Market Overview
The KSA HbA1c monitoring devices market is valued at USD ~ million, driven by the high prevalence of diabetes in the region. A substantial healthcare infrastructure and a growing focus on preventive healthcare have further fueled the adoption of diagnostic tools. The market is primarily driven by increasing health awareness among the population and expanding healthcare services supported by the government. Point-of-care devices are gaining significant traction due to their convenience and efficiency, addressing the growing demand for rapid and frequent HbA1c testing in healthcare settings.
The cities of Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dammam are major contributors to the market, accounting for the majority of the demand. Riyadh, as the capital and a hub for healthcare development, leads the market in terms of healthcare infrastructure and government-backed health initiatives. Jeddah, known for its medical tourism and the number of private healthcare institutions, also plays a pivotal role in driving demand. These cities dominate due to their strategic locations, population density, and advanced medical facilities.
Market Segmentation
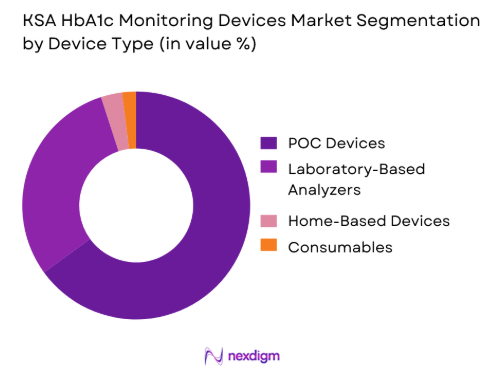
By Device Type
Point-of-care (POC) devices have the largest market share in the KSA HbA1c monitoring devices market due to their quick and reliable results. These devices cater to both professional healthcare providers and patients who require frequent monitoring of their HbA1c levels. Their growing popularity is driven by their portability, ease of use, and ability to deliver on-site results, which is crucial in emergency or outpatient settings. The adoption of POC devices is encouraged by healthcare policies that aim to provide faster and more accessible diagnostic solutions, especially in urban areas.
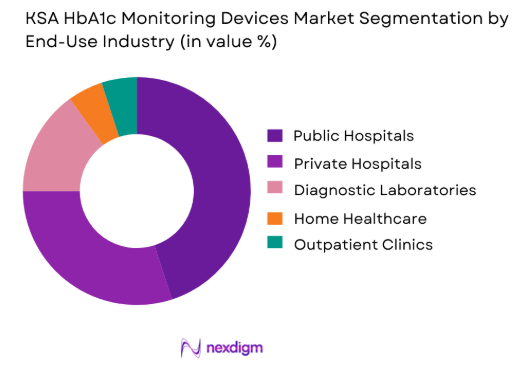
By End-Use Industry
Public hospitals represent the largest segment in the KSA HbA1c monitoring devices market due to the high demand for diabetes management in government-run facilities. These hospitals cater to a wide range of diabetes patients, supported by government healthcare programs that focus on improving chronic disease management. The KSA government continues to invest in healthcare infrastructure, which boosts the procurement of advanced diagnostic devices in public hospitals. The need for accuracy and efficiency in public healthcare drives the demand for laboratory-based and high-throughput HbA1c testing devices.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA HbA1c monitoring devices market is dominated by a few major players, including global brands like Abbott Laboratories, Roche Diagnostics, Siemens Healthineers, and local companies such as Al-Motakamel Medical Supplies. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies, which continue to lead in terms of product innovation, technology, and regional distribution networks. These players leverage their global and local presence to capture a substantial share of the market, meeting the increasing demand for diabetes diagnostic devices in Saudi Arabia.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Device Range | Technology Used | Market Focus | R&D Investment |
| Abbott Laboratories | 1888 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Roche Diagnostics | 1896 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Siemens Healthineers | 1847 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Trinity Biotech | 1992 | Ireland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Menarini Diagnostics | 2007 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA HbA1c Monitoring Devices Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
High Diabetes Prevalence Driving Repeat Monitoring Demand
The increasing global prevalence of diabetes is a major driver for repeat monitoring demand. As more individuals are diagnosed with diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, regular and ongoing monitoring of blood glucose and related parameters becomes essential for effective disease management. With diabetes requiring frequent testing to track blood sugar levels and prevent complications, there is a continuous demand for glucose meters, HbA1c tests, and other diagnostic tools. This rising prevalence ensures sustained demand for diabetes monitoring solutions, both in clinical settings and at home, making it a critical area for growth in the healthcare market.
Expansion of Primary Care Capacity and Chronic Disease Clinics
The expansion of primary care services and the establishment of chronic disease clinics contribute to the growth of diabetes monitoring technologies. As healthcare systems focus on managing long-term conditions like diabetes at the primary care level, there is an increasing need for tools that support routine monitoring and effective disease management. These clinics provide specialized care for chronic conditions, creating opportunities for the adoption of advanced diagnostic tools such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and point-of-care testing (POCT) solutions. The broader access to care drives the demand for efficient, cost-effective monitoring technologies in primary care and outpatient settings.
Challenges
Reagent Cost Pressure and Tender-Driven Pricing Compression
Reagent cost pressure and tender-driven pricing compression are significant challenges in the diabetes monitoring sector. Reagents used for tests like HbA1c, glucose monitoring, and other diagnostic assays can be expensive, especially for high-quality or specialized products. The need to keep costs down, particularly in public healthcare systems or for large-scale tender contracts, can drive pricing pressure. This often results in price reductions for testing services, leading to squeezed profit margins for manufacturers and testing providers. As a result, there is less room for investment in innovative solutions or for manufacturers to offer high-quality products without compromising on cost.
Method Standardization Gaps Across Decentralized Testing Sites
The lack of method standardization across decentralized testing sites presents another challenge. While central laboratories have strict quality control standards, decentralized testing environments, such as in primary care offices or home settings, can lack consistency in testing methods, leading to variability in results. Differences in device calibration, reagent quality, and user handling can cause discrepancies in test outcomes, making it difficult to ensure reliable and accurate results. This challenge is particularly critical when it comes to managing diabetes, where consistent, accurate monitoring is essential to patient care. Addressing these gaps in standardization is necessary to improve the quality and reliability of decentralized testing.
Opportunities
POCT Expansion in Primary Care and Remote Community Sites
The expansion of point-of-care testing (POCT) in primary care and remote community healthcare sites represents a significant opportunity. POCT solutions allow for rapid, accurate testing at the point of care, reducing the need for patients to visit specialized labs for routine monitoring. In primary care settings, POCT can enable faster diagnosis, timely adjustments to treatment plans, and more proactive management of chronic conditions like diabetes. Additionally, in remote or underserved communities, POCT helps bridge the healthcare gap by offering accessible and convenient testing options, thus improving diabetes care and overall patient outcomes in hard-to-reach areas.
Lab Automation Upgrades for Higher Throughput and Turnaround Time
The upgrade of lab automation systems offers a significant opportunity to improve testing efficiency and accuracy. As demand for diabetes monitoring increases, labs require higher throughput and faster turnaround times to handle growing testing volumes without sacrificing quality. By investing in lab automation technologies, including robotic systems and advanced analyzers, laboratories can reduce manual labor, minimize human error, and speed up processing times, leading to quicker results for patients. These upgrades not only enhance operational efficiency but also improve patient satisfaction by providing faster diagnostics and enabling healthcare providers to make timely treatment decisions.
Future Outlook
The KSA HbA1c monitoring devices market is poised for continued expansion, fueled by ongoing government healthcare investments, technological innovations, and the rising demand for quick, accessible diagnostic solutions. As the healthcare infrastructure improves, there will be increasing integration of Point-of-Care devices and digital health solutions, paving the way for broader market adoption.
Major Players
- Abbott Laboratories
- Roche Diagnostics
- Siemens Healthineers
- Trinity Biotech
- Menarini Diagnostics
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- A. Menarini Diagnostics
- Sysmex Corporation
- DiaSys Diagnostic Systems
- Acon Laboratories
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- AccuChek
- Arkray
- Nova Biomedical
Key Target Audience
- Government and regulatory bodies (Saudi Food and Drug Authority)
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Hospitals and healthcare facilities
- Diabetes clinics and specialists
- Insurance companies
- Public health departments
- Device manufacturers and distributors
- Healthcare providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves identifying the key stakeholders in the KSA HbA1c market, focusing on variables like the increasing prevalence of diabetes, healthcare infrastructure, and device adoption rates across different care settings.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This phase includes analyzing historical data and projecting market trends based on the current demand for HbA1c testing devices, alongside assessing the regulatory landscape and technological advancements that influence market adoption.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Our hypotheses will be validated through consultations with healthcare professionals, including laboratory managers, diabetes care specialists, and technology providers. These consultations ensure the accuracy of our market insights.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final step includes synthesizing the information gathered from secondary and primary sources to create a comprehensive, data-backed report that provides actionable insights into the KSA HbA1c market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, terminology and abbreviations, HbA1c testing taxonomy and care setting mapping, market sizing logic by installed base and test volume, revenue attribution across analyzers reagents cartridges and controls, primary interview program with hospitals labs distributors and payers, data triangulation and validation approach, assumptions limitations and data gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution of HbA1c Testing in KSA
- Diabetes Burden and Screening Frequency Drivers
- Care Pathway Mapping Across Primary Care Specialty Clinics and Hospitals
- Public Healthcare Procurement and Private Provider Adoption Dynamics
- Import Dependence and Authorized Distributor Ecosystem
- Growth Drivers
High diabetes prevalence driving repeat monitoring demand
Expansion of primary care capacity and chronic disease clinics
Rising adoption of point of care testing in ambulatory settings
Quality improvement focus on glycemic control targets
Growth of private healthcare and diagnostic chains - Challenges
Reagent cost pressure and tender driven pricing compression
Method standardization gaps across decentralized testing sites
Operator training and quality control burden in POCT
Connectivity and interoperability limitations across care settings
Supply continuity risk for imported reagents and consumables - Opportunities
POCT expansion in primary care and remote community sites
Lab automation upgrades for higher throughput and turnaround time
Distributor led service excellence and uptime based differentiation
Connectivity led QC analytics and compliance workflow tools
Screening programs through employers insurers and wellness providers - Trends
Migration toward cartridge based rapid HbA1c testing in clinics
Greater emphasis on method alignment and traceability practices
Integration of HbA1c results into chronic disease registries
Demand for low maintenance analyzers with simplified calibration
Stronger POCT governance and competency programs in hospitals - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Test Volume, 2019–2024
- By Installed Base, 2019–2024
- By Lab vs Point of Care Revenue Split, 2019–2024
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Government hospitals and medical cities
Primary healthcare centers
Private hospital networks
Independent diagnostic laboratories
Retail clinics and corporate health providers - By Application (in Value %)
Diabetes diagnosis support
Routine glycemic control monitoring
Therapy adjustment and titration support
Population screening programs
Preoperative and inpatient glycemic risk assessment - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
HPLC based HbA1c analyzers
Immunoassay based HbA1c analyzers
Enzymatic assay based HbA1c systems
Boronate affinity based HbA1c systems
Cartridge based point of care HbA1c devices - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone analyzers with local reporting
LIS integrated laboratory analyzers
EHR integrated point of care workflows
Cloud enabled quality management platforms
Remote service monitoring and uptime analytics - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Clinical laboratories and pathology networks
Primary care and family medicine clinics
Endocrinology and diabetes specialty centers
Hospital inpatient testing programs
Public health screening and wellness operators - By Region (in Value %)
Riyadh Region
Makkah Region
Eastern Province
Madinah Region
Asir and Southern Regions
- Positioning driven by accuracy standardization workflow integration and service footprint
- Partnership models with hospital groups diagnostic chains and distributor networks
- Cross Comparison Parameters (method alignment and traceability readiness, analytical precision and bias performance, throughput capacity and automation fit, turnaround time per test, sample type and minimum volume, LIS and EHR connectivity options, reagent stability and storage requirements, cost per reportable result)
- SWOT analysis of major players
- Pricing and commercial model benchmarking
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Roche Diagnostics
Abbott
Siemens Healthineers
Bio Rad Laboratories
Tosoh Bioscience
Beckman Coulter
EKF Diagnostics
Trinity Biotech
Nova Biomedical
Menarini Diagnostics
Randox Laboratories
Sebia
DiaSys Diagnostic Systems
ARKRAY
PTS Diagnostics
- Public sector procurement models and tender evaluation criteria
- Lab director priorities for accuracy throughput and standardization
- Clinic priorities for simplicity turnaround time and workflow fit
- POCT coordinator governance and compliance requirements
- Total cost of ownership drivers across reagent service and uptime
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Test Volume, 2025–2030
- By Installed Base, 2025–2030
- By Lab vs Point of Care Revenue Split, 2025–2030