Market Overview
The KSA military radars market is valued at USD~ billion, supported by sustained defense modernization programs, integrated air and missile defense investments, and multi-domain surveillance requirements. Defense expenditure levels of USD ~ billion and USD ~ billion underpin radar procurement across air defense, border security, and naval surveillance roles. Demand is driven by the need for early-warning coverage, counter-UAS detection, and integration with command-and-control architectures, as validated by defense budget disclosures and SIPRI defense expenditure datasets.
Riyadh dominates the market due to centralized defense procurement, national command infrastructure, and proximity to the Ministry of Defense and Air Defense Forces headquarters. Jeddah and Jubail hold strategic importance through naval surveillance and coastal radar deployments supporting Red Sea and Arabian Gulf security. International dominance is led by the United States, Israel, France, and Germany due to their mature AESA radar technologies, integrated air defense expertise, and long-standing government-to-government defense supply frameworks supporting high-end radar deployments.
Market Segmentation
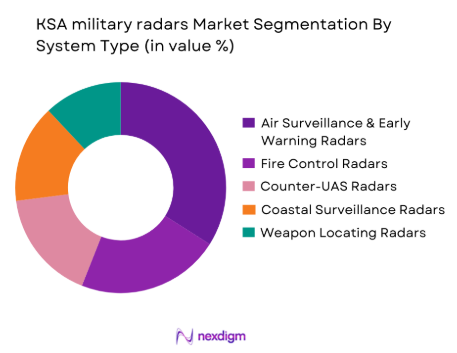
By System Type
The KSA military radars market is segmented by radar system type into air surveillance and early warning radars, fire control radars, counter-UAS radars, coastal surveillance radars, and weapon locating radars.Among these, air surveillance and early warning radars dominate the market share due to their critical role in national airspace protection and missile threat detection. These systems form the backbone of layered air defense networks, providing long-range detection and target tracking for ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and hostile aircraft. Saudi Arabia’s focus on integrating these radars with interceptor systems and command networks further strengthens demand. Their high unit cost, advanced AESA architecture, and strategic importance in national defense infrastructure contribute significantly to overall market value.
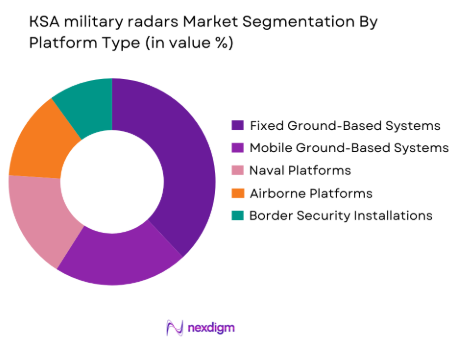
By Platform Type
By platform type, the market is segmented into fixed ground-based systems, mobile ground-based systems, naval platforms, airborne platforms, and border security installations. Fixed ground-based radar systems hold the dominant share as they support permanent air defense sites, strategic installations, and critical infrastructure protection. These systems offer higher power output, extended detection range, and long operational lifecycles compared to mobile alternatives. Their integration into national command networks and missile defense architectures makes them indispensable for continuous surveillance. High capital expenditure per installation and long-term sustainment contracts further reinforce their dominance within the platform segmentation.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA military radars market is highly consolidated, dominated by a limited number of global defense OEMs with advanced radar portfolios and long-standing defense relationships with Saudi Arabia. These players benefit from government-to-government contracts, localization initiatives, and integration capabilities across air defense and command systems. Competition is shaped by technology maturity, AESA capabilities, lifecycle support, and compliance with localization and offset requirements.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Radar Technology Depth | AESA Capability | IAMD Integration | Localization Presence | Lifecycle Support | Export Track Record |
| Raytheon | 1922 | United States | Very High | Yes | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | Very High | Yes | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales | 1893 | France | High | Yes | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | High | Yes | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| HENSOLDT | 2017 | Germany | High | Yes | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Military Radars Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expanding integrated air and missile defense requirements
The military radar market in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is strongly driven by expanding air and missile defense requirements across national airspace and critical infrastructure. Rising deployment of layered defense architectures has increased demand for long-range surveillance radars, fire-control radars, and early-warning systems capable of detecting ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, and low-observable aerial threats. Radar procurement is closely linked with investments in integrated command-and-control networks, where sensor fusion and real-time data sharing are essential. The need to protect energy infrastructure, population centers, airbases, and ports has accelerated the acquisition of fixed and mobile radar systems. Additionally, interoperability with allied platforms and coalition defense systems encourages adoption of advanced radar technologies with standardized interfaces and secure data links. Continuous system upgrades, rather than one-time purchases, further sustain demand by extending radar coverage, accuracy, and electronic counter-countermeasure performance across evolving threat environments.
Modernization of air, land, and naval platforms
Platform modernization across air, land, and naval forces is another major growth driver for the military radar market. New fighter aircraft, rotary-wing platforms, armored vehicles, and naval vessels require advanced radar suites for surveillance, targeting, navigation, and threat detection. Airborne radars with active electronically scanned array capabilities are increasingly preferred for their multi-mode operation and resilience against jamming. On land, ground surveillance and counter-battery radars support border security and force protection missions. Naval modernization programs drive demand for multifunction radars that combine air search, surface search, and missile guidance roles. Radar upgrades are also integral to extending the service life of legacy platforms, enabling improved situational awareness without full fleet replacement. As platform digitization progresses, radars are being integrated with electro-optical sensors, electronic warfare systems, and battle management software, reinforcing their central role in next-generation combat systems.
Market Challenges
High acquisition costs and complex lifecycle support
High acquisition costs present a significant challenge in the military radar market. Advanced radar systems require substantial upfront investment due to sophisticated hardware, specialized materials, and complex software architectures. Costs extend beyond procurement to include installation, integration, testing, training, and long-term maintenance. Lifecycle support demands highly skilled personnel, specialized calibration equipment, and periodic software and hardware upgrades to maintain performance against evolving threats. For large-area surveillance radars, infrastructure requirements such as dedicated power supply, cooling systems, and hardened installations add further expense. Budget prioritization across competing defense needs can delay radar acquisition or limit fleet-wide deployment. Additionally, dependence on foreign original equipment manufacturers for spares and technical support may increase sustainment costs and extend repair timelines, creating operational readiness challenges over the system’s service life.
Integration and interoperability complexity
Integration complexity remains a key challenge for military radar deployment. Modern defense operations require radars to operate seamlessly within network-centric environments, exchanging data with command systems, interceptors, aircraft, and allied forces. Integrating new radar systems with legacy platforms can be technically demanding, particularly when proprietary architectures or outdated interfaces are involved. Achieving interoperability across different service branches further increases complexity, as air, land, and naval forces often operate distinct command-and-control frameworks. Cybersecurity requirements add another layer of difficulty, as radars must be protected against cyber intrusion and data manipulation. Delays in integration testing or software certification can postpone operational deployment. These technical challenges can increase program risk, extend timelines, and raise total ownership costs, especially for multi-sensor, multi-domain defense architectures.
Opportunities
Localization, technology transfer, and domestic capability building
Localization initiatives create significant opportunities in the military radar market. Policies encouraging domestic manufacturing, assembly, and maintenance enable international radar suppliers to form partnerships with local defense firms. Establishing in-country production lines and support facilities can reduce long-term sustainment costs, improve system availability, and strengthen supply chain resilience. Technology transfer agreements allow local entities to develop expertise in radar subsystems, software integration, and lifecycle management. Over time, this supports the creation of indigenous radar variants tailored to specific operational requirements and environmental conditions. Localization also facilitates faster upgrades and customization, aligning radar performance with evolving threat profiles. For suppliers, participation in local industrial ecosystems enhances competitiveness in future procurement programs while contributing to national defense industrial growth objectives.
Demand for advanced technologies and multi-domain sensing
Growing interest in advanced radar technologies presents strong market opportunities. Demand is increasing for active electronically scanned array radars, digital beamforming, artificial intelligence–enabled signal processing, and multi-static radar concepts. These technologies enhance detection of low-altitude and low-observable targets, improve clutter rejection, and enable simultaneous multi-mission operation. There is also rising interest in radars optimized for counter-unmanned aerial system missions, border surveillance, and maritime domain awareness. Integration of radar data with space-based sensors and unmanned platforms supports multi-domain situational awareness. As threats become more diverse and complex, opportunities expand for modular, software-defined radar architectures that can be upgraded through software rather than hardware replacement, extending system relevance and creating recurring upgrade and support demand.
Future Outlook
Over the next decade, the KSA military radars market is expected to experience sustained growth driven by continued investments in air and missile defense, border surveillance modernization, and counter-UAS capabilities. The market is projected to register a forecast CAGR of 5.8% during the 2026–2035 period, supported by new radar acquisitions, system upgrades, and network-centric warfare initiatives. Increased focus on localization, electronic warfare resilience, and multi-mission radar platforms will further shape procurement strategies and long-term demand patterns.
Major Players
- Raytheon
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Thales
- Leonardo
- BAE Systems
- Saab
- HENSOLDT
- IAI ELTA Systems
- Elbit Systems
- L3Harris Technologies
- Indra Sistemas
- ASELSAN
- RTX Collins Aerospace
- Rheinmetall
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defense, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces
- Royal Saudi Air Force Procurement Command
- Royal Saudi Naval Forces Systems Directorate
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Border Guard Directorate, Ministry of Interior
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping the defense radar ecosystem in Saudi Arabia, identifying stakeholders, procurement bodies, and OEMs. Secondary sources, defense databases, and government publications are analyzed to define critical market variables influencing radar demand.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical defense procurement data and radar program announcements are analyzed to construct market size estimates. Platform penetration, deployment density, and system pricing benchmarks are evaluated to ensure accuracy.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions are validated through structured consultations with defense analysts, system integrators, and former procurement officials to confirm technology trends and investment priorities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights from OEM interactions and defense offset disclosures are synthesized with bottom-up analysis to finalize market sizing, segmentation, and competitive assessment.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Integrated air and missile defense modernization and layered coverage requirements
Border and critical infrastructure protection priorities driving persistent surveillance demand
Fleet upgrades and digital networking to improve detection, tracking, and resilience - Market Challenges
Dependence on export licensing, technology transfer constraints, and geopolitical approvals
Interoperability and integration complexity across heterogeneous legacy and new systems
High lifecycle costs driven by sustainment, spares, calibration, and obsolescence management - Market Opportunities
Localization and in-KSA assembly, testing, and depot-level maintenance under industrial policy goals
Expansion of counter-UAS and short-range air defense sensor layers around high-value assets
Advanced AESA and multi-mission radars enabling consolidation of roles and networked operations - Trends
Shift toward AESA, software-defined waveforms, and electronic protection enhancements
Greater sensor fusion with C2, IAMD, and multi-domain networks for real-time threat picture
Increased use of mobile and rapidly deployable radars to improve survivability and coverage flexibility
- By Market Value 2020-2025
- By Installed Units 2020-2025
- By Average System Price 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Air Surveillance & Early Warning Radars
Ground-Based Air Defense Fire-Control Radars
Counter-UAS / Short-Range Air Defense Radars
Coastal Surveillance & Maritime Domain Awareness Radars
Weapon Locating / Counter-Battery Radars - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Fixed Site / Tower-Based Radar Installations
Mobile Ground-Based Radar Vehicles
Naval Surface Combatants & Patrol Vessels
Airborne Platforms (AEW&C / ISR Aircraft)
Border Security Integrated Sensor Sites - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
New Acquisition for Greenfield Deployments
Retrofit / Mid-Life Upgrade of Legacy Radar Sites
System Replacement on Existing Sites
Network Integration into National C2 / IAMD Architecture
Mission Module Fitment for Multi-Role Platforms - By End User Segment (In Value%)
Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces (RSADF)
Royal Saudi Air Force (RSAF)
Royal Saudi Naval Forces (RSNF)
Ministry of Interior Border Guard / Security Forces
National Guard & Joint Force Protection Units - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Government-to-Government
Direct OEM Prime Contracting with KSA MOD
Local Integrator / Offset-Backed Procurement
Consortium / Joint Venture Programs with Localization
Sustainment Contracts
- Market Share Analysis
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Detection range vs target class, AESA adoption level, electronic counter-countermeasures performance, network interoperability with IAMD/C2, mobility and deployment time, lifecycle cost and in-country support depth)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Competitors
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Key Players
Raytheon
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
BAE Systems
Thales
Leonardo
Saab
HENSOLDT
Rheinmetall
IAI ELTA Systems
Elbit Systems
ASELSAN
Indra Sistemas
L3Harris Technologies
RTX Collins Aerospace
- Air defense end users prioritize low-altitude detection, track density, and rapid cueing to interceptors
- Air force operators emphasize long-range air picture, integration with AEW&C, and joint command networks
- Naval end users require coastal and maritime surveillance with clutter rejection and surface tracking performance
- Security and border forces focus on persistent coverage, easy maintainability, and integration with ISR and command centers.
- Forecast Market Value 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform 2026-2035