Market Overview
The KSA FCW value pool is best represented by the Saudi Arabia ADAS revenue base, which is USD ~ million in 2024, up from USD ~ million in 2023, reflecting higher fitment of safety stacks that include FCW within OEM option packs and standard trims. Growth is driven by premiumization of new-vehicle purchases where ADAS is packaged as a “safety suite”, fleet safety compliance programs that prioritize collision mitigation, and increasing sensor content per vehicle as platforms shift from single-camera FCW to fusion architectures.
Within the Kingdom, Riyadh, Jeddah, and the Eastern Province corridor (Dammam–Khobar) dominate adoption because they concentrate high-mileage commuting, dense expressway corridors, logistics fleets, and the strongest dealer/service ecosystems needed for ADAS calibration and windshield/radar service. Supply-side dominance is led by Germany, Japan, France, and the US/Israel software ecosystem, because global Tier-1s and perception-stack providers power OEM ADAS packages imported into KSA via high-volume passenger and SUV nameplates, accelerating FCW penetration through factory-fit channels.
Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Type
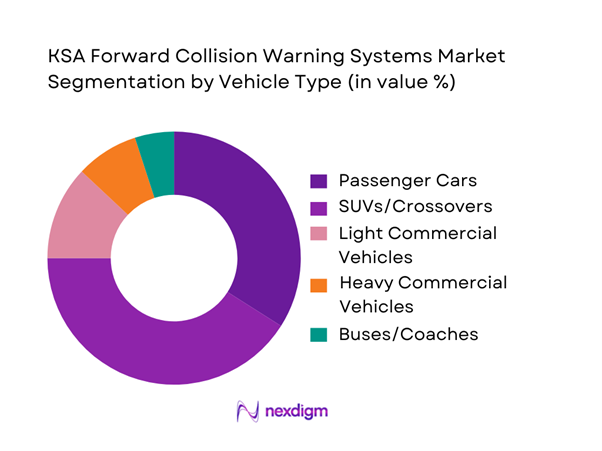
The KSA Forward Collision Warning Systems market is segmented by vehicle type into passenger cars, SUVs/crossovers, light commercial vehicles, heavy commercial vehicles, and buses/coaches. SUVs/crossovers hold the dominant share because KSA’s new-vehicle demand is structurally SUV-heavy, and these trims are more likely to include bundled safety suites where FCW is paired with AEB, ACC, lane functions, and richer HMI. SUVs also accumulate higher annual mileage on intercity corridors and ring roads, making fleets and retail buyers more willing to pay for collision-warning features that reduce high-speed rear-end risk and repair downtime. In parallel, dealer-led “higher trim mix” strategies pull ADAS packages into mainstream SUV variants faster than entry sedans, while corporate mobility and executive fleets standardize ADAS-equipped SUVs for duty-of-care and insurance requirements.
By Sensor Architecture
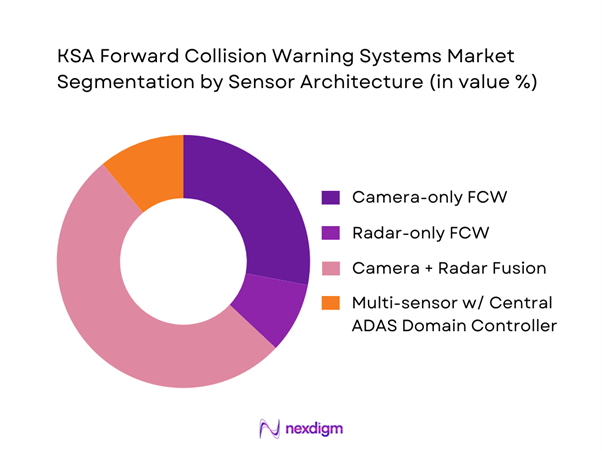
The KSA Forward Collision Warning Systems market is segmented by sensor architecture into camera-only, radar-only, camera+radar fusion, and multi-sensor centralized stacks. Camera + radar fusion dominates because it is increasingly the default architecture in modern OEM safety suites, balancing object classification accuracy (camera) with robust distance/velocity measurement (radar), which matters for high-speed, long-headway driving typical of KSA highways. Radar-centered ADAS demand is also rising in the Kingdom’s broader sensor ecosystem, reinforcing fusion adoption pathways through supplier roadmaps and vehicle platform refresh cycles. Fusion stacks reduce nuisance alerts versus camera-only FCW in glare and low-contrast conditions and provide better cut-in/cut-out tracking in dense urban ring-road traffic. Additionally, OEMs are migrating to E/E architectures that support centralized perception and updates, making fusion FCW “software upgradable,” which is attractive for fleets that want consistent performance and fewer recalibration events.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Forward Collision Warning Systems market is consolidated around global Tier-1 ADAS integrators and perception-stack leaders that supply camera/radar modules, ECUs, and embedded software into OEM safety suites. Competitive intensity is shaped by OEM platform awards, sensor supply resilience, local after-sales calibration capability, and software differentiation (false-positive control, cut-in logic, VRU extensions). As KSA’s premium trim mix expands and fleets formalize safety KPIs, suppliers with strong fusion performance in heat/dust conditions and robust service tool ecosystems gain advantage.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | FCW Product Stack Position | Sensor Portfolio Fit | Software/Compute Strategy | OEM Program Strength (KSA-import models) | Local Support Signal | Service/Calibration Enablement | Functional Safety & Cyber Readiness |
| Robert Bosch | 1886 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Continental | 1871 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ZF (Active Safety) | 1915 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| DENSO | 1949 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mobileye (Intel) | 1999 | Israel/USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Forward Collision Warning Systems Market Dynamics and Performance Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urban expressway density
Saudi Arabia’s FCW relevance rises with the scale and concentration of urban driving demand. The Kingdom has ~ residents, including ~ Saudi citizens and ~ non-Saudi residents, creating sustained commuter volumes in Riyadh–Makkah–Eastern Province city clusters where ring roads and expressways carry high peak-hour loads. The vehicle base reached ~ registered and roadworthy vehicles, and over ~ driving licenses were issued for the first time, with Riyadh accounting for ~—a strong proxy for traffic intensity in the largest urban expressway system. In that operating environment, FCW value increases because short headways, cut-ins, and stop-go waves elevate rear-end exposure and driver workload. The macro backdrop supports continued mobility throughput: Saudi GDP (current) is reported at USD ~ trillion, indicating a large consumer and fleet activity base that sustains urban vehicle kilometers traveled and safety-system pull-through in new models.
High-speed corridor expansion
FCW demand strengthens when long-distance corridors and cross-border road flows scale, because high closing speeds compress reaction time and make forward-warning more valuable. Government road-transport data shows ~ arriving and departing passengers moved through land ports, alongside ~ tons of road freight imports and ~ tons of exports through land ports—large, real-world proof of highway utilization and heavy vehicle mixing on high-speed routes. The vehicle parc expansion (to ~ vehicles) compounds corridor exposure because more passenger cars share space with freight and buses, increasing “speed-differential” interactions that FCW is designed to mitigate. The macro base supporting corridor traffic is also visible in population and output: a ~ population and GDP (current) of USD ~ trillion underpin sustained domestic travel, logistics demand, and fleet operations that amplify the use-case for forward collision alerts on intercity motorways. For OEMs and fleets, the corridor mix elevates priority for camera+radar fusion FCW configurations that can track lead vehicles at range and manage cut-in scenarios typical of freight-heavy highways.
Challenges
False positives in glare and dust conditions
False positives degrade FCW trust, especially in KSA where visibility and contrast can shift rapidly due to sun glare, haze, and suspended dust—raising the burden on perception stacks and warning logic. When drivers stop trusting alerts, fleets lose KPI value and OEM safety suites see lower “effective use.” Road safety exposure remains high enough that trust matters: government data records ~ serious accidents and ~ traffic accident fatalities, making it critical that alerts are timely, credible, and not ignored. The operational stakes are heightened by the sheer installed base—~ roadworthy vehicles—meaning even modest alert fatigue can translate into large absolute risk across the parc. On the macro side, GDP per capita of USD ~ indicates a large base of newer, feature-rich vehicles entering the fleet and retail market; these platforms can support improved sensor fusion and software tuning, but also increase the number of vehicles where poor tuning could create widespread nuisance-warning experiences.
Sensor occlusion due to sand exposure
Sensor occlusion is a structural constraint in KSA: cameras (windshield units) and radars (grilles/bumper modules) are exposed to dust deposition and sand abrasion that can reduce detection range and increase missed warnings unless cleaning, protective design, and diagnostics are robust. This matters at national scale because the parc is ~ vehicles, with over ~ newly registered vehicles in the year—meaning a continuously expanding installed base that must be serviced and kept calibrated to maintain FCW performance. Road safety consequences are non-trivial: ~ traffic accident injuries and ~ fatalities reinforce the need for consistent, maintained safety functionality rather than “degraded-mode” operation. KSA also operates a WMO-accredited Sand and Dust Storm regional capability hosted by the National Center for Meteorology, underscoring that sand/dust is treated as a national hazard class rather than a rare event—supporting why occlusion is not an edge-case in FCW deployment planning.
Opportunities
Arabic-first HMI localization
Arabic-first warning design is a tangible growth lever for FCW effectiveness in KSA because comprehension speed matters during high closing-speed events and because vehicles are used by a mix of citizen and expatriate cohorts. Government population estimates show ~ Saudi citizens and ~ non-Saudi residents within a ~ total population—an environment where FCW UX benefits from Arabic-default with clear bilingual fallbacks for mixed workforces. Digital behavior also supports HMI localization beyond the instrument cluster: internet penetration reached ~, and mobile phones accounted for ~ of internet usage—meaning driver coaching, alert explanations, and safety scorecards delivered via companion apps can be localized to Arabic-first flows to reduce misuse and alert fatigue. The safety need is validated by ~ serious accidents and ~ injuries, where better comprehension and lower nuisance warnings can increase real-world adoption and proper setting usage (alert timing, sensitivity) without adding hardware complexity.
Fleet retrofit bundles with cameras and telematics
Bundled offerings that combine forward-facing cameras (for FCW-like alerts) with telematics (for driver scoring, harsh event capture, and operations dashboards) are a scalable opportunity because they can be deployed across existing fleets without waiting for full vehicle replacement cycles. The addressable retrofit base is large: ~ roadworthy vehicles and over ~ new registrations indicate a fast-moving parc where fleets still retain many vehicles without full OEM ADAS while adding new units each year. Fleet operating intensity is evidenced by ~ tons of road freight imports and ~ tons of exports through land ports, and by ~ delivery orders fulfilled—conditions where small reductions in incidents translate into major uptime gains. Connectivity can support always-on deployment: mobile subscriptions reached ~ and median mobile internet speed reached ~, enabling video/telemetry uploads, near-real-time driver feedback, and centralized analytics for KPI governance.
Future Outlook
The KSA Forward Collision Warning Systems market is expected to expand steadily as FCW becomes a “baseline” safety expectation in new-vehicle trims and as fleets operationalize collision reduction targets with insurer and regulator alignment. ADAS revenue in Saudi Arabia is projected to rise from USD ~ million to USD ~ million, indicating a larger installed base of FCW-capable platforms entering the parc. Growth will be supported by smart-mobility investments and pilot programs (including NEOM’s autonomous mobility initiatives) that encourage higher sensing and compute content, strengthening the broader collision-warning ecosystem.
Major Players
- Robert Bosch
- Continental
- ZF
- DENSO
- Valeo
- Aptiv
- Mobileye
- Hyundai Mobis
- Magna International
- FORVIA HELLA
- Hitachi Astemo
- Autoliv
- NXP Semiconductors
- Texas Instruments
Key Target Audience
- Vehicle OEMs & National Sales Companies
- Authorized Dealer Groups & Dealer Principals
- Fleet Operators
- Ride-hailing and Mobility Platforms
- Insurance Providers & TPAs
- Vehicle Financing/Leasing Companies
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build a KSA-specific ecosystem map covering OEM import channels, dealer-fit programs, fleet retrofit pathways, and ADAS calibration networks. Desk research compiles regulations/standards signals, vehicle parc structure, and platform-level ADAS availability to define variables impacting FCW adoption.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We construct the market using historical revenue anchors for Saudi ADAS and collision-mitigation value pools, then allocate FCW-capable content through platform/trim mapping (OEM-fit) and service-channel validation (aftermarket). Sizing integrates shipment/value reconciliation with installed-base additions.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on fusion penetration, SUV dominance, fleet safety procurement, and calibration constraints are validated via CATIs with OEM channel managers, Tier-1 representatives, dealer service heads, fleet safety leads, and insurer risk engineers to triangulate operational realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We synthesize findings into segment shares, competitive positioning, and go-to-market implications for KSA. Bottom-up checks (platform/trim availability, service throughput, parts/logistics constraints) are used to validate top-down revenue trajectories and refine the final forecast narrative.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & System Boundary: FCW vs AEB/AEBS vs L2 Packages, Assumptions & Exclusions, Abbreviations, Data Triangulation Framework, Primary Research Approach (OEMs, Tier-1s, Dealers, Fleet Operators, Insurers, Regulators), Secondary Research Approach (standards, homologation sources, trade flows, road safety data), Market Engineering & Sizing Logic, Installation Base Modelling, Validation & Sensitivity Checks, Limitations & Confidence Scoring)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Adoption Narrative
- FCW as Part of the Active Safety Stack
- Demand Environment
- High-Level Value Chain Touchpoints
- Growth Drivers
Urban expressway density
High-speed corridor expansion
Insurance risk-pricing maturity
OEM safety packaging strategies
Fleet safety KPIs and telematics adoption - Challenges
False positives in glare and dust conditions
Sensor occlusion due to sand exposure
Calibration capability gaps
Cost-to-feature pressure in mid-segment vehicles
Retrofit quality variability - Opportunities
Arabic-first HMI localization
Fleet retrofit bundles with cameras and telematics
ADAS-as-a-service models for fleets
Training and calibration service networks
Data-led safety scoring solutions - Trends
Sensor fusion shift
Domain controller consolidation
OTA updateable FCW logic
Cybersecurity hardening
AI perception upgrades - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Units, 2019–2024
- By OEM-Fit vs Aftermarket Mix, 2019–2024
- By Vehicle Type Contribution, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Passenger Cars
SUVs
LCVs
HCV Trucks
Buses and Coaches
Specialty and Fleet Vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Urban Commuting
Intercity Highways
Logistics and Last-Mile Delivery
Ride-Hailing and Mobility Services
Industrial and Off-Road Fleet Operations - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Camera-Only FCW
Radar-Only FCW
Camera and Radar Sensor Fusion
Multi-Sensor Systems with Domain Controller - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone Embedded FCW
CAN-Based Integrated FCW
Ethernet-Based ADAS Integration
OTA-Enabled and Software-Defined FCW - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Private Retail Vehicle Owners
Corporate and Commercial Fleets
Logistics and E-Commerce
Ride-Hailing and Mobility Platforms
Government and Municipal Fleets - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Northern Region
Southern Region
- Competitive intensity map
Market share analysis by value and units - Cross Comparison Parameters (Sensor suite and redundancy, detection and warning performance, KSA environmental robustness, integration depth, compliance readiness, calibration footprint, cybersecurity posture, commercial model)
- Strategic plays and partnerships
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Company Profiles
Robert Bosch
Continental
ZF
DENSO
Valeo
Aptiv
Mobileye
Hyundai Mobis
Magna International
FORVIA HELLA
Hitachi Astemo
Qualcomm
NVIDIA
NXP Semiconductors
Texas Instruments
- Demand and utilization patterns
- Buyer personas and procurement roles
- Purchasing criteria and evaluation metrics
- Operational pain points
- Decision-making and rollout processes
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Units, 2025–2030
- By OEM-Fit vs Aftermarket Mix, 2025–2030
- By Vehicle Type Contribution, 2025–2030


