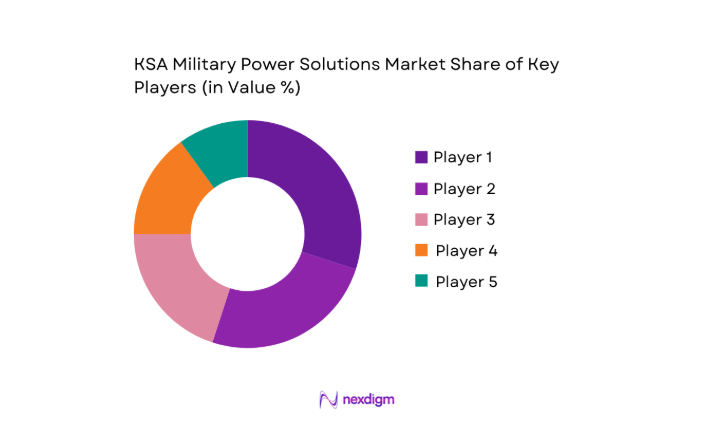
Market Overview
The KSA military power solutions market operates within a demand environment shaped by defense modernization and energy-resilience requirements across bases, platforms, and expeditionary deployments. Saudi Arabia’s military spending increased from USD ~ to USD ~, which expands the procurement envelope for power generation, conversion, storage, and distribution systems used across defense infrastructure and fleets. In parallel, the global military power solutions market reached USD ~, supported by rising demand for portable and non-portable power, maintenance-free systems, and higher-power electronics for modern missions.
Dominance in military power solutions demand is concentrated in locations where defense procurement, integration, and sustainment ecosystems are deepest. In KSA, Riyadh leads due to central defense procurement, program management, and headquarters-led modernization initiatives; Jeddah gains importance through Red Sea maritime infrastructure and naval support activities; and the Eastern Province (notably Dhahran/Dammam/Jubail) benefits from critical infrastructure density and industrial capability that supports large-scale facilities power needs. Globally, the United States, Western Europe, and select Asia-Pacific countries dominate due to larger defense-industrial bases, high operational tempo, and accelerated electrification of platforms and mission systems.
Market Segmentation
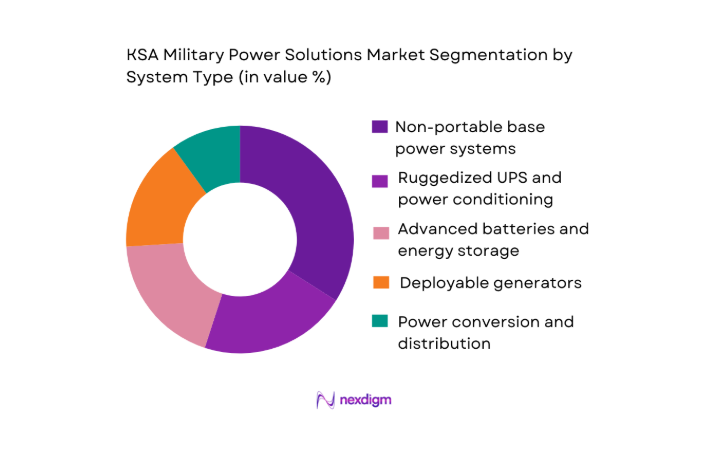
By System Type
By System Type: KSA military power solutions demand is segmented into non-portable base power systems, ruggedized UPS and conditioning, advanced batteries and energy storage, deployable generators, and power conversion/distribution equipment. Recently, non-portable base power systems have a dominant share because KSA’s defense posture relies on persistent readiness across fixed sites—airbases, command centers, radar locations, and critical defense infrastructure—where power continuity, redundancy, and hardening are decisive procurement criteria. These solutions also bundle high-value subsystems (switchgear, controls, power management software, cybersecurity-hardening, and integration services), which typically increases contract size versus discrete portable items. Their dominance is reinforced by sustainment-heavy buying behavior: multi-year service, spares, and upgrades for installed power architectures drive recurring spend beyond initial hardware.
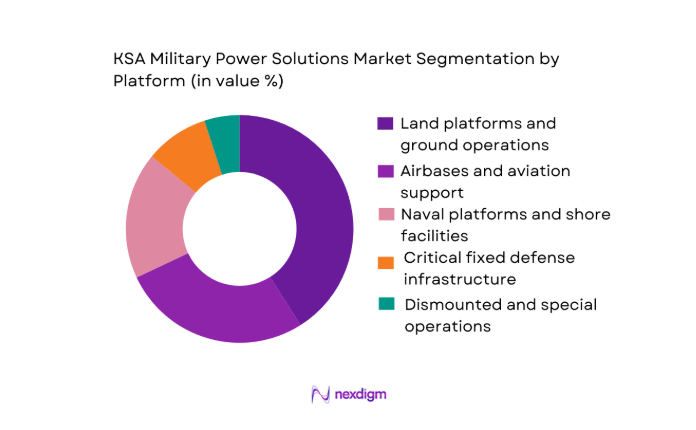
By Platform/Application
By Platform/Application: The KSA military power solutions market is segmented into land platforms and ground operations, airbases and aviation support, naval platforms and shore facilities, critical fixed defense infrastructure, and dismounted/special operations. Land platforms and ground operations dominate because ground formations and border/area security missions require the broadest mix of power products at scale—vehicle electrical upgrades, silent-watch batteries, tactical generators, field distribution, and deployable base packages. Land operations also tend to be power-intensive due to increasing electronics density (communications, sensors, counter-UAS, electronic warfare, mission computing) and the operational need to run these systems in austere environments where grid reliability is variable. In procurement terms, land dominance is further supported by higher unit counts (vehicles, shelters, field nodes) and frequent retrofit cycles to keep legacy fleets compatible with modern mission loads.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape for KSA military power solutions features a blend of global defense primes, specialized power-electronics/battery firms, and KSA-linked entities involved in integration and localization. Consolidation is visible at the program level because large power packages—especially for bases and platforms—are often bundled into prime contracts with stringent qualification, cybersecurity, and lifecycle support requirements. Players with proven MIL-STD ruggedization, regional sustainment capacity, and the ability to integrate power with broader C4ISR or platform upgrades are typically better positioned to win multi-year opportunities.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | KSA Presence/Partnership Readiness | Core Military Power Offerings | Ruggedization & Compliance | Integration Capability | Lifecycle Support Footprint | Localization/Industrial Participation |
| Raytheon (Raytheon Technologies) | 1922 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Cummins | 1919 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| EnerSys | 1999 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saft (TotalEnergies) | 1918 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Himoinsa (Yanmar Company) | 1982 | Spain | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA military power solutions Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Force modernization programs increasing onboard power demand for sensors, EW, and C4ISR
Modern military forces are integrating advanced sensor suites, electronic warfare modules, and command, control, communications, computers, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (C4ISR) systems that require persistent, high‑quality electrical power. Saudi Arabia’s military expenditure reached approximately USD ~ in 2024, reflecting substantial allocation toward platform upgrades and modernization. This budgetary environment supports procurement of sophisticated power solutions to support high throughput sensors and mission systems, as well as hardened electrical systems capable of uninterrupted performance in contested environments. The increased investment profile for defense systems directly correlates with the demand for rugged power generation, conditioning, and storage solutions across multiple platforms.
Expansion of forward‑deployed infrastructure requiring resilient power and microgrid capability
Military installations increasingly seek resilient power architectures that maintain continuous operations despite grid outages or hostile action. In 2024, the global military microgrid market was valued at USD ~, indicating rising deployment of microgrid solutions for uninterrupted power at bases and forward operating locations. These deployments enhance operational readiness by integrating generators, energy storage, and control systems to ensure critical systems remain powered during contingencies. The World Bank has noted that energy sector enhancements connect millions to reliable electricity while improving energy security, which aligns with defense requirements for resilient power infrastructures. Resilient microgrid architectures reduce reliance on vulnerable grid connections and support autonomous base functionality.
Market Challenges
Qualification and certification requirements for ruggedization, EMI/EMC, and environmental compliance
Military power solutions must meet stringent ruggedization, electromagnetic interference (EMI), and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards to operate in harsh environments and co‑exist with sensitive mission systems. Certification authorities require compliance with standards such as MIL‑STD‑188‑125 and similar frameworks to verify performance reliability. These requirements increase product development cycles, testing overhead, and supplier costs. For example, the 2024 military and aerospace EMC guide outlines testing and compliance processes that equipment must undergo to demonstrate EMI/EMC performance, necessitating extensive lab certification and field validation.
Supply chain constraints for high‑density batteries, power electronics, and specialized components
The global power electronics and high‑density battery supply chain faces pressure from competition across commercial and defense sectors. While precise defense supply chain volumes are not centrally published by macro bodies, the broader rugged electronics market was valued at USD ~ million in 2024, reflecting intense demand for components rated for extreme conditions. These high‑reliability components—necessary for military power systems—depend on specialized semiconductor fabrication, rare earth materials, and advanced manufacturing techniques. Constrained production capacities and geopolitical supply tensions have periodically restricted availability of these critical inputs, affecting lead times and procurement planning for defense integrators.
Opportunities
Hybridization and electrification upgrades for tactical vehicles to reduce fuel logistics and improve silent watch
Tactical vehicle fleets are exploring hybrid powertrain and electrification strategies to reduce logistical burdens associated with liquid fuel supply chains and improve mission capabilities like silent watch. Macroeconomic drivers for electric power adoption include global expansions in renewable energy and battery deployments, where record increases of 741 gigawatts in renewable capacity underscore broader power infrastructure shifts. Electrified tactical vehicles equipped with advanced battery systems can operate auxiliary systems silently without idling engines, reducing fuel consumption and heat/acoustic signatures. Such upgrades also align with military interest in sustainability and logistical efficiency, driving demand for high‑density batteries and power management electronics.
Deployment of containerized microgrids for bases with renewables integration and advanced energy management
The sector’s move toward containerized microgrid solutions allows bases to integrate renewable generation with storage and control systems, enhancing energy independence and reducing reliance on vulnerable supply lines. The World Bank’s energy programs, which supported access to electricity for ~ people and mobilized significant capital toward resilient energy frameworks, illustrate the broader momentum toward distributed and resilient power infrastructure. Such containerized solutions not only improve operational uptime but also enable defense facilities to experiment with renewable integration, predictive energy management, and grid independence functions that mirror civilian energy resilience strategies.
Future Outlook
Over the medium term, KSA’s military power solutions demand is expected to expand as electrification of platforms accelerates and base resilience becomes a core readiness requirement. Increased deployment of sensor-heavy systems, counter-UAS architectures, and networked C4ISR will keep pushing power density and uptime requirements. Global market indicators also point to sustained growth in military power solutions driven by modernization and energy resilience priorities. In addition, growth is likely to concentrate around hybrid systems, smart power management, hardened microgrids, and higher-density batteries that reduce fuel logistics while improving operational signatures.
Major Players
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Advanced Electronics Company
- Raytheon Technologies
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- General Dynamics
- BAE Systems
- Thales Group
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Rheinmetall AG
- Cummins Inc.
- EnerSys
- Saft
- SFC Energy AG
- Himoinsa
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Defense OEMs and prime contractors
- Base infrastructure operators and facility engineering procurement teams
- Energy storage and power electronics manufacturers
- System integrators for C4ISR, EW, and counter-UAS deployments
- Logistics and sustainment providers for deployed operations
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Critical infrastructure security operators supporting defense-linked sites
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study begins by mapping the ecosystem for the KSA military power solutions market, covering defense buyers, local integrators, global OEMs, and sustainment partners. Secondary research is used to define the operating boundary of “military power solutions” across generation, storage, conditioning, conversion, and distribution. This step identifies variables such as platform electrification intensity, base hardening needs, and lifecycle sustainment requirements.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical demand signals are compiled from defense spending context, modernization priorities, and global market benchmarks for military power solutions. The market structure is constructed by aligning power solutions with platform/application demand centers (land, airbase, naval, fixed sites, dismounted). Procurement patterns (prime-led bundling, retrofit cycles, sustainment contracts) are analyzed to understand revenue formation and solution mix.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on segment dominance and buying criteria are validated through structured expert inputs from OEM/channel participants and defense-industry practitioners. Interviews focus on qualification requirements, integration complexity, typical contract packaging (hardware + integration + services), and sustainment expectations. Insights are used to refine segmentation logic and competitive positioning.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are triangulated across disclosed market figures, defense spending context, and supplier capability assessments. The final output integrates market narrative, segment structure, competitive benchmarking parameters, and future opportunity areas (microgrids, hybridization, smart power management, higher-density batteries). The synthesis emphasizes consistency checks and alignment of assumptions with observable procurement and technology trends.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Definition and Scope
- Market dynamics
- Historical overview
- Timeline
- Growth Drivers
Force modernization programs increasing onboard power demand for sensors, EW, and C4ISR
Expansion of forward-deployed infrastructure requiring resilient power and microgrid capability
Lifecycle extension of legacy fleets driving retrofits for higher efficiency and reliability - Market Challenges
Qualification and certification requirements for ruggedization, EMI/EMC, and environmental compliance
Supply chain constraints for high-density batteries, power electronics, and specialized components
Integration complexity across mixed fleets with disparate voltage standards and legacy architectures - Opportunities
Hybridization and electrification upgrades for tactical vehicles to reduce fuel logistics and improve silent watch
Deployment of containerized microgrids for bases with renewables integration and advanced energy management
Localization of assembly and component manufacturing aligned with defense industrialization initiatives - Trends
Adoption of intelligent power management, health monitoring, and predictive maintenance for mission-critical systems
Rising demand for silent and low-signature power solutions supporting ISR and special operations - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Porters 5 forces
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Volume, 2020-2025
- By Average Price, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Tactical vehicle powertrain and alternator systems
Uninterruptible power supply and power conditioning units
Battery energy storage and smart battery packs
Deployable field generators and microgrids
Power distribution units, converters, and inverters - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Land combat vehicles and armored fleets
Naval vessels and shore-based naval facilities
Military aircraft and airbase ground support equipment
Fixed defense installations and command centers
Forward operating bases and expeditionary camps - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
OEM fitment for new platforms
Retrofit and upgrade fitment for legacy fleets
Modular mission-kit fitment for rapid deployment
Facility and infrastructure integration fitment
Ruggedized portable fitment for dismounted operations - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Ministry of Defense land forces units
Royal Saudi Air Force bases and squadrons
Royal Saudi Naval Forces fleets and ports
National Guard operational units
Border security and critical infrastructure protection units - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct government-to-OEM contracting
Prime contractor integration programs
Local defense manufacturing and offset partnerships
- Market Share Analysis
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Local content capability, Ruggedization and MIL-STD compliance, Power density and efficiency, Integration and interoperability, Lifecycle support and MRO footprint, Total cost of ownership)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing Analysis of Major Players
- Key Players
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
Advanced Electronics Company
Middle East Battery Company
Abunayyan Holding Energy Solutions
Zamil Power Systems
BAE Systems
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon Technologies
Northrop Grumman
General Dynamics Mission Systems
Thales Group
Saab AB
Leonardo S.p.A.
Rheinmetall AG
Rolls-Royce Power Systems
- Increasing requirement for silent watch and reduced thermal/acoustic signatures in tactical operations
- Preference for modular, rapidly deployable power packages to support expeditionary and border missions
- Growing emphasis on availability and sustainment, favoring solutions with local MRO and spares capability
- Higher specification demand for cybersecurity and system assurance in power management software and controllers
- By Market Value, 2026-2035
- By Volume, 2026-2035
- By Average Price, 2026-2035