Market Overview
The KSA Injectable Drug Solutions Market, proxied by generic injectables, is valued at USD ~ million, reflecting rapid penetration of cost-effective parenteral therapies in hospital and critical-care settings. This sits within a pharmaceuticals sector that reached about USD ~ billion in the recent past and has since expanded to roughly USD ~ billion, supported by rising chronic disease prevalence and hospital spending. The combination of growing hospital market value (over USD ~ billion in inpatient services) and high injectable use in acute and specialty care underpins sustained demand for sterile injectable drug solutions.
Injectable drug utilization is concentrated in major health hubs such as Riyadh, Jeddah and the Eastern Province. Riyadh alone hosts over 115 hospitals out of 516 nationally, while Jeddah accounts for around 9% of hospital capacity, reflecting dense tertiary-care and specialist facilities. Eastern clusters around Dammam and Dhahran combine high private insurance penetration and industrial workforce, driving higher procedure volumes and injectable usage. These cities anchor national referral networks, oncology and critical-care services, and are primary nodes for public tenders and NUPCO procurement of injectable drug solutions.

Market Segmentation
By Therapeutic Area
The KSA Injectable Drug Solutions Market is segmented by therapeutic area into anti-infectives and sepsis management, cardiovascular and metabolic, oncology and immuno-oncology, anesthesia and peri-operative care, parenteral nutrition and electrolytes, and CNS/GI and other use-cases. Anti-infective injectables currently dominate market share, driven by high inpatient burden of bacterial infections, sepsis and peri-operative prophylaxis. Hospital utilization is elevated: Saudi hospitals account for over 80,000 beds and more than 20,000 beds in Riyadh alone, with anti-infective injectables integral to ICU and surgical pathways. National antimicrobial guidelines, high surgical volumes, and reimbursement alignment via NUPCO tenders reinforce continuous volume pull for cephalosporins, carbapenems, and broader parenteral antibiotics, keeping this therapeutic block at the center of injectable spend.
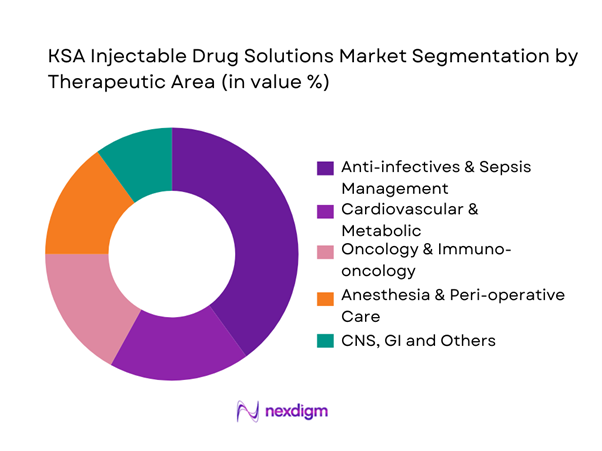
By Container / Delivery Format
The KSA Injectable Drug Solutions Market is segmented by container type into multi-/single-dose vials, glass ampoules, prefilled syringes, premix IV bags and lyophilized injectables. Vials hold the dominant share due to their compatibility with hospital compounding practices, dosing flexibility and better fit with SFDA procurement price controls. The hospital channel in Saudi Arabia, valued at over USD ~ billion, remains highly cost-sensitive and favors vial-based SKUs that can be used across multiple wards and indications. National and regional manufacturers such as Tabuk and SPIMACO have built significant vial and ampoule capacity, while PFS adoption grows fastest in vaccines, anticoagulation and biologics, supported by global suppliers like Hikma, Pfizer and Sanofi integrating KSA into MENA-wide injectable supply chains.
Competitive Landscape
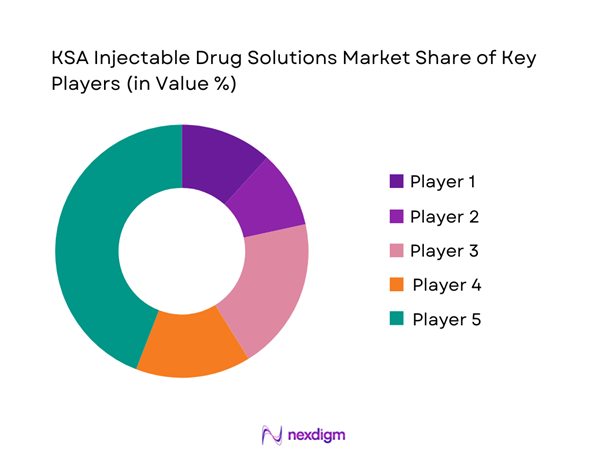
The KSA Injectable Drug Solutions Market is moderately consolidated around a mix of domestic champions and multinational injectable specialists. Local firms such as SPIMACO, Tabuk Pharmaceuticals and Jamjoom Pharma dominate tender-based small-molecule generics and certain sterile injectables, while multinationals like Hikma and Pfizer leverage regional hubs for high-complexity injectables and biosimilars. Vision 2030-driven localization, SFDA incentives, and NUPCO’s preference for local content are accelerating technology transfer, lyophilized injectable capacity and contract manufacturing partnerships, intensifying competition around oncology, parenteral nutrition and critical-care portfolios.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters (Core Market) | Core Injectable Focus in KSA (Therapy / Portfolio) | Key Dosage / Container Strength | Manufacturing Footprint in KSA | Hospital Tender & NUPCO Presence | Localization / Partnership Strategy (Vision 2030 Alignment) | Notable Competitive Edge in Injectable Drug Solutions |
| Saudi Pharmaceutical Industries & Medical Appliances Corp (SPIMACO) | 1986 | Al-Qassim, KSA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tabuk Pharmaceuticals | 1994 | Riyadh, KSA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Jamjoom Pharma | 1994 | Jeddah, KSA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hikma Pharmaceuticals | 1978 | London, UK (strong MENA base) | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pfizer (Injectables & Hospital Products in KSA) | 1849 | New York, USA / regional MENA hubs | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Injectable Drug Solutions Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising chronic disease burden requiring parenteral therapies
Saudi Arabia faces a growing burden of chronic and non-communicable diseases, notably chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes and hypertension, which drive demand for injectable therapies. A recent epidemiological population-based study found an overall CKD prevalence of 4.76% among the sampled population, with a high proportion in stage 3 disease. The same study emphasizes that CKD increases with age, and given the country’s population of approximately ~ million, even a 4.76% prevalence corresponds to over 1.5 million individuals potentially needing management, including injectable-based interventions for dialysis, fluid/electrolyte management, anemia correction, and supportive therapies.
Expansion of tertiary and quaternary care facilities
Saudi Arabia continues to invest in expanding its hospital infrastructure: as of a 2022 study, the country had 78,440 hospital beds serving a population of about ~ million, translating into a national average of 2.43 beds per 1,000 people. This indicates a significant hospital capacity, and yet the study notes a need for an additional 17,062 beds to meet common international standards of 2.9 beds per 1,000 people. The growth in bed capacity corresponds with the expansion of tertiary and quaternary-level hospitals, including specialized centers offering dialysis, oncology, transplant, intensive care, and high-dependency unit services. For example, prominent institutions like a large tertiary-level medical city in Riyadh operate hundreds of ICU, trauma, transplant, and critical-care beds.
Market Challenges and Constraints
High technical barrier and capital intensity for sterile injectable plants
Establishing sterile injectable manufacturing facilities in Saudi Arabia requires significant capital investment, specialized clean rooms, aseptic processing equipment, lyophilization units, sterile filling lines, quality-control labs and cold-chain infrastructure. Given that as of 2022 the national hospital bed-to-population ratio stands at 2.43 per 1,000 people, with noted needs for more than 17,000 additional beds to meet global benchmarks, the growth in hospital infrastructure may outpace the expansion of local sterile manufacturing capacity. Building and maintaining sterile injectable plants also demands highly trained personnel — scientists, pharmacists, quality control staff — which are relatively scarce. For instance, overall health workforce density in KSA remains lower compared to other high-income countries; physician and nursing densities lag behind global norms, constraining rapid scaling of high-complexity manufacturing while preserving regulatory and GMP standards.
Dependence on imported APIs and key excipients
Sterile injectables often rely on active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), excipients, vials, ampoules, glass components, stoppers, seals — many of which are produced globally. Saudi local manufacturing capabilities for APIs remain limited, which means injectable producers must import APIs and critical packaging components from international suppliers. Given global supply-chain instability, currency fluctuation and logistic constraints, this dependence introduces supply risk and potential cost volatility. Compounding this, biopharmaceutical injectables (e.g., biologics, biosimilars) often need specialized APIs and cold-chain sensitive excipients. Without domestic API production, any disruption in global supply (e.g., raw-material shortages, export restrictions) directly impacts the ability of Saudi manufacturers to fulfil local injectable demand. In a context where hospital demand for injectables is rising (due to growing CKD, dialysis, oncology, ICU volume), this external dependency remains a major constraint on reliable supply.
Opportunities
Localization of priority injectable classes
Given the increasing chronic disease burden, expansion of hospital capacity, and persistent demand for injectables in CKD, dialysis, oncology, critical care and supportive therapies, there is a strong opportunity to localize manufacturing of priority injectable classes in Saudi Arabia. Domestic production would reduce dependence on imports, mitigate supply-chain risk, and strengthen supply security for essential injectables (e.g., antibiotics, dialysis-related injectables, IV fluids, supportive medications). Moreover, localization aligns with national healthcare policy priorities and industrial diversification goals under Vision 2030. With a population of approximately 32.2 million and rising prevalence of CKD (4.76%) and increasing hospital bed capacity, the demand base is sufficiently large to support local production capacity investment.
Large-volume parenterals and parenteral nutrition
Given the significant number of CKD and dialysis patients (20,000+ on dialysis; 9,800 under follow-up) and expanding hospital and critical-care capacity, there is a growing need for large-volume parenterals (IV fluids, electrolytes, parenteral nutrition, infusion bags) and nutrient/rehydration solutions. Large-volume parenterals (LVPs) offer advantages: they are easier to standardize and produce at scale in central fill-finish plants, have lower sterility complexity compared to biologics, and fulfil routine hospital demands for hydration, fluid management, dialysis, ICU care, and supportive treatments. Local manufacturers can thus focus on building LVP production lines, pre-mix IV bags, and parenteral nutrition solutions — which are likely to see consistent demand given the rising chronic-disease and inpatient caseload.
Future Outlook
Over the next six years, the KSA Injectable Drug Solutions Market is expected to maintain a robust growth path, broadly aligned with the ~12% CAGR projected for Saudi generic. Growth will be fueled by expanding chronic disease burden (e.g., over 5.3 million people with diabetes), rising specialty-care capacity and continued public-investment in tertiary hospitals, alongside localization incentives that favor domestic sterile injectable manufacturing.
Major Players
- Saudi Pharmaceutical Industries & Medical Appliances Corp
- Tabuk Pharmaceuticals
- Jamjoom Pharma
- Avalon Pharma
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals
- Julphar Gulf Pharmaceutical Industries
- Pfizer
- Baxter International Inc.
- Sanofi
- AstraZeneca
- Viatris
- Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories
- Biocon
- Fresenius Kabi
- Merck & Co.
Key Target Audience
- Domestic pharmaceutical manufacturers and sterile injectable producers
- Multinational injectable and biosimilar companies
- Hospital groups and healthcare clusters
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Insurance companies and health-benefit administrators
- Hospital pharmacy chains and large retail pharmacy networks
- Industrial conglomerates and contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Market Scoping and Variable Identification
The initial phase involved defining the KSA Injectable Drug Solutions Market with a focus on generic injectables, biologic injectables, and hospital-dispensed parenterals. An ecosystem map was built covering SFDA, NUPCO, MOH, health clusters, hospital groups, domestic manufacturers and multinational suppliers. This was supported by peer-reviewed publications to identify key demand, pricing, capacity and regulatory variables.
Step 2: Market Construction and Quantification
In this phase, we compiled historical and current data on Saudi pharmaceutical sales, hospital spending, and generic injectable market size. Pharmaceutical market baselines (e.g., USD ~ billion in 2023) were combined with KSA generic injectables sizing (USD ~ million in 2024) to construct a bottom-up view of injectable solutions. We assessed import trends, local manufacturing output, tender volumes, and therapy-area mix using IQVIA MEA reports, MOH hospital statistics, and company disclosures to refine revenue allocation across therapeutic areas and container types.
Step 3: Hypothesis Testing and Expert Validation
Market hypotheses on growth drivers (localization, chronic disease burden), competitive positioning, and segmental shares were stress-tested through in-depth interviews with stakeholders—procurement managers at major hospitals, KSA-based regulatory experts, local manufacturing executives and regional commercial leaders. These conversations, typically run via structured or computer-assisted interviews, provided qualitative and quantitative validation on NUPCO tender behavior, contracting cycles, and price-pressure trends in key injectable classes, as well as ground-level insights into PFS and lyophilized capacity expansion.
Step 4: Synthesis, Forecasting and Final Output
The final step integrated validated inputs into a coherent market model projecting the KSA Injectable Drug Solutions Market through 2030.t 12% CAGR forecast for Saudi generic injectables (2025–2033) was aligned with Vision 2030 healthcare investments and chronic disease projections to derive a 2024–2030 CAGR assumption of ~12%, explicitly flagged as forecast. The synthesis reconciled top-down projections with bottom-up segment views, generating therapeutic-area and container-level splits, competitive landscaping, and opportunity maps tailored for business professionals considering greenfield manufacturing, M&A, or tender strategy optimization in the KSA injectable space.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (definition and taxonomy of injectable drug solutions, inclusion–exclusion criteria by dosage form and route, data sources: SFDA, Ministry of Health, NUPCO, GCC and global datasets, hospital-tender line-item extraction, top-down triangulation from national pharma spending and health budgets, bottom-up SKU and dose-based build-up for vials/ampoules/syringes/bags, validation with key opinion leaders and hospital pharmacists, forecasting and scenario-building approach, study limitations and assumptions)
- Definition and Scope of Injectable Drug Solutions
- Evolution of Parenteral Therapies and Hospital-Use Injectables in KSA
- Role of Injectables within the KSA Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Market
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Mapping for Sterile Injectables
- Institutional Procurement and Tendering Landscape
- Growth Drivers
Rising chronic disease burden requiring parenteral therapies
Expansion of tertiary and quaternary care facilities
Increased use of biologics and complex injectables
Higher procedure volumes in oncology
Dialysis and critical care - Market Challenges and Constraints
High technical barrier and capital intensity for sterile injectable plants
Dependence on imported APIs and key excipients
Cold-chain and logistics complexity
Drug shortage episodes and supply security
Tender-driven price pressure - Opportunities
Localization of priority injectable classes
Large-volume parenterals and parenteral nutrition
Oncology and biologic injectables
Ready-to-use formats for safety and efficiency
Contract manufacturing and CDMO opportunities - Emerging Trends in Injectable Drug Solutions
Shift from multi-dose to single-dose and ready-to-administer formats
Growth of prefilled syringes and pens
Adoption of safety-engineered devices
Biosimilar injectables uptake
Increased use of long-acting injectables for chronic disease - Regulatory and Quality Framework
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Mapping
- Porter’s Five Forces – Sterile Injectable Ecosystem
- Competition Ecosystem and Market Concentration
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Defined Daily Doses and Patient Encounters, 2019-2024
- Injectables’ Share of Total Pharmaceutical Spending, 2019-2024
- Import vs Local Manufacturing Contribution in Injectables, 2019-2024
- By Dosage Form (in Value %)
Small-Volume Parenterals
Large-Volume Parenterals
Prefilled Syringes and Pens
Lyophilized Powder Injectables
Ready-to-Use Infusion Bags - By Route of Administration (in Value %)
Intravenous
Intramuscular
Subcutaneous
Intra-articular and Intrathecal
Other Parenteral Routes - By Therapeutic Area (in Value %)
Anti-Infectives and Antimicrobials
Oncology and Immuno-Oncology Injectables
Diabetes and Metabolic Care Injectables
Vaccines and Immunoglobulins
Critical Care, Anaesthesia, Cardiovascular and Parenteral Nutrition - By End-User Setting (in Value %)
Public Sector Hospitals and Medical Cities
Military and Security Forces Hospitals
Private Hospitals and Polyclinics
Dialysis, Oncology and Day-Care Centres
Retail Pharmacies and Home-Care Providers - By Origin of Product (in Value %)
Local KSA Manufacturing
GCC-Origin Imports
Other MENA-Origin Imports
Europe and North America-Origin Injectables
Asia-Pacific-Origin Injectables - By Procurement and Distribution Channel (in Value %)
Centralized Government Tenders
Direct Hospital and Institutional Contracts
Private Distributors and Wholesalers
Retail Pharmacy Purchases
Speciality Pharmacy and Home-Infusion Channels
- Market Share of Major Players by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (company overview and injectable strategy, breadth and depth of injectable portfolio and SKUs, local sterile manufacturing and fill-finish capacity, share of sales through NUPCO and institutional tenders, proportion of biologics and high-value injectables in portfolio, penetration of ready-to-use and safety-engineered injectable formats, cold-chain infrastructure and service reach across regions, SFDA compliance track record and quality certifications)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing and Contracting Analysis for Injectable SKUs
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies in KSA Injectable Drug Solutions
Saudi Pharmaceutical Industries & Medical Appliances Corporation
Tabuk Pharmaceuticals
Jamjoom Pharma
Hikma Pharmaceuticals plc
Julphar Saudi Arabia
Pfizer Inc.
Sanofi S.A.
Novartis AG
AstraZeneca plc
Baxter International Inc.
Fresenius Kabi
Novo Nordisk A/S
Eli Lilly and Company
Amgen Inc.
- Hospital Demand, Utilization and Case-Mix
- Budget Allocation and Tender Behavior
- Clinical, Regulatory and Safety Requirements
- Needs, Pain Points and Unmet Requirements
- Decision-Making Process and Influencer Map
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Defined Daily Doses and Patient Encounters, 2025-2030
- Injectables’ Share of Total Pharmaceutical Spending, 2025-2030
- Import vs Local Manufacturing Contribution in Injectables, 2025-2030