Market Overview
The KSA Military Simulation and Training market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady expansion supported by defense modernization programs and rising adoption of synthetic training platforms. Recent annual spending levels have remained near USD ~ million in each of the last two periods, while active simulator deployments exceed ~ systems across air, land, and naval forces. Ongoing infrastructure investments of nearly USD ~ million annually continue to strengthen local training capacity and reduce dependence on overseas facilities.
The market is primarily concentrated in Riyadh, Dhahran, and Jeddah, where defense command centers, air bases, and naval training hubs create sustained demand for advanced simulation environments. These cities benefit from mature defense ecosystems, proximity to procurement authorities, and access to skilled technical workforces. Strong policy alignment with national defense localization goals further reinforces regional dominance, supported by expanding industrial clusters focused on digital defense solutions and mission-critical training technologies.
Market Segmentation
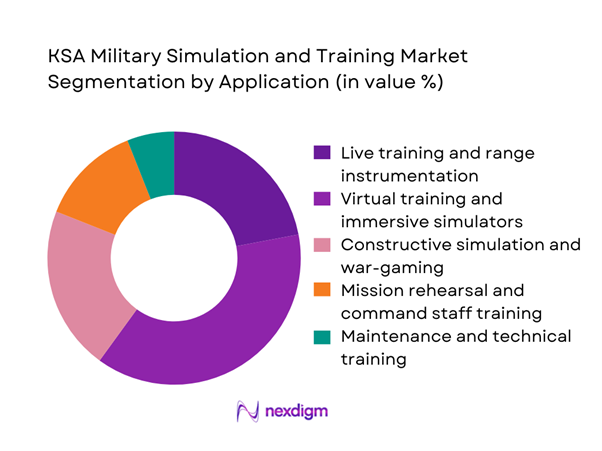
By Application
Virtual training and immersive simulators dominate the KSA Military Simulation and Training market, driven by the armed forces’ increasing reliance on cost-efficient and scalable alternatives to live exercises. Over ~ systems currently in operation are aligned with flight simulation, mission rehearsal, and tactical decision training. Annual deployment levels exceed ~ units, supported by infrastructure investments of nearly USD ~ million in centralized training hubs. These platforms offer consistent performance tracking, safer operational environments, and faster skill acquisition cycles, making them the preferred choice for both frontline units and specialized forces.
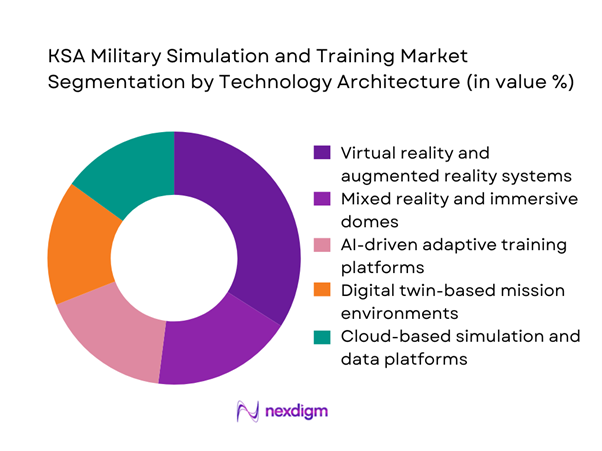
By Technology Architecture
Virtual reality and augmented reality systems represent the leading technology architecture in the market, supported by rapid adoption across air and land forces. More than ~ platforms are currently configured with immersive interfaces, while annual system upgrades average ~ units. Defense digitalization programs channel close to USD ~ million each cycle into advanced visualization and scenario modeling tools. These technologies enable realistic combat environments, reduce training downtime, and improve retention outcomes, positioning them as the cornerstone of next-generation military training strategies in the Kingdom.
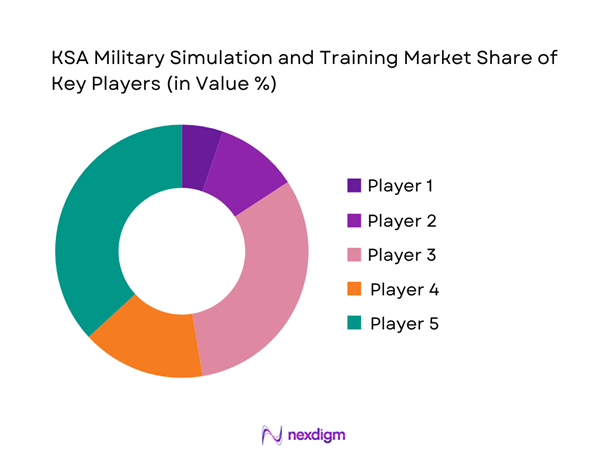
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Military Simulation and Training market shows moderate concentration, with a limited number of global defense technology leaders and regional champions controlling a large share of high-value contracts. Entry barriers remain high due to certification requirements, long procurement cycles, and the need for localized support capabilities. However, ongoing localization policies are gradually creating space for new partnerships and domestic system integrators.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| CAE | 1947 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Group | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 2019 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab AB | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo S.p.A. | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Military Simulation and Training Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising defense modernization under Vision 2030
Defense modernization programs have driven consistent capital allocation of nearly USD ~ million annually toward advanced training systems, with more than ~ platforms upgraded across air, land, and naval forces. The transition from legacy training tools to integrated digital environments has increased system deployments by over ~ units during the last two cycles. These investments support readiness benchmarks that require higher training throughput, pushing utilization levels to nearly ~ sessions per year across centralized academies and operational bases.
Increased focus on combat readiness and joint-force interoperability
Joint-force interoperability initiatives have accelerated the adoption of networked simulation systems, with over ~ systems now integrated across multiple service branches. Annual training volumes exceed ~ mission scenarios, supported by infrastructure upgrades worth USD ~ million. This focus ensures standardized operational doctrines, reduces coordination gaps, and improves response times during combined exercises, reinforcing simulation as a strategic enabler of national defense preparedness.
Challenges
High upfront capital costs of advanced simulation platforms
Advanced immersive simulators require initial investments of up to USD ~ million per deployment, creating budgetary pressure on training commands managing multiple bases. Installation programs often exceed ~ systems per phase, adding to lifecycle expenditure through maintenance and software upgrades. These cost structures can delay rollout schedules and limit rapid scaling, especially when procurement priorities shift toward frontline equipment acquisitions.
Lengthy defense procurement and approval cycles
Defense procurement timelines frequently extend beyond ~ months, slowing the adoption of newer simulation technologies. Approval workflows involve more than ~ stakeholder groups, increasing administrative complexity and project lead times. As a result, some training units continue operating ~ legacy systems longer than planned, constraining the pace of modernization and limiting access to next-generation training capabilities.
Opportunities
Localization and in-Kingdom manufacturing of simulators
Localization initiatives have opened opportunities for domestic production facilities capable of delivering ~ systems annually. Capital commitments nearing USD ~ million support the establishment of assembly lines, software labs, and maintenance hubs. These efforts reduce import dependence, improve response times, and create a sustainable ecosystem for long-term defense training innovation.
Public-private partnerships in defense training infrastructure
Public-private partnerships are enabling the development of multi-service training complexes, with infrastructure investments surpassing USD ~ million across recent projects. These facilities can host more than ~ trainees annually and support ~ concurrent simulation environments. Such models lower fiscal pressure on defense budgets while accelerating access to advanced training technologies and operational expertise.
Future Outlook
The KSA Military Simulation and Training market is expected to progress steadily through the next decade as defense digitalization, localization mandates, and multi-domain warfare requirements reshape training strategies. Greater integration of immersive technologies and data-driven performance management will define future procurement priorities. Partnerships between public entities and private defense technology providers are likely to expand, supporting scalable and resilient training ecosystems aligned with long-term national security objectives.
Major Players
- CAE
- Thales Group
- L3Harris Technologies
- Saab AB
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Lockheed Martin
- BAE Systems
- Raytheon Technologies
- Boeing Defense, Space & Security
- Rheinmetall AG
- Indra Sistemas
- Cubic Corporation
- Elbit Systems
- QinetiQ
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
Key Target Audience
- Saudi Ministry of Defense procurement departments
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries strategy teams
- Royal Saudi Air Force training command
- Saudi Arabian Army operational readiness units
- Royal Saudi Navy training and doctrine centers
- Investments and venture capital firms focused on defense technologies
- Government and regulatory bodies such as the Saudi Arabian Military Industries Authority
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key demand drivers, technology adoption patterns, and procurement cycles were mapped across air, land, and naval forces. Training infrastructure capacity, system deployment rates, and localization mandates were analyzed. Strategic defense priorities and operational readiness benchmarks were incorporated.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segment-level demand was structured by application and technology architecture. Deployment volumes and investment flows were modeled across major defense regions. Policy frameworks and industrial participation goals were integrated into the analysis.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through structured discussions with defense training planners and system integrators. Assumptions on adoption speed and localization impact were stress-tested. Feedback loops refined the market development pathways.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All quantitative and qualitative inputs were consolidated into a unified framework. Strategic implications for stakeholders were assessed. Findings were translated into actionable market intelligence.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, military simulation and training system taxonomy across live virtual and constructive solutions, market sizing logic by training seat demand and simulator deployment, revenue attribution across software licenses hardware platforms and support services, primary interview program with defense training commands OEMs and system integrators, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Training and readiness pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and delivery models
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising defense modernization under Vision 2030
Increased focus on combat readiness and joint-force interoperability
Shift toward cost-efficient synthetic training over live exercises
Expansion of domestic defense manufacturing and localization mandates
Growing complexity of modern warfare and multi-domain operations
Integration of advanced technologies such as AI and digital twins - Challenges
High upfront capital costs of advanced simulation platforms
Lengthy defense procurement and approval cycles
Cybersecurity and data sovereignty concerns
Interoperability issues across legacy and new systems
Limited local talent pool for advanced simulation engineering
Dependence on foreign technology providers for core platforms - Opportunities
Localization and in-Kingdom manufacturing of simulators
Public-private partnerships in defense training infrastructure
Export potential to GCC and allied regional forces
Development of indigenous software and content ecosystems
Integration of simulation with smart bases and digital command centers
Expansion into homeland security and critical infrastructure training - Trends
Adoption of immersive VR and mixed reality training environments
Use of AI for personalized and adaptive training scenarios
Convergence of live, virtual, and constructive training systems
Growth of networked and distributed simulation architectures
Increased use of data analytics for performance assessment
Shift toward modular and scalable simulation solutions - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Land forces simulation platforms
Air forces flight and mission simulators
Naval and maritime training systems
Joint and combined forces training environments - By Application (in Value %)
Live training and range instrumentation
Virtual training and immersive simulators
Constructive simulation and war-gaming
Mission rehearsal and command staff training
Maintenance and technical training - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Virtual reality and augmented reality systems
Mixed reality and immersive domes
AI-driven adaptive training platforms
Digital twin-based mission environments
Cloud-based simulation and data platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Saudi Arabian Army
Royal Saudi Air Force
Royal Saudi Navy
Special operations and homeland security forces
Defense academies and training institutes - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone and offline systems
Networked on-premise simulators
Cloud-enabled training platforms
5G and edge-enabled simulation systems
Secure tactical network-integrated systems - By Region (in Value %)
Riyadh and Central Region
Eastern Province
Western Region
Southern Region
Northern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology depth, localization capability, system interoperability, cybersecurity compliance, after-sales support, pricing flexibility, training content quality, integration with C4ISR systems)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
CAE
L3Harris Technologies
Thales Group
Lockheed Martin
Boeing Defense, Space & Security
Raytheon Technologies
BAE Systems
Saab AB
Rheinmetall AG
Leonardo S.p.A.
Indra Sistemas
Cubic Corporation
Elbit Systems
QinetiQ
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service and lifecycle support expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


