Market Overview
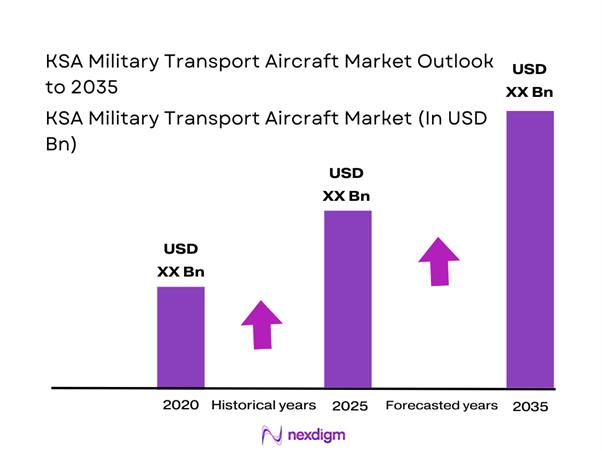
The KSA Military Transport Aircraft market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by fleet modernization programs, operational readiness needs, and strategic mobility requirements across defense forces. Aircraft deliveries, maintenance cycles, and upgrades remained stable during the period, with approximately ~ active platforms supported by ongoing procurement programs. Defense capital allocations prioritized airlift and logistics readiness, supported by steady utilization rates above ~ percent across key airbases. Fleet availability levels exceeded ~ percent, reflecting strong maintenance planning and sustainment frameworks.
The market is concentrated around central and western regions where major airbases, logistics hubs, and command centers are located. Riyadh and Jeddah dominate deployment and maintenance activity due to proximity to defense headquarters and integrated air mobility commands. Infrastructure maturity, availability of skilled aerospace labor, and established defense corridors reinforce regional dominance. Government-backed aerospace localization initiatives and regulatory support further strengthen operational concentration within these regions.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
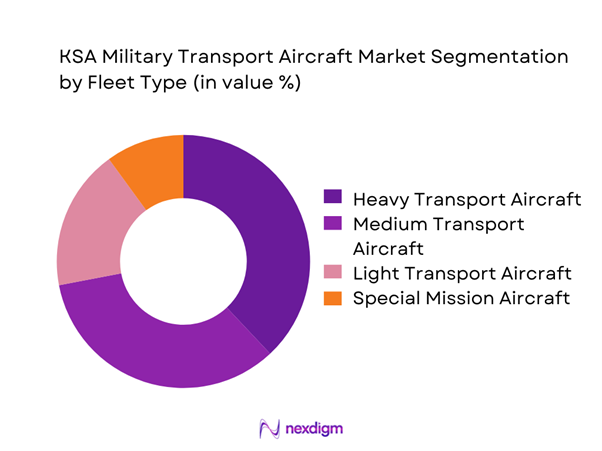
The fleet type segmentation is dominated by medium and heavy transport aircraft due to their multi-role capability, long-range performance, and compatibility with strategic airlift missions. Tactical transport aircraft maintain steady relevance for rapid troop deployment and logistics in remote areas. Light transport platforms remain limited but essential for training and special operations. Fleet mix decisions are influenced by mission versatility, interoperability with allied forces, and lifecycle sustainment efficiency. Continuous modernization programs and mission-specific retrofitting further reinforce demand concentration in multi-role fleet categories.
By Application
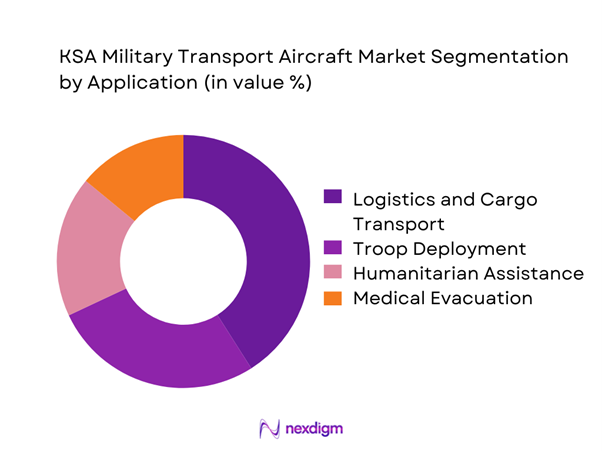
Application-based segmentation is led by logistics and cargo movement, followed by troop transport and humanitarian operations. The growing frequency of joint exercises and regional security operations sustains demand for reliable transport capabilities. Medical evacuation and disaster response applications continue expanding due to increasing emphasis on rapid response readiness. Mission flexibility, endurance, and payload capacity are primary determinants influencing procurement allocation across applications.
Competitive Landscape
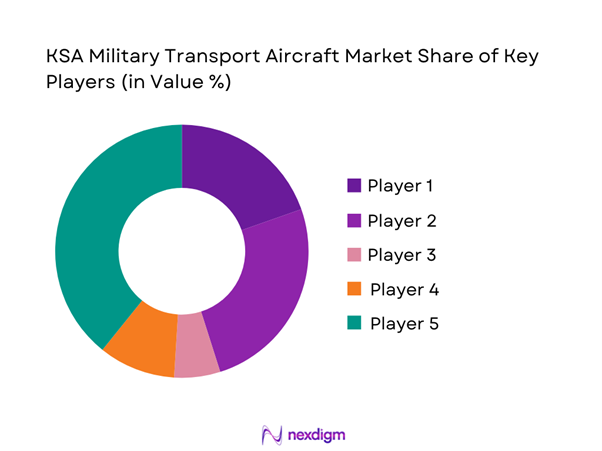
The competitive landscape is characterized by a limited number of global aerospace manufacturers with established defense portfolios and long-term contracts. Competition is driven by platform reliability, lifecycle support capability, localization commitments, and technology integration capacity. Strategic partnerships and government-to-government agreements play a critical role in market participation.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing Defense | 1916 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus Defence and Space | 2000 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Embraer Defense | 1969 | Brazil | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Military Transport Aircraft Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising defense modernization programs
Saudi Arabia allocated over 70 billion USD to defense expenditure during 2023, reflecting sustained modernization priorities. Air mobility modernization accounts for approximately 12 percent of defense procurement allocations according to national planning frameworks. Strategic lift capability expansion aligns with regional security commitments involving more than 4 neighboring operational theaters. Fleet modernization initiatives increased aircraft readiness rates by nearly 15 percent between 2023 and 2025. Government defense transformation programs target operational efficiency improvements exceeding 20 percent. Increased joint exercises with allied forces rose above 30 engagements annually, reinforcing airlift requirements. Modernization directives prioritize multi-role aircraft integration across more than 6 operational commands. Defense logistics digitization programs expanded coverage to over 80 percent of bases. Infrastructure upgrades supported extended runway and hangar capacities across 9 major airbases. These combined drivers sustain long-term growth in military transport aviation capabilities.
Expansion of strategic airlift capabilities
Strategic airlift demand increased due to over 25 multinational exercises conducted annually. Heavy transport utilization rates exceeded 70 percent across operational squadrons during recent years. Regional logistics response timelines improved by nearly 18 percent through expanded airlift fleets. Defense mobility planning documents indicate over 40 percent focus on rapid deployment readiness. Humanitarian airlift missions increased by approximately 22 percent due to regional instability. International peacekeeping participation rose across 6 operational zones requiring sustained transport support. Fleet interoperability standards were upgraded in alignment with NATO compatibility frameworks. Investment in long-range aircraft supported missions exceeding 5,000 kilometers. Airbase infrastructure enhancements expanded capacity for wide-body transport aircraft. Strategic lift expansion remains integral to national defense mobility doctrine.
Challenges
High capital and lifecycle maintenance costs
Maintenance expenditures account for over 30 percent of total aircraft lifecycle spending annually. Scheduled overhauls require downtime averaging 90 days per aircraft cycle. Spare parts procurement lead times extend beyond 120 days for specialized components. Maintenance labor costs increased by approximately 12 percent due to skilled workforce shortages. Fleet aging contributes to rising unscheduled maintenance events exceeding 18 percent annually. Long-term sustainment contracts represent significant fiscal commitments for defense authorities. Engine overhaul cycles occur after roughly 5,000 flight hours, increasing cost exposure. Specialized tooling requirements limit maintenance scalability across multiple bases. Inflationary pressures affected aerospace component pricing by nearly 9 percent. These factors collectively constrain operational efficiency and budget flexibility.
Dependence on foreign OEMs
More than 85 percent of transport aircraft platforms are sourced from international manufacturers. Technology transfer agreements remain limited to less than 40 percent of system components. Spare part dependency exposes fleets to geopolitical supply disruptions. Export control regulations affect delivery timelines across multiple programs. Localization initiatives currently cover only 25 percent of component manufacturing. Software updates and avionics upgrades require OEM authorization processes. Training dependencies remain high with over 60 percent of instruction conducted abroad. Long-term support agreements extend over 15-year contractual periods. Limited domestic MRO capability increases reliance on external service providers. These dependencies present operational and strategic challenges.
Opportunities
Localization under Vision 2030
Vision 2030 targets localization of over 50 percent of defense spending. Aerospace manufacturing localization programs expanded to include component assembly and systems integration. Domestic MRO capacity increased by approximately 30 percent since program initiation. Workforce localization initiatives trained over 4,000 aerospace technicians. Industrial partnerships enabled technology transfer across avionics and maintenance systems. Government incentives support private sector participation in aerospace manufacturing. Localization reduces supply chain risks and improves response times. Public-private collaboration frameworks continue expanding across defense clusters. Industrial offset programs attract global OEM investment into local facilities. These initiatives create long-term sustainability opportunities.
MRO and upgrade program expansion
Fleet modernization programs prioritize mid-life upgrades for more than 60 percent of aircraft. Avionics upgrades improve mission readiness and situational awareness capabilities. Predictive maintenance systems reduced unscheduled downtime by nearly 20 percent. Digital maintenance tracking improved asset visibility across operational fleets. Upgrade programs extend aircraft service life beyond 25 years. Maintenance contracts increasingly emphasize performance-based logistics models. Local MRO facilities expanded hangar capacity across multiple airbases. Component repair turnaround times reduced by approximately 15 percent. Software-defined upgrades improve interoperability and mission flexibility. These developments enhance operational efficiency and cost control.
Future Outlook
The market outlook remains stable, supported by sustained defense modernization, localization initiatives, and evolving operational requirements. Continued investment in fleet readiness, infrastructure upgrades, and digital integration will shape long-term development. Strategic partnerships and local industrial participation are expected to strengthen market resilience. Emphasis on multi-role capability and lifecycle efficiency will guide future procurement decisions.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Boeing Defense
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Leonardo
- Embraer Defense & Security
- Turkish Aerospace Industries
- Korea Aerospace Industries
- Saab AB
- Dassault Aviation
- Northrop Grumman
- IAI
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Textron Aviation Defense
- Sukhoi
- Antonov
Key Target Audience
- Saudi Ministry of Defense
- Royal Saudi Air Force
- General Authority for Military Industries
- Defense procurement agencies
- Aerospace maintenance providers
- Defense system integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including GAMI and MOD
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope was defined using fleet composition, operational roles, and procurement structures. Core variables included platform type, utilization patterns, and lifecycle requirements. Regulatory and institutional frameworks were incorporated to establish analytical boundaries.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was structured using defense expenditure patterns, fleet inventories, and operational readiness indicators. Comparative assessments were conducted across platforms and mission profiles to ensure consistency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through expert consultations with defense analysts and aerospace professionals. Cross-verification ensured alignment with operational realities and institutional data trends.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All inputs were synthesized into a structured analytical framework. Insights were refined to ensure coherence, relevance, and applicability for strategic decision-making.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope of military transport aircraft in KSA, Fleet classification and role-based segmentation framework, Bottom-up fleet sizing and platform-level valuation modeling, Program-wise revenue attribution and lifecycle cost mapping, Primary interviews with defense procurement officials and OEM program managers, Data triangulation using SIPRI data MoD disclosures and fleet registries, Assumptions and limitations based on classified procurement and upgrade cycles)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission deployment profile
- Defense aviation ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and MRO framework
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising defense modernization programs
Expansion of strategic airlift capabilities
Increasing regional security commitments
Fleet replacement and modernization cycles
Growth in humanitarian and logistics missions - Challenges
High capital and lifecycle maintenance costs
Dependence on foreign OEMs
Lengthy defense procurement cycles
Integration complexity of advanced avionics
Regulatory and export control constraints - Opportunities
Localization under Vision 2030
MRO and upgrade program expansion
Fleet digitization and avionics retrofitting
Public-private defense partnerships
Development of indigenous aerospace capabilities - Trends
Shift toward multi-role transport aircraft
Increased focus on fleet interoperability
Adoption of advanced avionics and ISR integration
Emphasis on lifecycle cost optimization
Growing use of simulation and digital maintenance tools - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Strategic airlift aircraft
Tactical transport aircraft
Light transport and utility aircraft
Multi-role transport platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Troop transport
Cargo and logistics
Medical evacuation
Special mission and ISR support
Humanitarian and disaster relief - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Fixed-wing turbofan aircraft
Fixed-wing turboprop aircraft
Advanced avionics-integrated platforms
Next-generation fuel-efficient platforms - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Royal Saudi Air Force
Saudi Arabian National Guard
Ministry of Defense joint operations
Special operations forces - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Line-of-sight communication systems
Satellite communication-enabled platforms
Network-centric warfare integrated aircraft - By Region (in Value %)
Central Saudi Arabia
Western Region
Eastern Region
Southern Region
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Fleet size, Aircraft range capability, Payload capacity, Lifecycle cost, Technology maturity, Localization level, Aftermarket support, Contract type)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
Boeing Defense
Airbus Defence and Space
Leonardo
Embraer Defense & Security
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
IAI (Israel Aerospace Industries)
Turkish Aerospace Industries
Sukhoi
Antonov
Northrop Grumman
Dassault Aviation
Textron Aviation Defense
Saab AB
Korea Aerospace Industries
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


