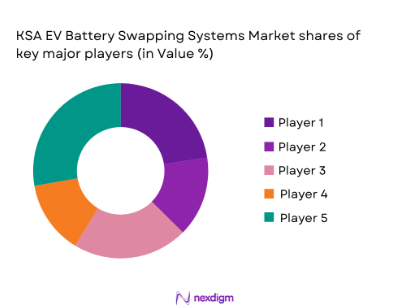
Competitive Landscape
The KSA EV battery swapping market is characterized by a few key players, both local and international, who are driving innovation and infrastructure development in the country. The market is dominated by a few large players, including NIO, Ample Inc., and SUN Mobility, which have partnered with Saudi entities to establish battery swapping stations. Local players such as Electromin, a subsidiary of Petromin, are also emerging as strong competitors, deploying EV infrastructure and offering battery-as-a-service (BaaS) solutions. The presence of these global and local players highlights the competitive nature of the market and the significant investments being made to support Saudi Arabia’s EV and sustainability goals.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Key Offerings | Market Focus | Technology Differentiator |
| NIO Inc. | 2014 | Shanghai, China | – | – | – |
| Ample Inc. | 2014 | San Francisco, USA | – | – | – |
| SUN Mobility | 2016 | Bengaluru, India | – | – | – |
| Electromin (Petromin Group) | 2019 | Jeddah, KSA | – | – | – |
| Blink Charging | 2009 | Miami, USA | – | – | – |
KSA EV Battery Swapping Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Vision 2030 Sustainable Mobility Mandates
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 sets a clear agenda for reducing carbon emissions and fostering sustainable energy solutions, including the promotion of electric vehicles (EVs) and associated infrastructure like battery swapping systems. The government’s emphasis on creating a greener economy aligns with ambitious targets to increase EV adoption in both passenger and commercial fleets. For instance, Saudi Arabia aims to achieve 30% EVs in public transport by 2030, which will undoubtedly drive the need for robust EV infrastructure. Additionally, the government is supporting initiatives like NEOM, which is designed to be a hub for clean and sustainable energy solutions, further enhancing the adoption of green mobility.
Rapid EV Fleet Electrification Initiatives
The electrification of Saudi Arabia’s commercial fleet, including logistics and public transport vehicles, is rapidly progressing, fueled by both national and corporate investments. In 2024, several government entities and private firms are committing to electrifying their fleets. The Saudi Arabian Public Transport Company (SAPTCO), for example, has already launched pilot EV buses, while logistics giants like Aramex and DHL are making strides in introducing EVs into their fleets. The shift toward electrification is a critical driver for the adoption of EV battery swapping systems, as these fleets require quick, convenient, and scalable charging and battery replacement options.
Market Challenges
High Capital Intensity of Swap Stations
Building and maintaining EV battery swapping stations requires significant capital investment, which is a major challenge for widespread deployment. In 2023, the cost to build a single automated swapping station in Saudi Arabia was estimated to be around USD 1.2 million. Given the scale of infrastructure needed, these costs could deter smaller players from entering the market. The need for high-capacity battery banks, automated robotic systems, and integration with grid power and renewable energy sources all contribute to high initial and operational costs.
Interoperability & Standard Protocol Gaps
One of the biggest barriers to the successful deployment of battery swapping systems in Saudi Arabia is the lack of interoperability between different EV models and swapping stations. Each EV manufacturer uses proprietary battery technology, and as of 2024, there is no universal standard for battery size or charging protocols across all vehicles. This fragmentation poses a challenge for infrastructure providers who must create compatible systems for various car models, hindering the scalability and efficiency of battery swapping operations.
Opportunities
BaaS & Subscription‑Based Revenue Streams
Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS) models offer significant growth potential for the Saudi EV battery swapping systems market. Under the BaaS model, consumers and fleet operators can subscribe to a service where they only pay for battery swaps, reducing the cost of owning an EV. This model allows for lower upfront costs and a more predictable total cost of ownership, which is expected to boost the adoption of EVs in Saudi Arabia. As of 2023, companies like Electromin have already implemented BaaS for commercial fleets, with plans to expand into passenger vehicles in the coming years.
Integration with Renewable Energy & Storage Assets
Integrating EV battery swapping stations with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, presents a compelling opportunity for Saudi Arabia. The country’s abundant sunlight makes it an ideal candidate for solar-powered EV infrastructure. By using solar panels to power swapping stations and store excess energy in batteries, Saudi Arabia can reduce the environmental impact of its EV fleet and provide a sustainable, cost-effective solution to energy demands. Several projects are already underway to integrate renewable energy with EV infrastructure, significantly improving the economic feasibility of battery swapping networks.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Saudi EV battery swapping market is poised for rapid growth, driven by continued government support under Vision 2030, increasing electrification of commercial fleets, and further advancements in battery technology. Saudi Arabia is investing heavily in smart city developments, such as NEOM, where sustainable transport solutions, including EVs and battery swapping, will be integral. As infrastructure matures and cross-border collaboration with GCC nations expands, the market for EV battery swapping systems in Saudi Arabia is expected to see exponential growth.
Major Players in the KSA EV Battery Swapping Systems Market
- NIO Inc.
- Ample Inc.
- SUN Mobility
- Electromin (Petromin Group)
- Blink Charging
- Aulton Technology Co. Ltd.
- Gogoro Inc.
- Better Place
- EVgo Services LLC
- TotalEnergies
- ChargePoint
- Shell Recharge
- GlobalMed
- Enel X
- Kibbutz Yavneh EV Solutions
Key Target Audience
- Government Agencies (e.g., Ministry of Energy, Saudi Arabian Standards Organization)
- Automotive OEMs (Electric Vehicle Manufacturers)
- Electric Mobility Startups
- Energy Providers & Utilities (e.g., Saudi Electricity Company)
- Public Transport Authorities (e.g., Saudi Public Transport Company)
- Commercial Fleet Operators
- Private Investors and Venture Capital Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO))
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The first step involves mapping all key stakeholders in the EV battery swapping value chain, including EV manufacturers, energy providers, and technology vendors. This is done through extensive desk research, utilizing proprietary and public industry databases, with the objective of identifying key variables affecting market dynamics such as pricing, adoption rates, and infrastructure development.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data on EV adoption rates, infrastructure deployment, and government policies will be analyzed. Key factors such as station density, capacity, service usage, and regional demand will be assessed to understand the historical evolution and growth trajectories of the market.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses related to market growth drivers, barriers, and technological innovations will be validated through consultations with industry experts, including OEM representatives, EV infrastructure developers, and government officials involved in smart city planning. These insights will be instrumental in refining market models.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Finally, the data will be synthesized, and key findings will be presented through a comprehensive analysis of the KSA EV battery swapping systems market. This includes both quantitative data and qualitative insights, ensuring a complete picture of the market landscape for strategic decision-making.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Data Collection Framework, Primary & Secondary Research Protocols, Forecasting & Scenario Analysis, Forecast methodology bottom‑up revenue build, station deployment modeling) Quality & bias mitigation)
- Definition and Scope of EV Battery Swapping Systems
- Genesis of Battery Swapping Systems in KSA
- Timeline of Major Deployments and Policy Milestones
- Business Cycle and Operational Models
- Supply Chain, Energy Integration & Value Chain
- Standards, Safety & Interoperability Requirements
- Growth Drivers
Vision 2030 Sustainable Mobility Mandates
Rapid EV Fleet Electrification Initiatives
Infrastructure Investments (Charging, Grid & Swap Nodes)
Battery Technology Advancements & Standardization - Market Challenges
High Capital Intensity of Swap Stations
Interoperability & Standard Protocol Gaps
Consumer & Fleet Adoption Barriers - Opportunities
BaaS & Subscription‑Based Revenue Streams
Integration with Renewable Energy & Storage Assets
Smart City & Logistics Fleet Swap Hubs
Cross‑Border Swap Networks (GCC Connectivity) - Trends
Modular, Automated Swap System Adoption
Fleet‑First Deployment Strategies
Digital Wallet & Payment Integration
Data‑Driven Predictive Maintenance & Analytics - Regulatory & Standards Framework
EV Policy, Decarbonization Mandates
Interoperability & Safety Protocols
Utility Tariff & Grid Access Rules
Public‑Private Partnership Guidelines - Stakeholder Ecosystem
- SWOT Analysis – KSA Swap Systems Market
- Porter’s Five Forces – Competitive Pressure
- Competitive Intensity & Innovation Ecosystem
- Market Value, 2019-2024
- Installed Swap Stations & Infrastructure Count, 2019-2024
- Deployment by Swap Station Capacity, 2019-2024
- Average Revenue per Swap Station, 2019-2024
- Revenue by Business Model, 2019-2024
- By Infrastructure Type (In Value %)
Modular Automated Swap Stations
Robotic & Mechanized Swap Systems
Semi‑Automated Swapping Units
Portable Swap Modules
Station Power Storage & Grid Buffer Systems - By EV Type Supported (In Value %)
Passenger EV Swap
Commercial Fleet EV Swap
Two/Three‑Wheeler Swap Units
Public Transit (Bus) Swap Infrastructure
Logistics/Last‑Mile Fleet Swap Solutions - By End User (In Value %)
Individual EV Owners
Commercial Fleet Operators
Municipal & Public Transport Entities
Retail and Shared Mobility Providers
Automotive OEM Strategic Deployments - By Deployment Model (In Value %)
Battery‑as‑a‑Service (BaaS)
Fleet‑Managed Swap Networks
Utility‑Integrated Smart Grid Swap Hubs
Hybrid Swap/Charge Integrated Hubs - By Geography within KSA (In Value %)
Riyadh Metro & Urban Corridors
Jeddah & Western Economic Zones
NEOM & Smart City Projects
Secondary Cities & Highway Networks
- Market Share by Value & Swap Infrastructure Count
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Swap Station Deployment Scale & Geographic Footprint, Partnerships (OEMs, Utilities, Government, BaaS & Revenue Model Diversity, Data & Network Analytics Platform Strength, Maintenance & Service Support Infrastructure)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players (Regional & Global)
- Pricing & BaaS Subscription Benchmarking
- Detailed Company Profiles
NIO Inc.
SUN Mobility
Aulton Technology Co. Ltd.
Ample Inc.
Gogoro Inc.
Better Place
EVgo Services LLC
Blink Charging Co.
Battery Swap Technologies
Greenway Infrastructure
ChargePoint, Inc.
TotalEnergies SE
Shell Recharge Solutions
EDF Renewables
Electromin (Local Infrastructure Partner)
- Adoption Demand (Private Owners vs Fleet) (Usage Patterns)
- Purchasing & Subscription Behavior (BaaS vs Ownership)
- Technology Needs & Compatibility Requirements
- Decision‑Making Units & Buyer Profiles (Procurement Dynamics)
- Future Market Value (Swap Stations, BaaS Revenues, Services), 2026-2030
- Revenue by Business Model Scenario (BaaS, Per‑Swap Fees), 2026-2030
- Forecast by End User (Private, Fleet, Public Transport), 2026-2030
Infrastructure Evolution & Revenue Contribution, 2026-2030


