Market Overview
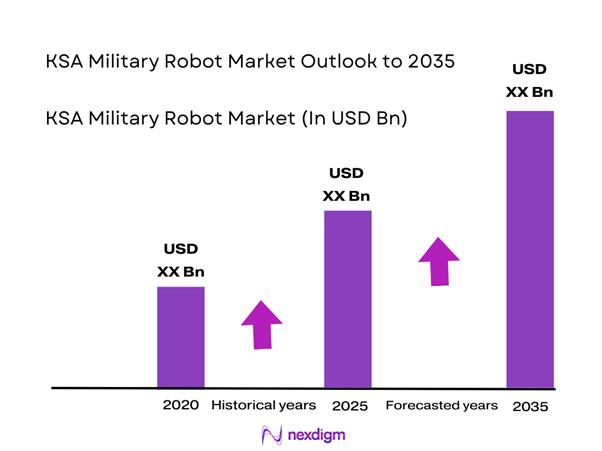
The KSA Military Robot market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady expansion driven by modernization priorities and operational demand for autonomous platforms. In the most recent year, spending on robotic ground and aerial systems reached nearly USD ~ million, rising from approximately USD ~ million in the preceding period. Active deployments now exceed ~ systems across surveillance, logistics, and explosive ordnance disposal missions. Procurement pipelines indicate sustained volume additions of ~ units annually, supported by long-term defense programs and multiyear acquisition frameworks.
The market is primarily concentrated in Riyadh, Jeddah, and the Eastern Province, where major defense headquarters, military bases, and industrial zones create strong demand density. These regions benefit from advanced testing infrastructure, proximity to command centers, and established defense manufacturing clusters. The presence of system integrators, training facilities, and secure logistics corridors further reinforces dominance. Supportive procurement policies and localization mandates also attract technology partnerships, accelerating ecosystem maturity and reinforcing these cities as strategic hubs for military robotics deployment.
Market Segmentation
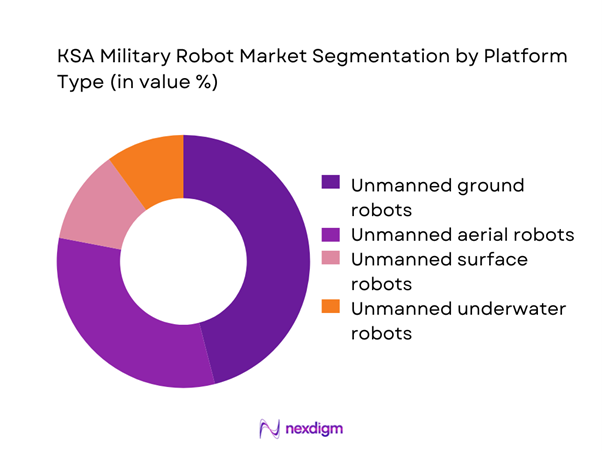
By Platform Type
Unmanned ground platforms dominate this segmentation due to their extensive use in border patrol, convoy protection, and explosive ordnance disposal missions. High utilization rates stem from terrain suitability and immediate operational impact, with deployments exceeding ~ systems in active service. Aerial robotic platforms follow closely, driven by surveillance and reconnaissance needs, while surface and underwater systems remain niche but strategic for naval security. Continuous upgrades in payload capacity and autonomous navigation have strengthened the position of ground-based robots, making them the preferred choice for near-term force modernization programs and sustained procurement pipelines.
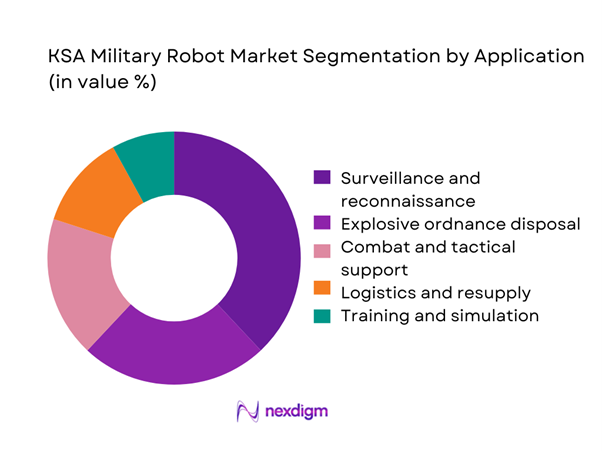
By Application
Surveillance and reconnaissance applications account for the largest share, supported by extensive border monitoring requirements and critical infrastructure protection. Annual deployments in this segment exceed ~ systems, driven by real-time intelligence needs and persistent monitoring capabilities. Explosive ordnance disposal remains a core application, reflecting continuous operational demand in urban security environments. Logistics support and combat assistance applications are gaining traction as forces seek to reduce manpower exposure in high-risk zones. The growing role of training and simulation platforms further diversifies application demand, strengthening long-term adoption trends across defense units.
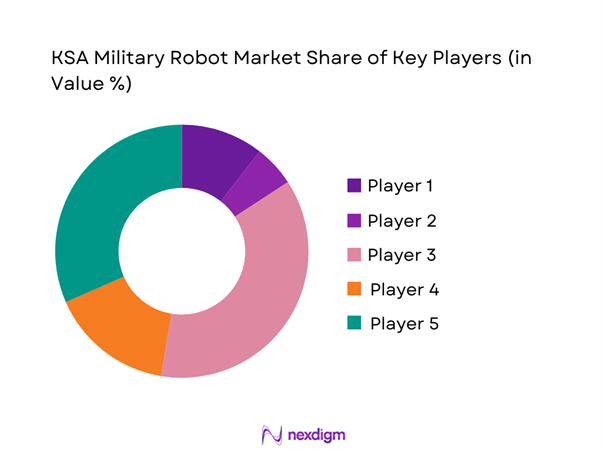
Competitive Landscape
The KSA military robot market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of domestic defense champions and established global system providers. Local firms benefit from procurement preferences and localization mandates, while international players bring advanced autonomy and combat-proven platforms. Strategic partnerships and joint ventures shape competitive dynamics, enabling technology transfer and long-term service contracts that reinforce market positioning.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Saudi Arabian Military Industries | 2017 | Riyadh | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BAE Systems | 1910 | London | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | Bethesda | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Haifa | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| QinetiQ | 2001 | Farnborough | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Military Robot Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising defense modernization under Vision 2030
Defense modernization programs have accelerated procurement of autonomous platforms, with annual allocations for advanced systems reaching USD ~ million across recent budget cycles. The introduction of new robotic fleets has added more than ~ systems into active service, strengthening surveillance, logistics, and force protection missions. Localization initiatives tied to national industrial strategies have driven contracts valued at nearly USD ~ million for domestic assembly and integration. These investments are reshaping force structure, enabling higher operational tempo while reducing personnel exposure in high-risk zones, thereby reinforcing sustained demand for military robotics across all service branches.
Increasing focus on force protection and soldier safety
Operational losses and risk mitigation strategies have intensified adoption of unmanned platforms, with deployments exceeding ~ systems dedicated to hazardous missions such as explosive disposal and forward reconnaissance. Annual procurement volumes have stabilized at ~ units to replace manual operations in high-threat environments. Defense planners now allocate close to USD ~ million per cycle toward robotic solutions that reduce casualty rates and improve mission endurance. This strategic shift toward automation in frontline operations continues to drive consistent spending and integration of robotics across tactical and support roles.
Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle maintenance costs
The average lifecycle investment per robotic platform now exceeds USD ~ million when factoring procurement, upgrades, and sustainment. Annual maintenance expenditures across deployed fleets approach USD ~ million, creating budgetary pressure for defense planners balancing multiple modernization priorities. Replacement cycles of ~ systems each year further elevate capital requirements, limiting rapid fleet expansion. These cost dynamics slow adoption among specialized units and necessitate phased procurement strategies, affecting near-term market scalability despite strong operational need.
Cybersecurity and electronic warfare vulnerabilities
Increased connectivity has exposed robotic platforms to electronic interference risks, prompting defense agencies to allocate nearly USD ~ million annually to secure communication upgrades. More than ~ systems have undergone cybersecurity retrofits to mitigate jamming and data interception threats. The complexity of protecting autonomous networks raises development costs and lengthens deployment timelines. Persistent vulnerability concerns also influence procurement approvals, as decision-makers prioritize hardened systems, which constrains rapid adoption of newer but less-tested robotic technologies.
Opportunities
Expansion of indigenous defense robotics manufacturing
Localization mandates have opened opportunities for domestic production facilities valued at over USD ~ million in planned capacity expansion. New assembly lines are expected to deliver ~ units annually, reducing reliance on imports and strengthening supply resilience. Technology transfer agreements tied to these facilities accelerate skills development and enable long-term export positioning. This shift toward indigenous manufacturing enhances cost control, shortens delivery cycles, and aligns with national industrial growth objectives, positioning local players to capture a larger share of future defense robotics demand.
Export potential to GCC and allied markets
Regional security cooperation creates export avenues for Saudi-developed platforms, with initial contract pipelines estimated at USD ~ million across neighboring states. Demonstration deployments of ~ systems in joint exercises have increased interest in standardized robotic solutions. Shared operational requirements and interoperability frameworks support cross-border sales, while competitive pricing and localized support models enhance appeal. Expanding exports strengthens economies of scale for manufacturers and diversifies revenue streams, reinforcing long-term market sustainability beyond domestic demand alone.
Future Outlook
The KSA military robot market is set to evolve rapidly as defense forces deepen reliance on autonomous and semi-autonomous systems across land, air, and maritime domains. Continued localization policies and technology partnerships will strengthen domestic capabilities, while operational experience will refine deployment models. Over the coming years, robotics will become integral to force structure, reshaping mission planning, logistics, and base security, and positioning the market as a strategic pillar of national defense modernization.
Major Players
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Advanced Electronics Company
- Intra Defense Technologies
- QinetiQ
- Teledyne FLIR Defense
- Rheinmetall Defence
- Elbit Systems
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- BAE Systems
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- Saab AB
- Thales Group
- Leonardo S.p.A.
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defense procurement divisions
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries strategic sourcing teams
- Border Guard and homeland security agencies
- Naval forces modernization departments
- Special operations command units
- Defense-focused investments and venture capital firms
- General Authority for Military Industries regulatory bodies
- Communications, Space and Technology Commission oversight agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Assessment of operational requirements, procurement cycles, and technology readiness levels across defense units. Mapping of platform categories and application areas shaping demand patterns. Compilation of deployment intensity and sustainment needs influencing lifecycle value.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Evaluation of procurement flows, contract structures, and localization mandates. Integration of deployment scale indicators and platform replacement cycles. Construction of demand scenarios aligned with defense modernization programs.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Consultation with defense program managers and system integrators. Validation of adoption drivers and operational constraints through field insights. Refinement of opportunity areas based on capability gaps and mission needs.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Consolidation of quantitative indicators and qualitative assessments. Alignment of findings with strategic defense priorities. Development of actionable market narratives for stakeholders.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, military robot taxonomy across ground aerial and maritime unmanned systems, market sizing logic by platform deployment and modernization programs, revenue attribution across system sales upgrades and support services, primary interview program with defense operators OEMs and system integrators, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and mission usage pathways
- Ecosystem structure across OEMs, system integrators, and defense agencies
- Supply chain and localization strategy
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising defense modernization under Vision 2030
Increasing focus on force protection and soldier safety
Expansion of border surveillance and counter-infiltration needs
Growth in asymmetric warfare and urban combat scenarios
Localization of defense manufacturing and technology transfer
Higher adoption of AI-enabled ISR capabilities - Challenges
High acquisition and lifecycle maintenance costs
Cybersecurity and electronic warfare vulnerabilities
Integration complexity with legacy command systems
Limited domestic supply of advanced robotics components
Skill gaps in autonomous system operation and maintenance
Regulatory constraints on autonomous weapon deployment - Opportunities
Expansion of indigenous defense robotics manufacturing
Export potential to GCC and allied markets
Development of dual-use military and homeland security robots
Growth in simulation-based robotic training platforms
Strategic partnerships with global defense OEMs
Adoption of swarm robotics for surveillance missions - Trends
Shift from teleoperated to autonomous combat support systems
Integration of AI-driven perception and targeting modules
Use of robotics in base security and perimeter defense
Increased use of unmanned logistics convoys
Adoption of digital twins for robotic fleet management
Emphasis on modular and upgradeable robot architectures - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Unmanned ground vehicles
Unmanned aerial systems
Unmanned surface vehicles
Unmanned underwater vehicles
Hybrid multi-domain robotic platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Surveillance and reconnaissance
Explosive ordnance disposal
Combat and tactical support
Logistics and resupply
Training and simulation
Border and critical infrastructure security - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Teleoperated systems
Semi-autonomous systems
Fully autonomous systems
AI-enabled decision support platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Land forces
Air forces
Naval forces
Border security and homeland defense
Special operations forces - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Line-of-sight radio control
Satellite communication enabled systems
Mesh network enabled systems
Secure tactical data link platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (autonomy level, payload capacity, mission endurance, cybersecurity resilience, system modularity, local manufacturing presence, lifecycle cost, after-sales support depth)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
Advanced Electronics Company
Intra Defense Technologies
QinetiQ
Teledyne FLIR Defense
Rheinmetall Defence
Elbit Systems
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
BAE Systems
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
General Dynamics Mission Systems
Saab AB
Thales Group
Leonardo S.p.A.
- Demand and mission utilization drivers
- Defense procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and system validation processes
- Budget allocation and multi-year defense financing models
- Implementation barriers and operational risk factors
- Post-deployment support and lifecycle service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


