Market Overview
The KSA EV Traction Inverters Market is valued at USD ~ million and represents a critical enabler within the electric vehicle powertrain stack as Saudi Arabia scales localized EV production and fleet electrification. Demand is structurally driven by the inverter’s role in converting battery DC power into controlled AC output, directly impacting vehicle efficiency, torque delivery, thermal stability, and driving range. As EV penetration expands across passenger vehicles, buses, and commercial fleets, traction inverters transition from a component purchase to a platform-level engineering decision. The market is further reinforced by national industrial localization objectives, high ambient operating conditions that require advanced power electronics design, and OEM preference for integrated inverter-motor architectures. Unlike commoditized electronics, traction inverters are specification-driven assets tied to long qualification cycles, anchoring long-term supplier relationships and creating sustained replacement and upgrade demand across vehicle lifecycles.
Within Saudi Arabia, traction inverter demand is concentrated in the Central and Western regions due to their dominance in EV assembly, logistics access, and public-sector electrification initiatives. Riyadh anchors demand through policy-led EV manufacturing and fleet programs, while Jeddah and the Western corridor benefit from port access and public transport electrification pilots. These regions dominate because inverter sourcing decisions are closely tied to vehicle assembly locations and fleet deployment density. On the supply side, global automotive power electronics vendors exert strong influence due to proprietary inverter control software, silicon carbide switching expertise, and established OEM qualification credentials. Domestic players increasingly participate through assembly, systems integration, and localization partnerships, but core semiconductor design, firmware, and high-voltage architecture leadership remains concentrated among established global suppliers.
Market Segmentation
By Semiconductor Technology
The KSA EV traction inverters market is segmented by semiconductor technology into Silicon IGBT-based inverters, Silicon MOSFET-based inverters, and Silicon Carbide (SiC) MOSFET inverters. Among these, silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFET inverters dominate market share, accounting for the largest portion of installed value. This dominance is driven by the operational realities of Saudi Arabia, where high ambient temperatures, long driving ranges, and heavy-duty usage place strong emphasis on efficiency and thermal resilience. SiC inverters offer lower switching losses, higher power density, and superior performance in high-voltage platforms, making them the preferred choice for premium passenger EVs, electric buses, and long-range fleet vehicles. OEMs increasingly prioritize SiC-based traction inverters to extend driving range, reduce cooling system load, and improve reliability under extreme climatic conditions.
![]()
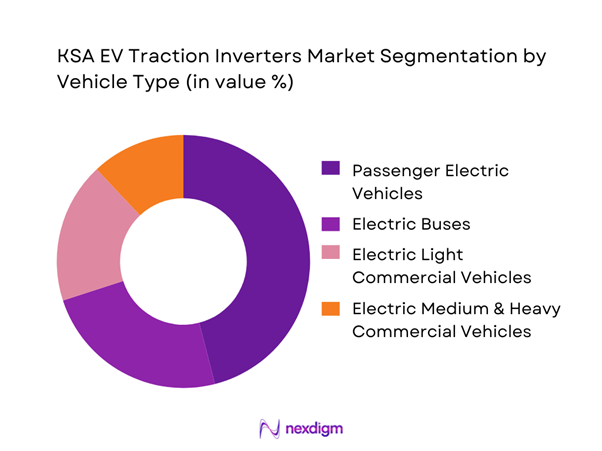
By Vehicle Type
Battery electric passenger vehicles dominate the KSA EV traction inverters market due to their role as the primary entry point for electrified mobility adoption in the country. Government-backed EV programs, premium electric sedan and SUV launches, and localization of passenger EV assembly have driven sustained demand for medium-to-high power traction inverters optimized for efficiency and thermal performance. Passenger EV platforms typically require sophisticated inverter control software, high switching frequencies, and compact packaging to support range optimization and vehicle integration targets. Additionally, passenger EV volumes create scale advantages that encourage OEMs to standardize inverter architectures across multiple models, reinforcing dominance of this segment. The focus on premium vehicle performance, acceleration characteristics, and high ambient temperature reliability further elevates the importance of advanced traction inverter solutions in this category.
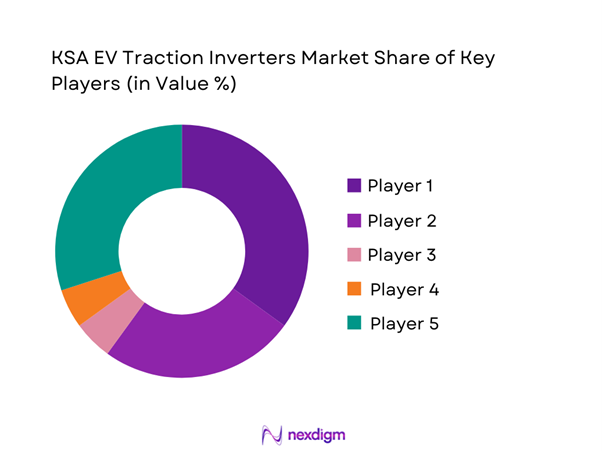
Competitive Landscape
The KSA EV Traction Inverters market is dominated by a few major players, including domestic EV ecosystem participants and global or regional brands like leading automotive power electronics suppliers. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Semiconductor Focus | Voltage Support | Local Presence | Key Vehicle Segments | Thermal Strategy |
| Bosch | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Continental | 1871 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ZF Friedrichshafen | 1915 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Denso | 1949 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BorgWarner | 1928 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA EV Traction Inverters Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
EV Manufacturing Localization and Platform Scale-Up
Localization of electric vehicle manufacturing in Saudi Arabia is a primary growth driver for the EV traction inverters market, as inverters are mandatory powertrain components with limited substitution flexibility. Each locally assembled EV platform requires inverter systems that meet vehicle-specific voltage, power density, and thermal endurance requirements, embedding inverter sourcing into long-term production contracts. As assembly volumes rise, OEMs prioritize inverter suppliers capable of platform scalability, localized support, and engineering collaboration. Traction inverters also benefit from platform reuse, where a single inverter architecture is deployed across multiple vehicle models, amplifying demand as model lineups expand. Unlike downstream components, inverter adoption scales directly with vehicle output rather than discretionary replacement cycles, making localization a structurally compounding demand driver rather than a one-time capacity addition.
Thermal and Efficiency Optimization Requirements
Saudi Arabia’s high ambient temperature profile significantly elevates the technical importance of traction inverters, driving demand for advanced thermal management and high-efficiency switching architectures. Elevated operating temperatures increase inverter stress, power loss, and reliability risks, pushing OEMs toward higher-grade inverter designs with robust cooling, optimized switching frequencies, and enhanced power density. This environment accelerates adoption of advanced semiconductor technologies and integrated inverter systems that reduce heat generation while maintaining performance. As EV range expectations increase, inverter efficiency becomes directly linked to customer acceptance and fleet operating economics. These conditions transform traction inverters from standardized electronics into performance-critical systems, supporting premium pricing, extended validation cycles, and deeper OEM–supplier integration.
Challenges
Dependence on Imported Semiconductor Power Modules
A major challenge facing the KSA EV traction inverters market is continued reliance on imported semiconductor power modules and control chips, which are essential for inverter functionality. These components are subject to long lead times, global allocation cycles, and stringent automotive qualification standards. Any disruption in upstream semiconductor supply can delay vehicle production schedules and increase system costs. For local assembly operations, this dependency limits supply chain flexibility and constrains rapid production ramp-ups. While inverter housings and assembly can be localized, core switching devices remain externally sourced, creating structural exposure to global semiconductor cycles and limiting full vertical integration in the near term.
Extended Qualification and Validation Timelines
Traction inverters require extensive validation across electrical endurance, vibration resistance, thermal cycling, and software stability, particularly under Saudi operating conditions. These qualification processes can span multiple vehicle development cycles, delaying market entry for new inverter platforms and discouraging rapid supplier switching. For newer domestic entrants, the cost and time required to achieve OEM validation act as significant barriers to scale. This challenge reinforces supplier concentration and slows innovation diffusion, as OEMs prioritize proven inverter platforms over experimental or unvalidated designs to mitigate operational and warranty risks.
Opportunities
Localization of Silicon Carbide Inverter Platforms
The transition toward silicon carbide-based traction inverters presents a high-value localization opportunity within Saudi Arabia’s EV ecosystem. SiC inverters offer superior efficiency, higher switching speeds, and improved thermal performance, aligning closely with regional operating requirements. Establishing local assembly, testing, or packaging capabilities for SiC inverter platforms would reduce import exposure while positioning Saudi Arabia as a regional hub for next-generation EV power electronics. As OEMs increasingly mandate SiC adoption for premium and high-performance EV platforms, early localization can secure long-term supply contracts and export-oriented manufacturing potential.
Integrated Drive Unit and System-Level Integration
Growing OEM preference for integrated drive units that combine inverter, motor, and gearbox functions creates an opportunity for system-level traction inverter suppliers. Integration reduces weight, improves efficiency, and simplifies vehicle assembly, making it attractive for localized EV manufacturing. Suppliers capable of delivering inverter designs optimized for integrated architectures gain strategic relevance beyond component supply. This shift enables higher value capture, longer platform lock-in, and deeper engineering collaboration with OEMs, strengthening the market position of advanced inverter providers within Saudi Arabia’s evolving EV manufacturing landscape.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the KSA EV traction inverters market is shaped by continued EV adoption, increasing localization of powertrain components, and technological transition toward higher efficiency inverter architectures. Strategic focus will remain on thermal resilience, integration with drive units, and long-term supply chain security as the market matures.
Major Players
- Infineon Technologies
- STMicroelectronics
- Onsemi
- Wolfspeed
- ROHM Semiconductor
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Hitachi Energy
- Denso
- BorgWarner
- Bosch
- Valeo
- ZF Friedrichshafen
- Vitesco Technologies
- Continental
- Nidec
Key Target Audience
- Electric vehicle OEMs
- Tier-1 automotive suppliers
- Power electronics manufacturers
- Public transport authorities
- Fleet and logistics operators
- Industrial investors and strategic partners
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies in KSA
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study identifies vehicle production volumes, inverter adoption rates, powertrain architectures, and technology platforms relevant to KSA. Key demand drivers and constraints are mapped across EV categories.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure is developed using bottom-up assessment of EV platforms and inverter integration points. Revenue attribution aligns with vehicle deployment and system configuration logic.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings are validated through structured interviews with OEM engineers, power electronics experts, and procurement stakeholders operating within the KSA EV ecosystem.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All insights are synthesized into a cohesive market narrative with consistent assumptions, clearly defined limitations, and transparent analytical logic.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- EV Powertrain Value-Chain Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- KSA Automotive and EV Manufacturing Architecture
- Growth Drivers
National EV industrial localization push
Rapid expansion of domestic EV assembly
High-performance power electronics demand
Public transport electrification mandates
Thermal efficiency and range optimization needs - Challenges
Dependence on imported semiconductor components
High qualification and validation cycles
Limited local power electronics talent pool
Harsh operating temperature requirements
Cost sensitivity in fleet procurement - Opportunities
Localization of SiC inverter manufacturing
Platform standardization across EV models
Integration with e-axle and drive units
Export-oriented manufacturing hubs
Government-backed supplier development programs - Trends
Shift from silicon to SiC architectures
Higher voltage platforms adoption
Integrated inverter-motor systems
Software-defined power electronics
Reliability-driven thermal design innovation - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Volume, 2019–2024
- By Average Selling Price, 2019–2024
- By Vehicle Type (in Value %)
Battery Electric Passenger Vehicles
Battery Electric Commercial Vehicles
Electric Buses
Electric Two and Three Wheelers
Specialty and Off-Highway EVs - By Power Output Rating (in Value %)
Below 50 kW
50–100 kW
100–200 kW
200–300 kW
Above 300 kW - By Technology / Product / Platform Type (in Value %)
Silicon IGBT-Based Inverters
Silicon Carbide MOSFET Inverters
Integrated Drive Units
Standalone Traction Inverters
Dual-Motor Inverter Platforms - By Deployment / Delivery / Distribution Model (in Value %)
OEM Direct Supply
Tier-1 Module Supply
CKD/SKD Assembly Integration
Aftermarket and Retrofit Supply - By End-Use Industry / Customer Type (in Value %)
Passenger EV OEMs
Commercial Vehicle OEMs
Public Transport Authorities
Fleet and Logistics Operators
Defense and Specialty Vehicle Operators - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (voltage rating, power density, switching technology, thermal management design, integration level, localization readiness, OEM qualification status, lifecycle reliability)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Infineon Technologies
STMicroelectronics
onsemi
Wolfspeed
ROHM Semiconductor
Mitsubishi Electric
Hitachi Energy
Denso
BorgWarner
Bosch
Valeo
ZF Friedrichshafen
Vitesco Technologies
Continental
Nidec
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Selling Price, 2025-2030


