Market Overview
The KSA Military Radars Market market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady expansion driven by sustained defense modernization and heightened airspace security requirements. Over the most recent two fiscal cycles, annual spending levels have moved from approximately USD ~ million to nearly USD ~ million, supported by multi-year acquisition programs and system upgrades. Active deployments now exceed ~ systems across air, land, and naval forces, with ongoing investments directed toward advanced detection, tracking, and integrated command networks.
Market activity is concentrated around Riyadh, Jeddah, and Dhahran due to the presence of defense command centers, air bases, naval ports, and major procurement authorities. These locations benefit from dense infrastructure, skilled engineering pools, and proximity to logistics corridors that support system installation and lifecycle services. Strong policy backing for domestic defense production and technology transfer further strengthens ecosystem maturity, making these hubs central to demand generation and long-term industry development.
Market Segmentation
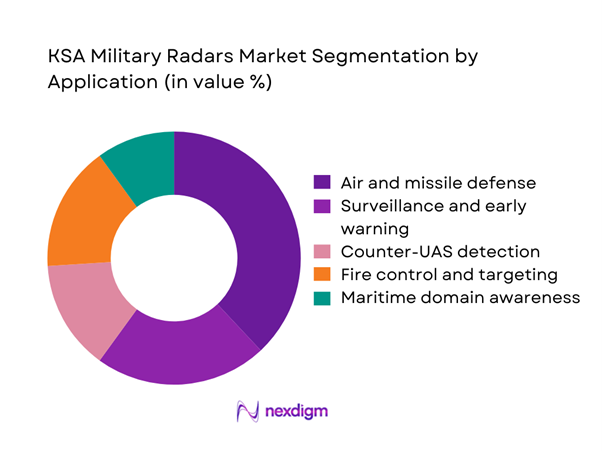
By Application
Air and missile defense remains the dominant application segment as national security priorities emphasize protection against aerial threats and strategic assets. Continuous upgrades of interception networks and early warning capabilities have accelerated demand for long-range and multi-mission radar platforms. Surveillance and border monitoring also contribute significantly, driven by the need for persistent situational awareness across extensive land and maritime frontiers. Fire control and targeting systems support precision engagement, while counter-UAS solutions are gaining traction in response to asymmetric threats. The combined effect of defense modernization, rising operational complexity, and the push toward integrated command structures sustains strong growth across these application areas.
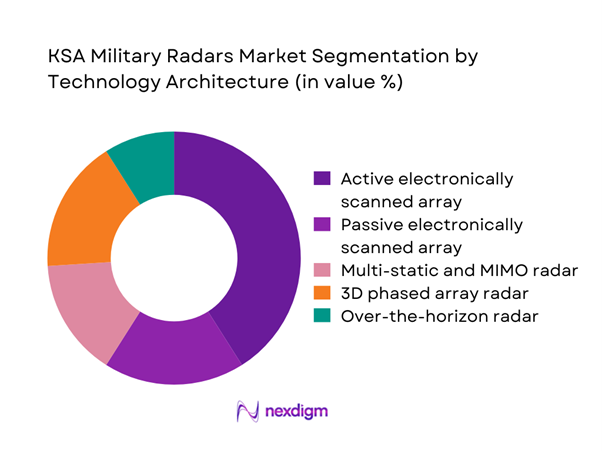
By Technology Architecture
Active electronically scanned array technology leads the market due to its superior detection range, tracking accuracy, and multi-target engagement capability. Defense forces increasingly favor software-defined and reconfigurable systems that can adapt to evolving threat environments without extensive hardware changes. Passive and multi-static radar architectures are gaining relevance for stealth detection and low-probability-of-intercept operations. Over-the-horizon systems remain niche but strategically important for long-range surveillance. Overall, the shift toward network-centric warfare and sensor fusion reinforces demand for advanced architectures that integrate seamlessly into national air defense and command frameworks.
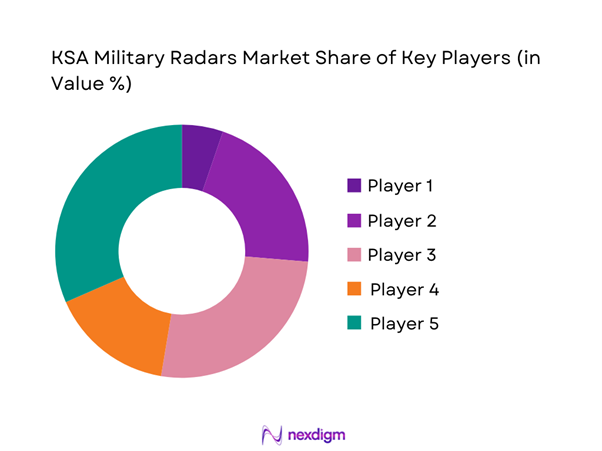
Competitive Landscape
The market is moderately concentrated, with a limited group of global defense electronics leaders and emerging domestic manufacturers shaping technology standards and procurement dynamics. Long-term supply contracts, system integration capabilities, and localized support services play a critical role in competitive positioning, while government initiatives to expand local content are gradually reshaping market structure.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saudi Arabian Military Industries | 2017 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Military Radars Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising regional security threats and missile proliferation
In the most recent operational cycles, defense agencies increased surveillance coverage across ~ km of strategic airspace, deploying over ~ systems to strengthen early warning and interception layers. Annual allocations equivalent to USD ~ million have supported accelerated procurement of long-range detection platforms and mobile radar units. The expansion of missile defense networks has led to the installation of ~ integrated command nodes, improving response coordination. Border monitoring programs added ~ mobile stations to enhance situational awareness. These numeric shifts highlight how escalating regional risks are translating directly into higher deployment volumes and sustained capital inflows for advanced radar infrastructure.
Modernization of air defense under Vision 2030
Modernization initiatives have driven the replacement of ~ legacy platforms with digitally networked systems across major air bases and naval facilities. Over the past planning cycles, defense authorities committed close to USD ~ million toward system upgrades, including the rollout of ~ new-generation radar arrays. Integration programs connected ~ command centers into unified air defense networks, reducing response times and improving threat tracking accuracy. Workforce development efforts trained ~ technical specialists in radar maintenance and data analytics. These quantified investments demonstrate how long-term transformation agendas are reshaping procurement volumes and accelerating technology adoption.
Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle costs of advanced radar systems
Recent procurement programs show that deploying a single multi-mission radar platform requires capital commitments approaching USD ~ million, with lifecycle support adding nearly USD ~ million over operational periods. Annual maintenance for ~ deployed systems absorbs a significant share of defense electronics budgets, limiting the pace of fleet expansion. Spare parts inventories now exceed ~ components to ensure readiness, increasing storage and logistics demands. Training costs for ~ technicians further elevate total ownership expenditure. These numeric pressures constrain procurement cycles and necessitate careful prioritization across competing defense modernization needs.
Dependence on foreign technology for key subsystems
Current supply chains indicate that over ~ critical components per system originate from overseas manufacturers, resulting in extended lead times of ~ months for specialized modules. Import programs valued at USD ~ million annually underline the scale of reliance on external sources. Delays affecting ~ scheduled installations have highlighted vulnerabilities in deployment timelines. Localization efforts have so far replaced only ~ subsystems with domestic alternatives, leaving a substantial technology gap. These figures emphasize the operational and strategic risks associated with continued dependence on foreign inputs.
Opportunities
Expansion of local manufacturing and technology transfer programs
Industrial development plans target the establishment of ~ new defense electronics facilities capable of assembling ~ systems annually. Public and private commitments totaling USD ~ million are earmarked for joint ventures focused on radar production and testing. Workforce initiatives aim to certify ~ engineers in advanced RF and signal processing disciplines. Localization roadmaps project the substitution of ~ imported components with domestically produced alternatives, reducing lead times by ~ weeks. These quantified initiatives signal strong potential for building a resilient local supply base and enhancing long-term self-reliance.
Development of indigenous AESA and counter-UAS radar solutions
Research programs have allocated nearly USD ~ million toward prototype development of next-generation AESA platforms, with field trials covering ~ operational sites. Early deployments include ~ counter-UAS detection units protecting critical facilities and air bases. Performance testing across ~ scenarios has demonstrated improved target classification and reduced false alerts. Planned scale-up envisions the production of ~ indigenous systems over upcoming procurement cycles. These numeric indicators reflect a growing opportunity to establish homegrown technologies that meet evolving threat profiles and support export ambitions.
Future Outlook
The market is positioned for sustained expansion as national defense priorities continue to emphasize integrated air and missile defense capabilities. Ongoing localization initiatives and technology transfer programs are expected to reshape supply chains and enhance domestic manufacturing depth. Increased adoption of software-defined and network-centric radar systems will strengthen interoperability across forces. Over the coming years, strategic investments are likely to balance immediate security needs with long-term industrial development objectives.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Raytheon
- Northrop Grumman
- Thales
- Leonardo
- Saab
- BAE Systems
- Indra Sistemas
- Hensoldt
- Elta Systems
- ASELSAN
- Rheinmetall
- Kongsberg Defence and Aerospace
- L3Harris Technologies
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
Key Target Audience
- Saudi Ministry of Defense and procurement directorates
- Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces and operational commands
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Ministry of Interior security agencies
- Border Guard and coastal protection authorities
- State-owned defense manufacturing enterprises
- Investments and venture capital firms focused on defense technologies
- National security and strategic planning councils
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope was defined around defense radar applications, technology architectures, and end-user segments. Key demand indicators included deployment volumes, system upgrades, and integration programs. Supply-side variables focused on manufacturing capacity, localization initiatives, and technology readiness. Regulatory and procurement frameworks were mapped to understand purchasing cycles and approval processes.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Quantitative modeling incorporated masked financial indicators, deployment counts, and infrastructure expansion metrics. Segment-wise assessment evaluated application demand, regional concentration, and technology adoption patterns. Scenario development considered policy direction, security dynamics, and industrial participation. Data consistency checks ensured alignment across demand and supply perspectives.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry experts and defense practitioners reviewed key assumptions on procurement trends, localization impact, and technology pathways. Validation workshops tested scenario robustness against operational realities. Feedback loops refined growth drivers, challenge severity, and opportunity potential. Iterative reviews strengthened analytical accuracy and strategic relevance.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated into a cohesive narrative linking market dynamics with policy and industrial objectives. Comparative assessment highlighted structural shifts and competitive positioning. Final outputs emphasized actionable intelligence for stakeholders across procurement, manufacturing, and investment domains. Quality assurance ensured clarity, consistency, and publication readiness.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, military radar system taxonomy across surveillance fire control and air defense applications, market sizing logic by platform deployment and modernization cycles, revenue attribution across equipment upgrades spares and support services, primary interview program with defense operators OEMs and system integrators, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and mission usage pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and local manufacturing landscape
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising regional security threats and missile proliferation
Modernization of air defense under Vision 2030
Increased defense budgets and force transformation programs
Shift toward network-centric and integrated air defense systems
Localization mandates boosting domestic radar production
Expansion of border security and critical infrastructure protection - Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle costs of advanced radar systems
Dependence on foreign technology for key subsystems
Complex integration with legacy command and control platforms
Skilled workforce shortages in advanced RF and signal processing
Long procurement cycles and multi-layered approval processes
Cybersecurity risks in networked radar architectures - Opportunities
Expansion of local manufacturing and technology transfer programs
Development of indigenous AESA and counter-UAS radar solutions
Upgrades and mid-life modernization of legacy radar fleets
Export potential to GCC and MENA allied defense forces
Adoption of AI-enabled signal processing and threat classification
Public-private partnerships in defense electronics production - Trends
Transition toward multi-mission and software-defined radars
Growing deployment of mobile and rapidly deployable radar units
Integration of radars into joint all-domain command frameworks
Increased use of passive and low-probability-of-intercept radars
Emphasis on interoperability with allied defense systems
Adoption of predictive maintenance and digital twins - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Royal Saudi Land Forces
Royal Saudi Air Force
Royal Saudi Naval Forces
Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces
Border Guard and Internal Security Forces - By Application (in Value %)
Air and missile defense
Surveillance and early warning
Counter-UAS and asymmetric threat detection
Fire control and targeting
Maritime domain awareness
Ballistic missile defense - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Active Electronically Scanned Array radar
Passive Electronically Scanned Array radar
MIMO and multi-static radar systems
3D phased array radar
Over-the-horizon radar - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Ministry of Defense
Ministry of Interior and Homeland Security
Border security and coastal protection agencies
Critical infrastructure protection authorities
Strategic and space defense organizations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone radar systems
C2-integrated networked radars
Sensor-fusion enabled systems
Cloud-enabled defense networks
SATCOM-linked remote radar nodes - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology maturity, local content ratio, integration capability, lifecycle support, pricing competitiveness, delivery timelines, cybersecurity compliance, interoperability standards)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Raytheon
Northrop Grumman
Thales
Leonardo
Saab
BAE Systems
Indra Sistemas
Hensoldt
Elta Systems
ASELSAN
Rheinmetall
Kongsberg Defence and Aerospace
L3Harris Technologies
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Demand and utilization drivers across air, land, and naval forces
- Procurement and tender dynamics under centralized defense buying
- Buying criteria and vendor selection for mission-critical systems
- Budget allocation and financing preferences in multi-year programs
- Implementation barriers and operational risk factors
- Post-purchase support, MRO, and upgrade expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


