Market Overview
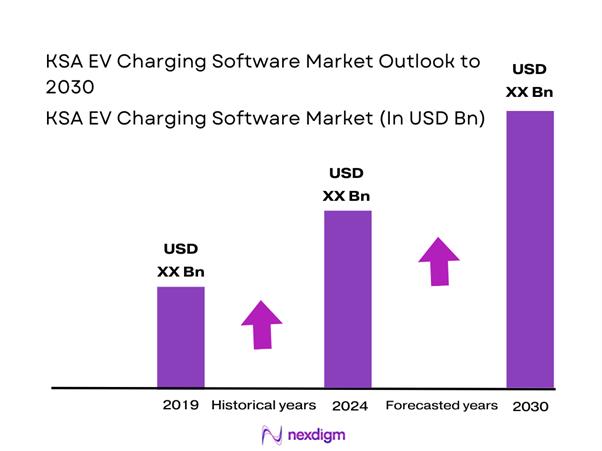
The KSA EV Charging Software market is valued at USD ~ billion in 2024, driven by strong growth in electric vehicle adoption, government policies promoting sustainable transport, and advancements in smart charging technologies. The market serves a growing need for seamless and efficient electric vehicle charging solutions across residential, commercial, and public infrastructure sectors. EV charging software plays a pivotal role in optimizing charging station management, energy consumption, and user experience, driving demand for innovative and scalable solutions.
Saudi Arabia’s dominant regions for EV charging software adoption are the Central and Western regions, where urbanization and government incentives for electric vehicles are most pronounced. These regions are home to key urban centers such as Riyadh and Jeddah, which have seen increased investments in charging infrastructure and electric vehicle adoption. Additionally, global leaders in EV charging, including European and American companies, influence the supply of technology and solutions in the market due to their advanced platforms and global expertise.
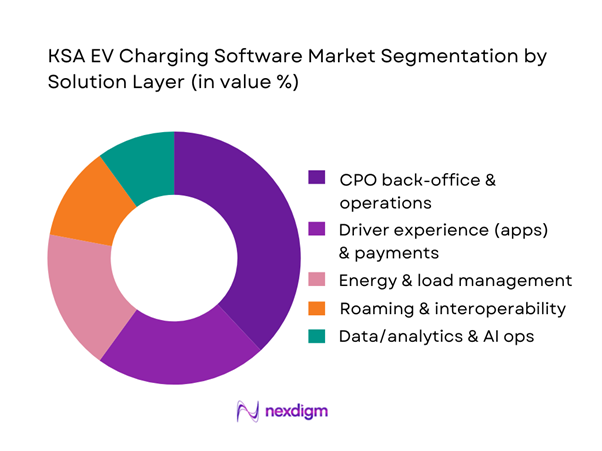
Market Segmentation
By Solution Layer
The KSA EV charging software market is segmented by solution layer into CPO back-office & operations, driver experience (eMSP) & payments, roaming/interoperability, energy & load management, and data/analytics. CPO back-office & operations dominates because Saudi deployments are still in “scale-up + reliability hardening” mode: operators prioritize uptime, remote diagnostics, session success rate, and SLA reporting before advanced monetization layers fully mature. The harsh operating environment and corridor-distance realities raise the cost of downtime, pushing CPOs to invest in NOC tooling, automated ticketing, proactive alerts, and device lifecycle management (including firmware workflows). Additionally, tender-led rollouts typically specify integration needs (payments, reporting, OCPP compliance), making a strong operational core the default budget winner.
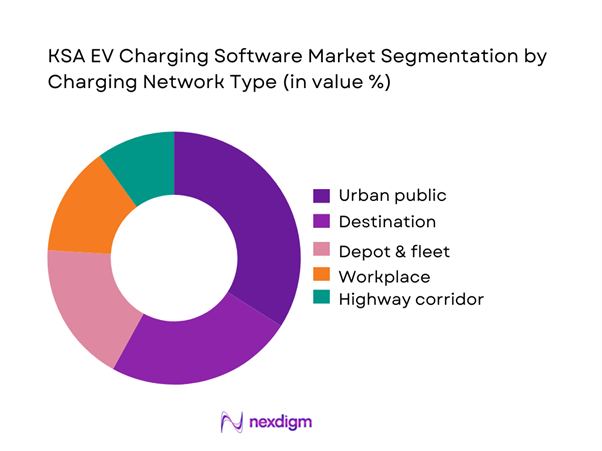
By Charging Network Type
The market is segmented into urban public, destination, workplace, and depot/fleet, alongside highway corridor deployments. Urban public leads because it is the fastest way to increase visible coverage in major cities (municipal sites, retail parking, mixed-use developments), and it forces immediate software requirements: multi-tariff pricing, idle fee policies, parking validation, consumer payments, customer care workflows, and incident management. Urban public sites also create the highest variability in demand by time-of-day, which increases the value of tariff engines and utilization analytics. As the number of stations expands from a low base and operators compete for prime sites, the ability to optimize utilization and reduce churn through a reliable driver experience becomes a key differentiator.
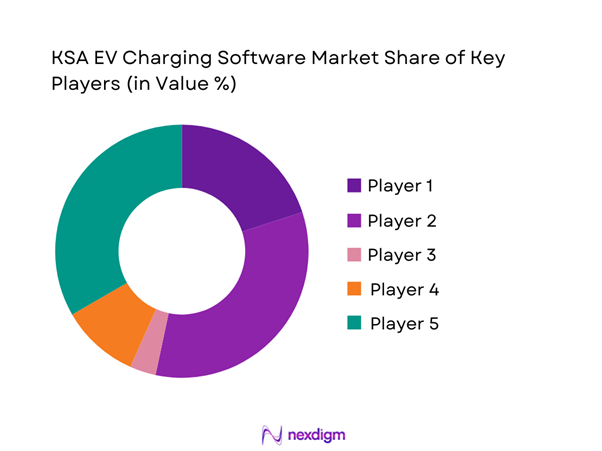
Competitive Landscape
The KSA EV Charging Software market is dominated by a few major players, including ChargePoint and global or regional brands like ABB, Siemens, and Schneider Electric. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Establishment Year | HQ | KSA relevance lever | Platform orientation | Interoperability stance | Payments readiness | Enterprise integrations | Typical buyer |
| ChargePoint | 2007 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Siemens | 1847 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ABB | 1988 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Schneider Electric | 1836 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Driivz | 2013 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA EV Charging Software Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Government Incentives
Government incentives have played a significant role in accelerating the growth of the EV charging software market. These incentives come in various forms such as tax credits, rebates, grants, and subsidies to support infrastructure development. By making investments in EV infrastructure more attractive, governments are driving adoption of EV charging networks. Policies supporting energy efficiency, carbon reduction goals, and renewable energy are also pushing the transition toward electric mobility, creating a more favorable market environment for EV charging software solutions. Government support provides stability and confidence, ensuring that investments in EV infrastructure are more financially viable for operators.
Increasing Electric Vehicle Adoption
As electric vehicle adoption increases globally, the demand for efficient and scalable charging infrastructure grows, boosting the need for advanced charging software. Rising consumer awareness about environmental sustainability, coupled with improved EV models, has led to a steady increase in EV sales. This trend is further reinforced by government regulations, urban development plans, and corporate sustainability goals. A growing number of electric vehicles on the roads creates the necessity for more charging stations, ultimately driving the demand for sophisticated software solutions that can manage operations, billing, customer experience, and connectivity to support these infrastructures efficiently.
Challenges
High Initial Costs
The high initial costs of setting up EV charging infrastructure represent a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Installing charging stations requires substantial capital investment in hardware, software, and grid upgrades, with additional operational costs related to maintenance, power management, and regulatory compliance. These upfront costs can be prohibitive for smaller operators or fleet owners, leading to slower market penetration. Although operational costs are expected to decline over time, the initial financial burden remains a key challenge, particularly in regions where subsidies or government support are limited, affecting both operators and customers in adopting electric vehicles.
Lack of Charging Infrastructure
One of the primary challenges in the EV charging software market is the inadequate availability of charging infrastructure, especially in emerging markets or rural areas. Despite growth in major cities, many regions still lack a comprehensive charging network, which hinders electric vehicle adoption. This gap in infrastructure creates uncertainty for EV owners, who may face issues like range anxiety and longer charging times. A fragmented charging network with inconsistent quality and service offerings makes it difficult for drivers to rely on public charging stations. This lack of robust infrastructure also affects the deployment of advanced charging software, limiting its full potential.
Opportunities
Rise in Demand for Smart Charging Solutions
The increasing complexity of electric vehicle charging operations creates a significant opportunity for the development and implementation of smart charging solutions. These solutions include features like dynamic load balancing, real-time energy monitoring, and intelligent billing. As electric vehicle penetration rises, software solutions that enable efficient energy use, optimize charging schedules, and integrate renewable energy sources will become essential. Furthermore, smart charging can help reduce grid strain and improve the overall user experience by providing features such as contactless payments, remote monitoring, and location-based charging recommendations, making it a highly promising area for growth.
Private-Public Partnerships
Private-public partnerships (PPP) offer a tremendous opportunity for the expansion of EV charging infrastructure. Governments are increasingly recognizing the importance of EV adoption and are looking to collaborate with private companies to accelerate the deployment of charging stations. By leveraging private sector expertise and capital, public entities can facilitate faster installation of charging stations, while the private sector benefits from regulatory support and financial incentives. These partnerships enable a more robust and widespread charging network, ensuring a seamless user experience across cities and regions. PPPs are vital for scaling up infrastructure and making EV adoption more accessible to the general public.
Future Outlook
The KSA EV Charging Software market is poised for continued growth as electric vehicle adoption accelerates and the government continues to prioritize green technologies. The future of the market will focus on the integration of smart, scalable solutions capable of supporting an increasing number of users, and partnerships will be key to expanding infrastructure and services.
Major Players
- ChargePoint
- ABB
- Siemens
- Schneider Electric
- EVBox
- Tesla
- Alfen
- Wallbox
- Delta Electronics
- BP Chargemaster
- Electrify America
- Shell Recharge
- Pod Point
- E.ON
- Greenlots
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies (KSA)
- Energy providers
- Automotive manufacturers
- Fleet operators
- Commercial real estate developers
- Public infrastructure developers
- Technology solution providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The key variables identified for the market analysis include government incentives, adoption rates of electric vehicles, charging infrastructure expansion, and technological advancements in software solutions.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market sizing was derived through primary research, including expert interviews and secondary research, focusing on regional demand patterns, government policies, and technology adoption.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validated our market hypotheses with a series of interviews with stakeholders across the electric vehicle and charging ecosystem to ensure our findings align with the broader industry trends.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Our final analysis synthesizes the collected data, providing a comprehensive understanding of the market dynamics, growth drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the KSA EV Charging Software market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- EV Charging Software Usage / Value-Chain / Care-Continuum Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- KSA Industry / Service / Delivery Architecture
- Growth Drivers
Government Incentives
Increasing Electric Vehicle Adoption
Urban Infrastructure Development
Technological Advancements in EV Charging
Investment from Private Sector - Challenges
High Initial Costs
Lack of Charging Infrastructure
Interoperability Issues
Regulatory Hurdles
Consumer Awareness - Opportunities
Rise in Demand for Smart Charging Solutions
Private-Public Partnerships
Integration with Renewable Energy
Expansion of Charging Networks
International Collaborations - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By value, 2019–2024
- By revenue model, 2019–2024
- By customer type, 2019–2024
- By Software business Model (in Value %)
Subsscription-Based
Pay-Per-Use
Freemium Model
Licensing
Other Models - By Technology / Product / Platform Type (in Value %)
Cloud-Based
On-Premise
Hybrid
Mobile Applications
Integrated Charging Solutions - By Deployment / Delivery / Distribution Model (in Value %)
Direct Sales
Channel Partnerships
Subscription Services
Cloud Platforms - By End-Use Industry / Customer Type (in Value %)
Automotive Manufacturers
Energy Providers
Commercial Real Estate
Government/Public Sector
Fleet Operators - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Northern Region
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology Integration, Market Presence, Cost Leadership, Customer Service, Product Differentiation, Partnership Networks, Innovation, Brand Strength, Regulatory Compliance, Scalability)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Detailed profiles of major competitors
ChargePoint
Siemens
ABB
Schneider Electric
Tesla
Blink Charging
EVBox
Tritium
Webasto
Noodoe
Shell Recharge / Greenlots
Electrify America
Ionity
Enel X Way
Driivz
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By value, 2025–2030
- By revenue model, 2025–2030
- By customer type, 2025–2030


