Market Overview
The KSA Hypersonic Weapons market is valued at approximately USD ~ billion and is expected to see steady growth over the next several years. This market is primarily driven by the Kingdom’s strategic defense requirements and rapid advancements in hypersonic technology. KSA’s defense budget allocations for modernizing its air and missile defense systems, as well as procuring advanced strike weapons, contribute significantly to the market’s expansion. Furthermore, regional geopolitical factors, such as the need to counter emerging threats from neighboring nations, drive the demand for hypersonic systems. Additionally, KSA’s commitment to enhancing its military capabilities through defense modernization programs is expected to propel the market forward.
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) is the dominant country in the KSA Hypersonic Weapons market, owing to its robust defense expenditure and strategic investment in cutting-edge military technologies. The country has been aggressively pursuing advanced hypersonic missile systems to bolster its deterrence capabilities and maintain regional superiority. Major cities such as Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dhahran play a key role in the defense infrastructure, with Riyadh serving as the central hub for strategic decision-making and military acquisitions. The country’s collaboration with international defense contractors further strengthens its position, making it a critical player in the Middle East hypersonic weapons market.
Market Segmentation
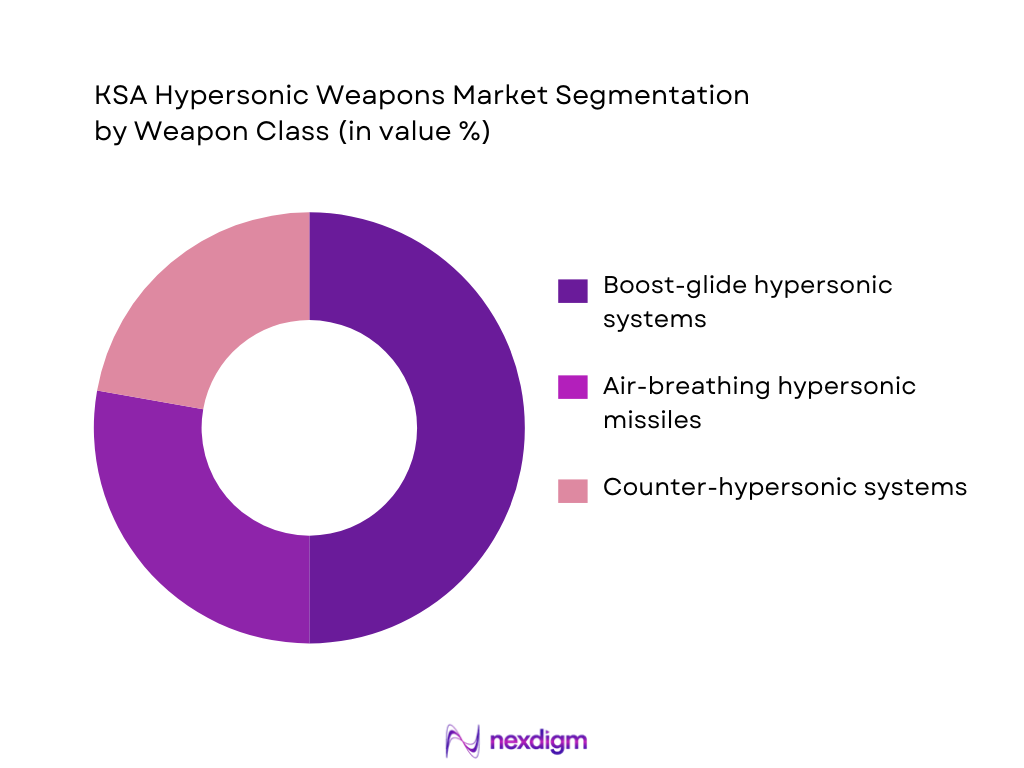
By Weapon Class
The KSA Hypersonic Weapons market is divided into several weapon classes, including boost-glide hypersonic systems, air-breathing hypersonic cruise missiles, and counter-hypersonic systems. The boost-glide hypersonic systems segment dominates the market due to their high speed and maneuverability, making them ideal for deep strike and counter-force operations. These systems are capable of evading current missile defense systems, providing KSA with a strategic advantage in any conflict. The increasing investment in research and development in these systems, coupled with international collaborations, ensures continued growth in this segment.
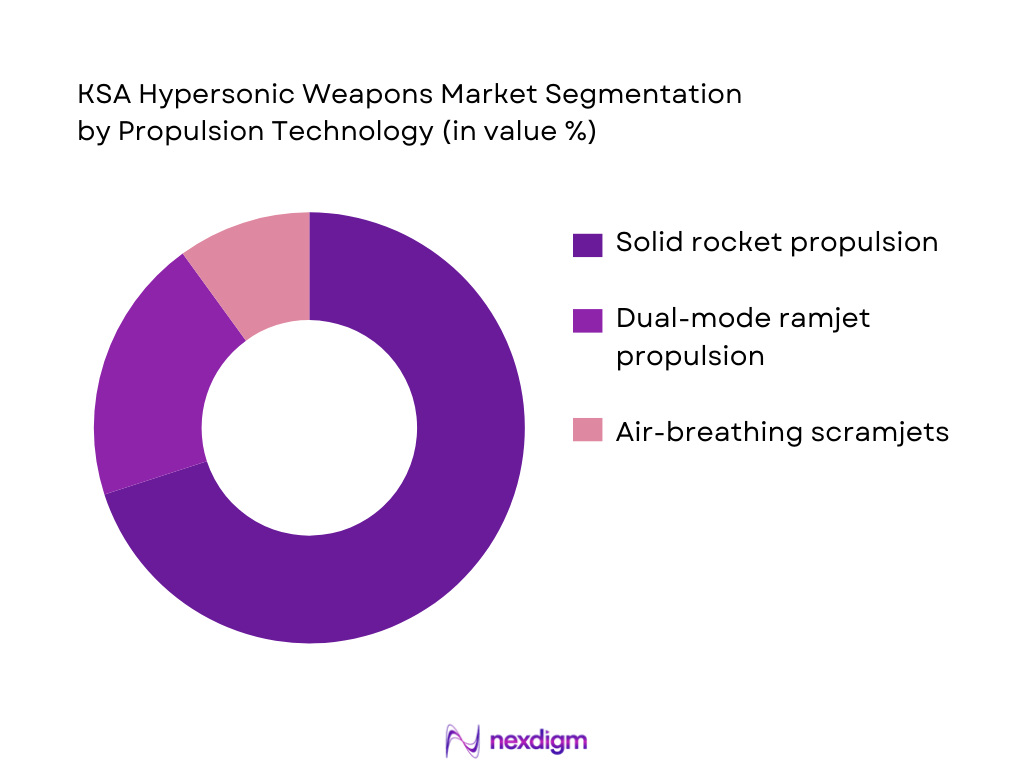
By Propulsion Technology
The propulsion technology used in hypersonic weapons in KSA includes solid rocket propulsion, dual-mode ramjet propulsion, and air-breathing scramjet systems. Solid rocket propulsion is the most dominant in the market, mainly because of its reliability and high thrust capability, which is critical for achieving the required speed and range of hypersonic systems. Additionally, dual-mode ramjet propulsion systems are gaining traction as they allow for a more efficient boost and glide trajectory, making them suitable for long-range strike missions. These propulsion systems are key to KSA’s strategy of achieving rapid strike capabilities across various mission profiles.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Hypersonic Weapons market is highly competitive, with a few key global players dominating the landscape. The market is led by defense contractors such as Lockheed Martin, Raytheon Technologies, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and BAE Systems. These players bring advanced technology and strategic collaborations that are essential for KSA’s hypersonic capabilities. Lockheed Martin and Boeing have strong ties with KSA’s defense sector, providing technological solutions such as the hypersonic missiles and related defense systems. These major players have significant R&D investments in hypersonic technology and benefit from their existing relationships with the KSA Ministry of Defense (MoD) and the General Authority for Military Industries (GAMI).
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Market Expertise | Technology Focus | R&D Investments | Regional Collaborations |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | Bethesda, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon Technologies | 1922 | Waltham, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing | 1916 | Chicago, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | Falls Church, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | London, UK | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Hypersonic Weapons Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Demand for advanced strike capabilities
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s strategic defense posture increasingly prioritizes long-range precision strike capabilities as a central element of its deterrence and force projection doctrine. Hypersonic weapons—capable of sustained speeds above Mach 5 and highly maneuverable flight profiles—offer the ability to strike high-value, time‑sensitive targets deep within adversary territory before effective defensive responses can be mounted. In the context of the Middle East’s evolving threat environment, where adversaries continue to field sophisticated air defenses and ballistic missile systems, traditional kinetic strike platforms may have limited effectiveness. Hypersonic strike systems provide Saudi Arabia with an advanced operational edge by compressing the adversary’s decision cycle, complicating defensive targeting solutions, and enhancing strategic deterrence signaling.
Air defense saturation and the need for counter‑A2/AD capabilities
Saudi Arabia’s security planners increasingly confront scenarios where adversaries employ Anti‑Access/Area Denial (A2/AD) strategies designed to restrict freedom of maneuver and complicate conventional force employment. A2/AD architectures typically integrate overlapping layers of air defenses, long‑range artillery, and anti‑ship missiles, supported by advanced sensors and integrated fire control. In such environments, traditional cruise missiles and fixed‑wing strike aircraft may face unsustainable attrition or require extensive support to penetrate defended airspace. Hypersonic weapons—with their high speed, unpredictable flight paths, and reduced engagement windows—are uniquely suited to complicate and overwhelm A2/AD networks. By compressing engagement timelines and reducing the effectiveness of layered defenses, hypersonic systems enable Saudi forces to maintain operational access and achieve strategic effects against hardened or deeply buried targets.
Market Challenges
Technical complexity and integration with existing defense systems
Hypersonic weapons represent some of the most technically demanding systems in modern defense portfolios, requiring advanced propulsion, high‑temperature materials, precision guidance, and sophisticated command and control integration. These systems must operate at extreme speeds and in harsh thermal environments, demanding cutting‑edge research and development, rigorous testing, and specialized manufacturing capabilities. For Saudi Arabia, integrating hypersonic systems into an existing defense architecture—built around legacy air and missile defense platforms, conventional strike aircraft, and layered sensor networks—poses substantial technical challenges. Ensuring interoperability between hypersonic weapons and current fire‑control systems, sensor fusion networks, and logistical support chains requires significant systems engineering investments.
Procurement delays due to global supply chain disruptions
The global defense industrial base has faced ongoing supply chain pressures driven by geopolitical tensions, pandemic‑induced logistics bottlenecks, and resource competition across strategic sectors. Hypersonic weapons, with their reliance on specialized components—such as advanced propellants, high‑temperature alloys, microelectronics with stringent performance criteria, and precision guidance subsystems—are particularly vulnerable to supply chain disruptions. Delays in sourcing critical materials or subsystems can cascade into program schedule slippages, cost overruns, and deferred capability fielding.
Opportunities
Future procurement of hypersonic defense systems
As adversaries and regional powers invest in hypersonic strike capabilities, the corresponding need for effective counter‑hypersonic defenses becomes increasingly urgent. Hypersonic defense systems—including advanced detection radars, space‑based tracking assets, and interceptors capable of engaging high‑speed maneuvering threats—represent a substantial and growing segment of the broader hypersonic weapons ecosystem. For Saudi Arabia, procuring and integrating hypersonic defense solutions offers the opportunity to enhance national resilience against advanced missile threats and strengthen comprehensive air and missile defense architectures. Investments in early‑warning sensors, multi‑domain tracking networks, and interceptor technologies can not only protect critical infrastructure and population centers but also support coalition defense postures in the Gulf.
Potential for local MRO centers
The complexity of hypersonic weapons systems underscores the importance of robust Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) infrastructure to ensure sustained operational readiness. Establishing local MRO centers within Saudi Arabia presents significant strategic and economic opportunities. These facilities would support routine maintenance, upgrades, component refurbishment, and lifecycle sustainment for both indigenous and imported hypersonic assets. By localizing MRO capabilities, the Kingdom can reduce dependence on foreign service providers, shorten turnaround times, and cultivate a skilled defense workforce. Furthermore, MRO centers can serve as hubs for technology transfer, knowledge accumulation, and workforce development in high‑end defense engineering disciplines.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the KSA Hypersonic Weapons market is expected to continue growing due to increased investment in hypersonic technologies and the Kingdom’s strategic need to bolster its defense capabilities in the face of regional instability. The primary drivers of growth will be the procurement of more advanced hypersonic systems, both offensive and defensive, as well as the shift towards modernizing the air defense and missile systems in KSA. Additionally, KSA’s ongoing defense partnerships with global powers such as the US and UK will ensure the continuous flow of cutting-edge technology into the Kingdom.
Major Players in the Market
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon Technologies
- Boeing
- Northrop Grumman
- BAE Systems
- Thales Group
- Safran
- Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
- Kongsberg Defense
- Aerojet Rocketdyne
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- MBDA
- China Aerospace Corporation (CASIC)
- Tactical Missiles Corporation (KTRV)
- Rostec
Key Target Audience
- Government and Regulatory Bodies
- Defense Contractors and Suppliers
- Investment and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Defense Integrators
- Military Agencies
- Technology Developers and R&D Institutions
- International Defense Collaborators
- Military Procurement Officers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves mapping all stakeholders in the KSA Hypersonic Weapons market, identifying key drivers such as procurement trends, military strategy, and technological advancements. The primary goal is to identify critical market variables that influence defense procurements and regional security.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This step includes gathering and analyzing historical data from secondary sources such as defense budgets, government procurement records, and publicly available market reports. The objective is to create a market forecast based on current and historical trends, providing a clearer view of the future growth trajectory.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
After developing initial market hypotheses, these will be validated through interviews with key industry players, including experts from defense OEMs and KSA’s military procurement divisions. These consultations will provide crucial insights into the actual demand, challenges, and market trends.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
In this phase, we will synthesize the data collected, verify it against known benchmarks, and ensure that all aspects of the KSA Hypersonic Weapons market have been accounted for. The outcome will be a validated, comprehensive report detailing the market’s future outlook, potential growth drivers, and competitive landscape.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions (Hypersonic weapon systems, KSA defense strategy alignment, mission sets), Abbreviations (e.g., HGV, HCM, AEW, GNSS, GAMI), Market Sizing Approach (Top-down approach based on defense budget allocation, bottom-up based on procurement patterns), Consolidated Research Approach (Primary data from defense OEMs, secondary from government sources and defense contracts), Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews (Stakeholder insights: Military analysts, defense contractors, MoD procurement officers), Primary Research Approach (Survey design, structured interviews with industry experts), Limitations and Future Conclusions (Data gaps, emerging trends, forecast reliability))
- Definition and Scope (Weapon classes: Boost-glide, air-breathing hypersonics, counter-hypersonic systems)
- Overview Genesis (Evolution of hypersonic technology in the KSA context, strategic defense priorities)
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Demand for advanced strike capabilities
Air defense saturation and the need for counter-A2/AD capabilities
Increasing military R&D investments
Geopolitical tensions and evolving defense priorities - Market Challenges
Technical complexity and integration with existing defense systems
Procurement delays due to global supply chain disruptions
Technology transfer restrictions and export controls
Budget constraints and prioritization within defense programs - Opportunities
Future procurement of hypersonic defense systems
Potential for local MRO centers
Technology licensing and collaboration with foreign OEMs - Market Trends
The shift towards modular missile systems
Increased emphasis on sensor fusion and hypersonic defense layer integration
Advanced cyber defense integration into hypersonic systems
Investments in hypersonic weapons as deterrence tools - Government Regulation
Regulatory frameworks for technology exports
Defense budget allocation constraints for non-nuclear missile systems
Offset obligations linked to local technology and manufacturing capacity - SWOT Analysis
- PESTLE
- Market Value, 2020-2025
- Volume Consumption Across Subsegments, 2020-2025
- Composite Adoption Intensity, 2020-2025
- By Weapon Class (In Value %)
Boost-glide hypersonic systems
Air-breathing hypersonic cruise missiles
Aero-ballistic hypersonic variants
Counter-hypersonic systems
Test and evaluation hypersonic vehicles - By Propulsion Technology (In Value %)
Solid rocket propulsion
Dual-mode ramjet propulsion
Air-breathing scramjet systems
Hybrid propulsion - By Launch Platform (In Value %)
Air-launched hypersonics
Ground-launched systems
Sea-launched hypersonic weapons
Multi-domain adaptable systems - By Application (In Value %)
Conventional strike missions
Counter-force capabilities
Maritime strike and sea-denial
Anti-access/Area denial (A2/AD)
Strategic infrastructure attacks - By Region (In Value %)
Central Region
Eastern Region
Western Region
Southern Region
- Market Share of Major Players (By weapon type, system category)
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Weapon Portfolio, Contract Backlog, Combat Capability Index, Integration Support Network, After-Sales Sustainment Capability, Local Presence / Defense Offset Engagement, R&D Technology Roadmap)
- Detailed Profiles of Major Competitors
Lockheed Martin
Boeing Defense
Raytheon Technologies
Northrop Grumman
MBDA
BAE Systems
Thales Group
Safran
Israel Aerospace Industries
Kongsberg Defense
Aerojet Rocketdyne
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
China Aerospace Corporation (CASIC)
Tactical Missiles Corporation (KTRV)
Rostec (Russian Technologies)
- Market Demand and Utilization
- Purchasing Power and Budget Allocations
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision-Making Process
- Forecast by Value & Growth Scenarios, 2026-2035
- Forecast by Volume & Composite Penetration, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Aircraft Segment, 2026-2035


