Market Overview
The KSA EV Power Electronics Market is valued at USD ~, reflecting the value of traction inverters, on-board chargers, DC-DC converters, power distribution units, and embedded power semiconductor modules deployed in electric vehicles operating within the country. Market demand is structurally linked to domestic electric vehicle assembly programs, government-backed electrification targets, and charging infrastructure investments. The market’s importance lies in its role as the core enabler of drivetrain efficiency, energy conversion, and vehicle reliability under high-temperature operating conditions, making power electronics a critical subsystem in every electric vehicle platform deployed locally.
Within the country, Riyadh, Jeddah, and the Eastern industrial corridor dominate demand due to their concentration of vehicle registrations, fleet electrification initiatives, and charging infrastructure density. Riyadh leads due to government fleet procurement and early private adoption, while Jeddah benefits from proximity to manufacturing and logistics hubs. Globally, technology leadership influencing the KSA market is driven by suppliers headquartered in Europe, Japan, and East Asia, where advanced semiconductor fabrication, power module packaging, and automotive-grade validation capabilities are concentrated, shaping product specifications used by local OEM and Tier-1 sourcing programs.
Market Segmentation
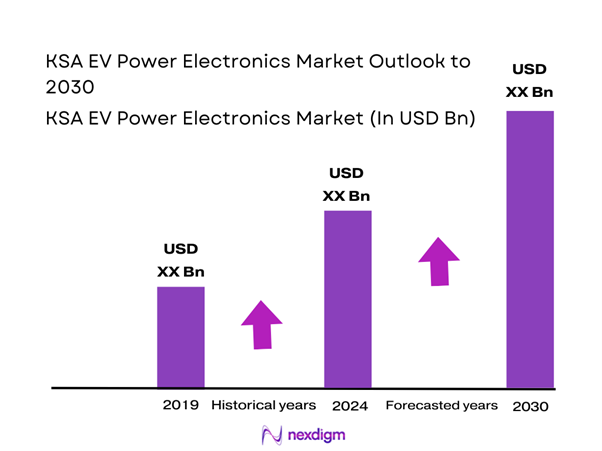
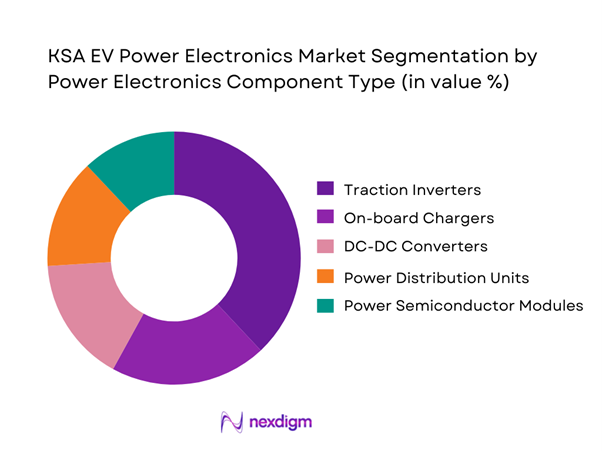
By Power Electronics Component Type
The KSA EV Power Electronics market is segmented by component type into traction inverters, on-board chargers, DC-DC converters, power distribution units, and power semiconductor modules. Traction inverters dominate this segmentation because they represent the highest value and performance-critical element in an electric drivetrain. Every battery electric vehicle requires at least one traction inverter to convert high-voltage DC energy into controlled AC power for propulsion. In the Saudi operating environment, elevated ambient temperatures necessitate higher-specification cooling systems, advanced packaging, and conservative derating, increasing per-unit value. Additionally, local assembly programs emphasize drivetrain localization first, reinforcing inverter demand relative to auxiliary power components.
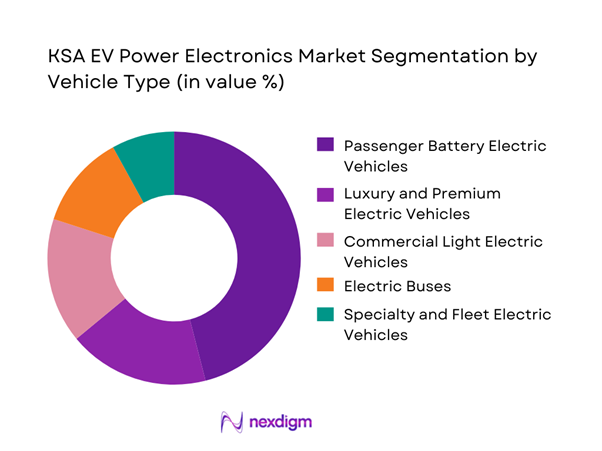
By Vehicle Type
The market is segmented into passenger battery electric vehicles, luxury and premium electric vehicles, commercial light electric vehicles, electric buses, and specialty fleet electric vehicles. Passenger battery electric vehicles dominate due to higher adoption among private consumers, corporate fleets, and government entities focused on urban mobility decarbonization. These vehicles typically use higher-voltage architectures and more sophisticated inverter and charging solutions to meet performance expectations under harsh climatic conditions. The dominance is further reinforced by early-stage fleet conversions in ride-hailing, corporate leasing, and municipal use cases, where passenger EVs are prioritized for predictable duty cycles and centralized charging access.
Competitive Landscape
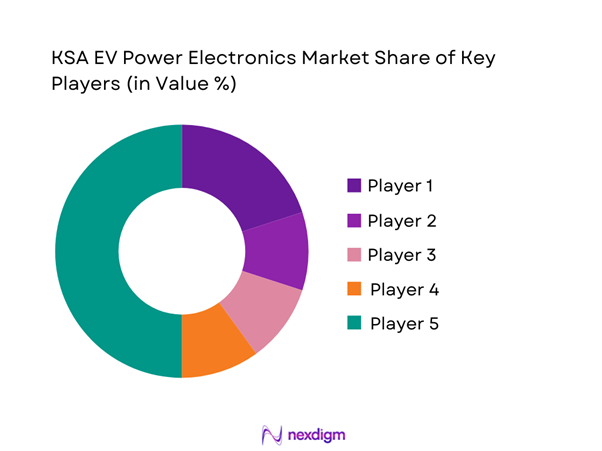
The KSA EV Power Electronics market is dominated by a few major players, including Infineon Technologies and global or regional brands like STMicroelectronics, Bosch Mobility, DENSO, and Valeo. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | KSA Presence Model | EV Power Electronics Focus | Wide-Bandgap Roadmap | Automotive Safety/Quality | Power Module Packaging Strength | Tier-1/OEM Alignment | Thermal/Derating Capability |
| Infineon Technologies | 1999 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| STMicroelectronics | 1987 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Robert Bosch GmbH | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| DENSO | 1949 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Valeo | 1923 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA EV Power Electronics Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Localization of EV Manufacturing
Localization of electric vehicle manufacturing is a critical growth driver for the KSA EV Power Electronics market, as it fundamentally reshapes sourcing, qualification, and supplier engagement models. With domestic EV assembly programs gaining momentum, OEMs increasingly prefer power electronics solutions that can be locally validated, supported, and serviced. This shift reduces dependence on fully imported subsystems and encourages long-term sourcing agreements with suppliers capable of operating within the Kingdom. Localization also expands demand for application engineering, thermal validation, EMC testing, and functional safety alignment, all of which add depth to the power electronics value chain. As suppliers establish local footprints, knowledge transfer improves system optimization for Saudi operating conditions such as high ambient temperatures, long driving cycles, and fast-charging stress. Over time, this strengthens ecosystem maturity and increases recurring demand across inverter, DC-DC, and on-board charger platforms.
Government Electrification Programs
Government-led electrification initiatives play a decisive role in accelerating demand for EV power electronics across Saudi Arabia. Large-scale programs targeting public transportation, municipal fleets, logistics vehicles, and government-owned enterprises create structured, predictable procurement pipelines for electric vehicles and their critical subsystems. These initiatives prioritize operational reliability, lifecycle durability, and energy efficiency rather than short-term cost considerations, which directly favors advanced power electronics architectures. Centralized procurement frameworks and long-term fleet contracts encourage OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers to deploy higher-efficiency inverters, robust DC-DC converters, and charging systems capable of sustained operation under harsh environmental conditions. Additionally, government programs often mandate compliance with national standards and localization benchmarks, reinforcing the need for suppliers to invest in local engineering, testing, and aftersales support. This policy-driven demand significantly strengthens long-term market visibility for power electronics suppliers.
Challenges
High Cost of Advanced Semiconductors
The high cost of advanced power semiconductors represents a persistent challenge for the KSA EV Power Electronics market, particularly as platforms transition toward wide-bandgap technologies such as silicon carbide. These devices involve complex crystal growth, wafer processing, and advanced packaging techniques, which significantly increase production costs compared to conventional silicon-based components. When integrated into inverters or chargers, these higher component costs translate into increased system-level expenditure. This can create resistance among cost-sensitive buyers, especially fleet operators and public-sector purchasers operating under fixed budgets. In addition, price volatility in upstream materials and limited global manufacturing capacity for wide-bandgap devices further complicate cost planning. Until economies of scale improve and local value addition increases, balancing performance benefits against cost constraints will remain a key challenge for widespread adoption.
Supply Chain Dependence on Imports
Despite ongoing localization initiatives, the KSA EV Power Electronics market continues to rely heavily on imported wafers, semiconductor devices, control ICs, and passive components. This dependence exposes local assemblers and OEMs to global supply chain disruptions, including extended lead times, allocation risks, and geopolitical uncertainties. Any disruption in international logistics or semiconductor manufacturing can directly affect production schedules and delivery commitments. Furthermore, reliance on imports limits flexibility in responding to sudden demand shifts or design modifications, particularly for customized power electronics solutions. Inventory buffering to mitigate these risks often increases working capital requirements, putting additional pressure on local players. Reducing import dependence will require sustained investment in regional assembly, testing, and supplier development, which takes time and coordinated policy support.
Opportunities
Local Assembly and Packaging
Local assembly and packaging of power electronics modules present a significant opportunity to enhance competitiveness and resilience within the KSA EV Power Electronics market. Establishing regional assembly capabilities allows suppliers to shorten lead times, improve responsiveness to OEM requirements, and tailor designs to local operating conditions. Local packaging also enables better thermal management optimization, which is critical for performance in high-temperature environments. From a strategic perspective, localized assembly supports compliance with national industrial policies and localization targets, improving supplier eligibility for government and OEM contracts. It also facilitates closer collaboration between OEMs, Tier-1s, and component suppliers during validation and testing phases. Over time, this capability can evolve into regional export hubs serving neighboring markets, further strengthening Saudi Arabia’s position in the EV power electronics value chain.
SiC Adoption Acceleration
The accelerating adoption of silicon carbide-based power electronics creates a strong opportunity for technology leaders within the Saudi EV ecosystem. SiC devices offer superior switching efficiency, higher power density, and improved thermal performance, making them well-suited for demanding applications such as fast charging and high-voltage traction systems. As EV platforms evolve toward higher efficiency and extended driving range, OEMs increasingly value these performance advantages. Suppliers with proven SiC designs, robust reliability data, and experience in automotive qualification are well-positioned to secure early design wins. Early adoption also enables long-term partnerships, as power electronics platforms are typically locked in for multiple vehicle generations. This transition opens pathways for premium positioning, differentiation through performance, and deeper integration into OEM development roadmaps.
Future Outlook
The KSA EV Power Electronics market is expected to progress toward deeper localization, higher technology intensity, and stronger alignment with national electrification goals. Strategic partnerships between OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, and semiconductor manufacturers will shape competitive outcomes, while performance under extreme environmental conditions will remain a defining differentiator.
Major Players
- Infineon Technologies
- STMicroelectronics
- Onsemi
- NXP Semiconductors
- Texas Instruments
- Renesas Electronics
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Fuji Electric
- Hitachi Astemo
- Bosch Mobility
- Continental
- ZF Friedrichshafen
- Valeo
- DENSO
- Hyundai Mobis
Key Target Audience
- Vehicle OEMs and electric vehicle manufacturers
- Tier-1 powertrain and electrification suppliers
- Fleet operators and mobility service providers
- Charging infrastructure developers and operators
- Utilities and grid integration entities
- Public transport authorities
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study begins by mapping the EV power electronics ecosystem, identifying OEMs, suppliers, distributors, and regulators. Secondary research is used to define demand drivers, technology variables, and procurement structures.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical deployment patterns, vehicle volumes, and component attachment rates are analyzed to construct the market framework. Segmentation logic aligns component demand with vehicle and application categories.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions are validated through structured interviews with industry participants across manufacturing, sourcing, and deployment functions. Feedback is used to refine demand and competitive assumptions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All insights are triangulated and synthesized into a coherent market narrative. The final output integrates quantitative structure with qualitative insights to ensure decision-ready analysis.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Power Electronics Value-Chain Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- KSA EV Manufacturing and Delivery Architecture
- Growth Drivers
Localization of EV Manufacturing
Government Electrification Programs
Expansion of Charging Infrastructure
Thermal Efficiency Requirements
Fleet Electrification Initiatives - Challenges
High Cost of Advanced Semiconductors
Supply Chain Dependence on Imports
Thermal Stress and Reliability Constraints
Limited Local Engineering Ecosystem
Qualification and Certification Timelines - Opportunities
Local Assembly and Packaging
SiC Adoption Acceleration
Aftermarket and Lifecycle Services
Strategic OEM–Supplier Partnerships
Grid-Integrated Power Electronics - Trends
Transition to High-Voltage Architectures
Integration of Power Modules
Focus on High-Temperature Performance
Digital Power Management
Standardization of EV Platforms - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Units Shipped, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Power Electronics Component Type (in Value %)
Traction Inverters
On-board Chargers
DC-DC Converters
Power Distribution Units
Power Semiconductor Modules - By Vehicle Type (in Value %)
Passenger Battery Electric Vehicles
Luxury and Premium Electric Vehicles
Commercial Light Electric Vehicles
Electric Buses
Specialty and Fleet Electric Vehicles - By Semiconductor Technology (in Value %)
Silicon IGBT
Silicon MOSFET
Silicon Carbide MOSFET
Hybrid Si-SiC Modules
Discrete Power Devices - By Distribution Model (in Value %)
OEM Direct Supply
Tier-1 System Integrators
Authorized Distributors
Aftermarket and Service Replacement - By End-Use Customer Type (in Value %)
Vehicle OEMs
Fleet Operators
Charging Infrastructure Operators
Public Transport Authorities
Government Procurement Programs - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (power density, thermal derating capability, semiconductor technology roadmap, localization readiness, functional safety compliance, OEM integration depth, cost competitiveness, supply reliability)
- SWOT analysis of major players
Pricing and commercial model benchmarking - Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Infineon Technologies
STMicroelectronics
onsemi
NXP Semiconductors
Texas Instruments
Renesas Electronics
Mitsubishi Electric
Fuji Electric
Hitachi Astemo
Bosch Mobility
Continental
ZF Friedrichshafen
Valeo
DENSO
Hyundai Mobis
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Units Shipped, 2025–2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025–2030