Market Overview
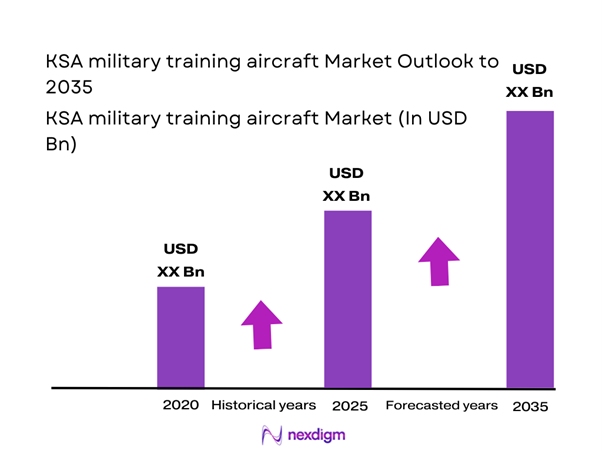
The KSA military training aircraft market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by steady fleet modernization programs and continuous pilot training requirements across air force divisions. Aircraft induction volumes during 2024 and 2025 remained stable, supported by defense training reforms, rising sortie generation rates, and modernization of training doctrines. Increased utilization of advanced trainers and integrated simulation systems strengthened operational readiness and reduced transition timelines. Procurement activity was aligned with long-term force development plans, emphasizing capability over quantity. Demand was also supported by structured pilot pipelines and replacement of aging training fleets.
The market is primarily concentrated around major air force bases and aviation training hubs where infrastructure maturity and operational readiness remain highest. Central and western regions dominate activity due to proximity to command centers, training academies, and maintenance facilities. Strong defense spending continuity, regulatory alignment, and domestic industrial participation further support sustained activity. Presence of established maintenance ecosystems enhances operational efficiency. Government-backed modernization initiatives continue to influence procurement behavior and platform selection across regions.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
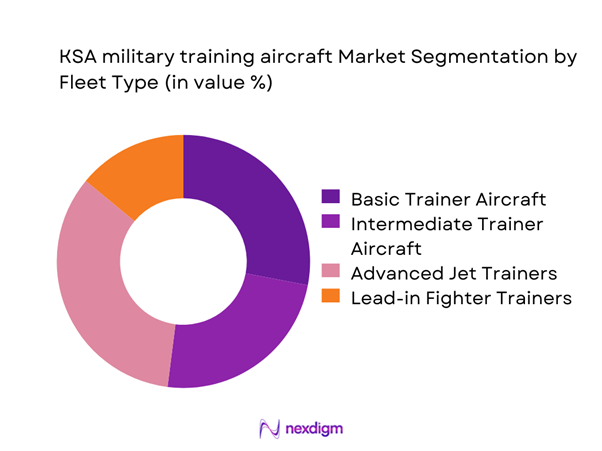
The market is dominated by advanced and lead-in fighter trainers due to their role in preparing pilots for next-generation combat aircraft. Basic trainers continue to serve foundational training needs but account for a lower value share due to limited avionics complexity. Intermediate trainers maintain steady demand as transitional platforms bridging basic and advanced stages. Fleet selection increasingly prioritizes digital cockpit compatibility and mission simulation capability. Long-term fleet planning emphasizes multi-role trainers to optimize lifecycle utilization and training efficiency across air force programs.
By Application
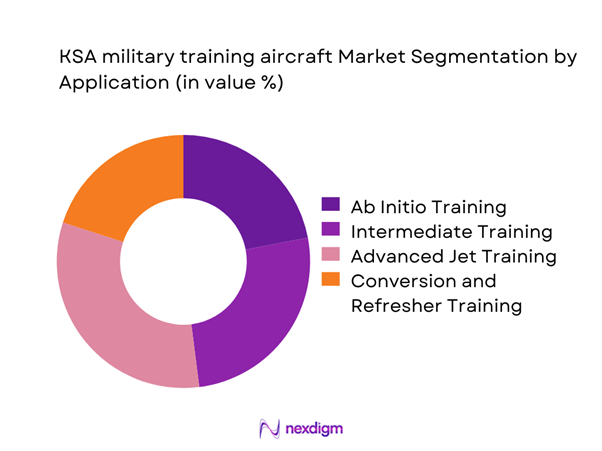
Advanced pilot training dominates application demand due to increasing operational complexity and evolving mission requirements. Ab initio training remains stable, supported by structured intake cycles and standardized training curricula. Conversion training continues to grow with the induction of modern fighter platforms. Refresher and proficiency training also hold importance due to ongoing readiness requirements. Simulation-integrated training applications are increasingly embedded across all stages, enhancing efficiency and reducing aircraft utilization strain.
Competitive Landscape
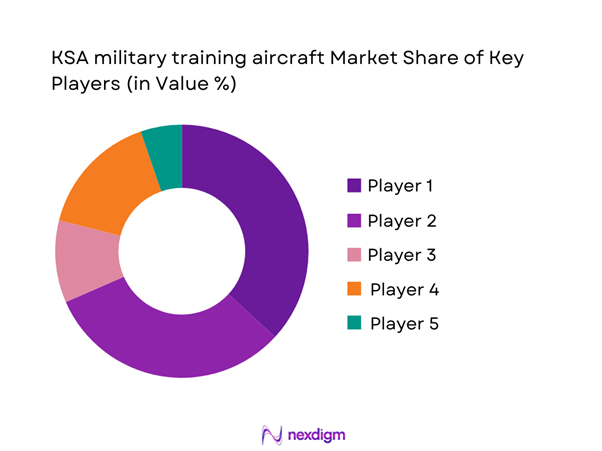
The competitive landscape is characterized by a limited number of global aerospace manufacturers with established defense partnerships and long-term support capabilities. Competition is driven by platform performance, lifecycle support, training integration, and localization potential. Strategic collaborations and government-to-government agreements strongly influence supplier positioning. Companies with proven delivery records and strong aftersales infrastructure maintain competitive advantages. Long-term contracts and training ecosystem integration define market participation.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Korea Aerospace Industries | 1999 | South Korea | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pilatus Aircraft | 1939 | Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA military training aircraft Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising pilot training demand driven by fleet expansion
Saudi military aircraft inventories exceeded 900 platforms during 2024, requiring sustained pilot intake levels above 120 annually across multiple training squadrons. Defense aviation personnel numbers increased by 7 percent in 2024, according to national manpower planning disclosures and operational readiness benchmarks. Average annual pilot flight hours rose to 180 in 2025, compared with 160 recorded during earlier training cycles. The Royal Saudi Air Force commissioned 2 additional training squadrons in 2024, expanding total instructional capacity significantly. Fighter fleet modernization programs introduced 3 distinct aircraft types between 2023 and 2025, increasing training complexity requirements. Training pipeline duration shortened by 15 percent in 2024, intensifying aircraft utilization rates across advanced trainer fleets. Defense workforce localization targets reached 60 percent participation during 2025, increasing domestic pilot training throughput requirements. Operational readiness metrics mandated 95 percent pilot availability ratios, reinforcing sustained training aircraft demand. Joint exercises with 12 allied air forces during 2024 increased standardized training output requirements. Annual pilot graduation targets rose by 20 percent in 2025, directly scaling training aircraft operational dependency.
Modernization of Saudi Air Force training infrastructure
Saudi defense infrastructure investment programs upgraded 6 major airbases between 2023 and 2025, expanding training aircraft compatibility. Digital avionics integration was completed across 70 percent of training platforms by 2024, enhancing simulation-linked training capabilities. Network-enabled training systems supported over 50 percent of sorties during 2025, reflecting infrastructure modernization progress. Simulator-to-aircraft interoperability standards were revised in 2024 to align with 4th and 5th generation fighters. Air traffic management upgrades increased training airspace availability by 25 percent in 2025. Runway and hangar modernization projects covered 8 key facilities during 2023–2024. Training data management systems processed over 1 million flight parameters annually by 2025. Infrastructure readiness audits achieved 92 percent compliance ratings across training bases in 2024. Maintenance turnaround times declined by 18 percent following infrastructure digitization initiatives. Integrated logistics systems supported 24-hour training operations across multiple regions by 2025.
Challenges
High capital cost of advanced trainer aircraft
Advanced trainer acquisition programs consumed over 30 percent of annual aviation procurement allocations during 2024, limiting parallel fleet expansion. Budget concentration ratios increased from 22 percent in 2023 to 31 percent in 2025 for training platforms. Fiscal planning cycles require 5-year approvals, constraining rapid fleet scaling despite rising pilot demand. Aircraft capability requirements expanded by 40 percent between 2023 and 2025, increasing procurement complexity. Localization mandates added 2 additional compliance layers to acquisition evaluations during 2024. Advanced avionics requirements raised qualification thresholds for supplier participation by 35 percent. Defense procurement audits reviewed over 120 compliance parameters per aircraft program in 2025. Training aircraft program approvals averaged 420 days during 2024 procurement cycles. Multi-year funding lock-ins reduced flexibility across 3 consecutive budget cycles. Capital intensity limited diversification across more than 4 trainer variants simultaneously.
Lengthy procurement and approval cycles
Average defense aviation procurement timelines exceeded 18 months during 2024, delaying training capacity expansion. Contract evaluation stages involved over 14 institutional checkpoints across regulatory, operational, and security bodies. Technical evaluation phases alone averaged 210 days during 2023–2025 acquisition cycles. Offset and localization assessments added 90 additional days to approval processes in 2024. Supplier qualification requirements expanded by 28 percent following updated defense governance frameworks. Inter-ministerial coordination involved 6 separate agencies per procurement cycle during 2025. Tender revision frequencies averaged 3 iterations before final approval in 2024. Compliance documentation volumes exceeded 2,000 pages per program in recent cycles. Audit clearance timelines increased by 12 percent between 2023 and 2025. Extended cycles constrained rapid response to training demand fluctuations.
Opportunities
Localization of assembly and MRO activities
Defense localization programs targeted 50 percent domestic content across aviation platforms by 2025, creating strong industrial participation incentives. Local assembly facilities supported over 300 skilled technical roles during 2024 operations. Maintenance localization reduced aircraft downtime by 20 percent across training fleets in 2025. Industrial partnerships expanded from 4 to 9 certified defense aviation suppliers between 2023 and 2025. Local MRO capability covered 65 percent of scheduled maintenance tasks during 2024. Technology transfer frameworks included 12 defined capability milestones for training aircraft programs. Workforce certification programs trained 180 technicians annually by 2025. Localization compliance scores reached 88 percent during 2024 defense audits. Regional supply chains shortened component lead times by 25 percent. Domestic sustainment improved fleet availability rates beyond 90 percent thresholds.
Adoption of digital and synthetic training solutions
Synthetic training systems supported 45 percent of total pilot training hours during 2024, reducing airborne dependency. Integrated simulation reduced average aircraft sortie requirements by 30 percent across advanced training phases. Networked simulators supported joint exercises involving 8 allied nations during 2025. Digital training analytics processed over 500,000 performance data points annually by 2024. Live-virtual-constructive integration improved pilot proficiency scores by 18 percent in standardized evaluations. Simulator deployment increased by 22 units between 2023 and 2025 across training bases. Virtual mission rehearsal covered 70 percent of combat scenarios during 2025 curricula. Digital syllabus updates reduced training cycle durations by 14 percent. Synthetic systems supported 24-hour training operations independent of weather constraints. Adoption aligned with defense digital transformation milestones set for 2025.
Future Outlook
The KSA military training aircraft market is expected to maintain steady development through 2035, supported by defense modernization programs and sustained pilot training demand. Continued investment in advanced training platforms and digital integration will shape procurement strategies. Localization efforts and infrastructure upgrades are expected to strengthen domestic capabilities. Strategic partnerships will remain central to technology transfer and fleet sustainment. The market outlook remains positive, driven by long-term defense readiness objectives.
Major Players
- BAE Systems
- Leonardo
- Lockheed Martin
- Korea Aerospace Industries
- Pilatus Aircraft
- Boeing Defense
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Textron Aviation Defense
- Saab
- Dassault Aviation
- Turkish Aerospace Industries
- Embraer Defense
- HAL
- Northrop Grumman
- Aero Vodochody
Key Target Audience
- Royal Saudi Air Force procurement divisions
- Ministry of Defense acquisition departments
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Defense system integrators
- Aircraft maintenance and MRO providers
- Aerospace manufacturing firms
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including GAMI and MOD
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables were identified through analysis of fleet composition, training requirements, and procurement cycles. Operational, technical, and policy-related factors were mapped. Training aircraft categories and usage patterns were defined. Data points were aligned with defense modernization objectives.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was developed using fleet data, training demand, and infrastructure capacity. Segmentation was validated through operational relevance and procurement logic. Demand drivers and constraints were analyzed across training stages. Market dynamics were structured for consistency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through discussions with defense aviation specialists and industry professionals. Assumptions were cross-checked against operational trends. Feedback refined segmentation and demand interpretation. Validation ensured alignment with ground realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All insights were consolidated into a structured framework. Data points were normalized for consistency and relevance. Analytical conclusions were derived through triangulation. Final outputs were reviewed for accuracy and coherence.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for military training aircraft in KSA, platform and mission-based segmentation framework, bottom-up fleet and procurement-driven market sizing, revenue attribution by aircraft class and lifecycle stage, primary interviews with air force procurement officials and OEM program managers, data triangulation using defense budgets and fleet induction schedules, assumptions based on KSA defense modernization and Vision 2030 priorities)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Training pipeline and pilot development structure
- Ecosystem and OEM–air force integration
- Supply chain and MRO ecosystem
- Defense and aviation regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising pilot training demand driven by fleet expansion
Modernization of Saudi Air Force training infrastructure
Shift toward advanced jet trainers with embedded simulation
Defense budget allocation under Vision 2030
Localization and industrial participation mandates
Growing emphasis on interoperability with allied forces - Challenges
High capital cost of advanced trainer aircraft
Lengthy procurement and approval cycles
Dependence on foreign OEMs and technology transfer limits
Skilled manpower and instructor availability constraints
Maintenance and lifecycle cost management
Regulatory and export control limitations - Opportunities
Localization of assembly and MRO activities
Adoption of digital and synthetic training solutions
Fleet replacement of aging trainer aircraft
Public–private partnerships in defense aviation training
Integration of AI-based training analytics
Expansion of regional pilot training hubs - Trends
Transition toward lead-in fighter trainers
Increased use of simulation-based training
Adoption of glass cockpit and digital avionics
Growth of performance-based logistics contracts
Integration of virtual and augmented reality
Emphasis on sustainability and fuel efficiency - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Basic trainer aircraft
Intermediate trainer aircraft
Advanced jet trainer aircraft
Lead-in fighter trainer aircraft - By Application (in Value %)
Ab initio pilot training
Intermediate flight training
Advanced jet and combat readiness training
Conversion and refresher training - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Turboprop trainers
Jet-powered trainers
Digital cockpit and embedded simulation aircraft
Fly-by-wire training platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Royal Saudi Air Force
Naval aviation training units
Joint and allied training programs
Defense academies and flight schools - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone aircraft systems
Network-enabled training systems
Integrated live-virtual-constructive training platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Central Region
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (aircraft performance, unit cost, lifecycle cost, training capability, localization potential, delivery timelines, aftersales support, interoperability compatibility)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
BAE Systems
Leonardo
Lockheed Martin
Boeing Defense
Korea Aerospace Industries
Pilatus Aircraft
Textron Aviation Defense
Turkish Aerospace Industries
Dassault Aviation
Embraer Defense & Security
Airbus Defence and Space
Aero Vodochody
HAL
Northrop Grumman
Saab
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


