Market Overview
The KSA military vehicle electrification market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by expanding defense modernization programs and rising emphasis on energy-efficient platforms. Fleet electrification adoption accelerated during 2024 and 2025 as hybrid drivetrains, auxiliary power units, and silent mobility systems gained acceptance. Vehicle electrification integration increased across logistics, reconnaissance, and tactical support segments. Development programs emphasized endurance optimization, reduced acoustic signatures, and enhanced onboard power management. Procurement activity remained concentrated within government-led defense modernization frameworks.
The market is primarily concentrated in Riyadh, Eastern Province, and Western military zones where defense infrastructure and command centers are established. These regions benefit from mature defense supply chains, testing facilities, and localized assembly capabilities. Strategic alignment with industrial localization policies supports ecosystem expansion. Demand is reinforced by centralized procurement practices and structured fleet renewal programs. The presence of defense clusters and vehicle integration facilities strengthens long-term adoption prospects.
Market Segmentation
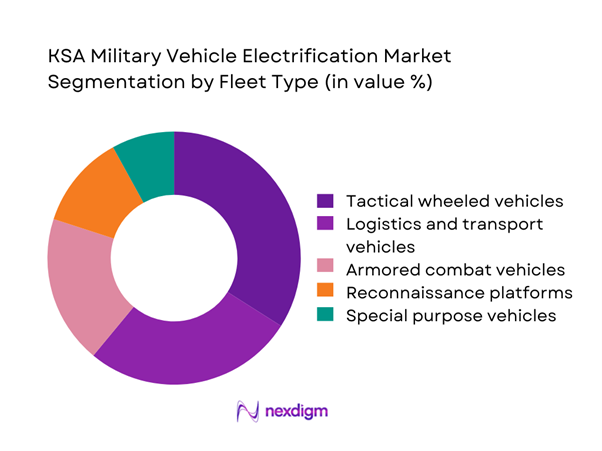
By Fleet Type
The fleet type segmentation is dominated by tactical wheeled vehicles and logistics platforms due to their high deployment frequency and suitability for hybridization. Armored combat vehicles are gradually integrating electrified subsystems to support silent watch and auxiliary power needs. Logistics and transport fleets represent the highest electrification penetration because of predictable routes and fuel efficiency priorities. Reconnaissance and support vehicles are increasingly adopting electric drivetrains for reduced thermal and acoustic signatures. Specialized vehicles follow selectively based on mission requirements and operational compatibility.
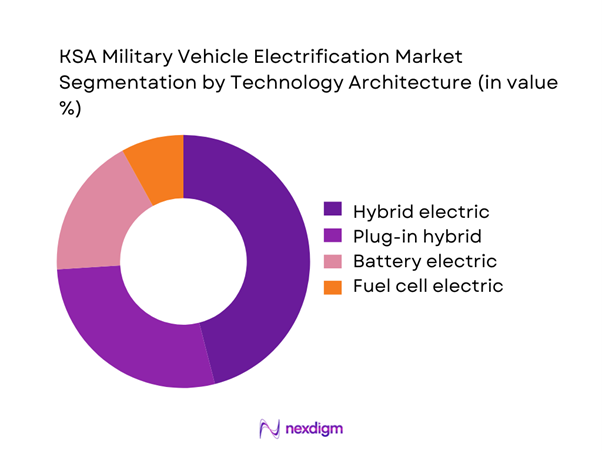
By Technology Architecture
Hybrid electric platforms dominate technology adoption due to operational flexibility and reduced dependency on charging infrastructure. Plug-in hybrid configurations are expanding within base operations and controlled mobility environments. Battery electric vehicles remain limited to non-combat and logistics applications due to range considerations. Fuel cell technologies are under evaluation for future deployment but remain at early development stages. Architecture selection is strongly influenced by mission duration, payload requirements, and energy security objectives.
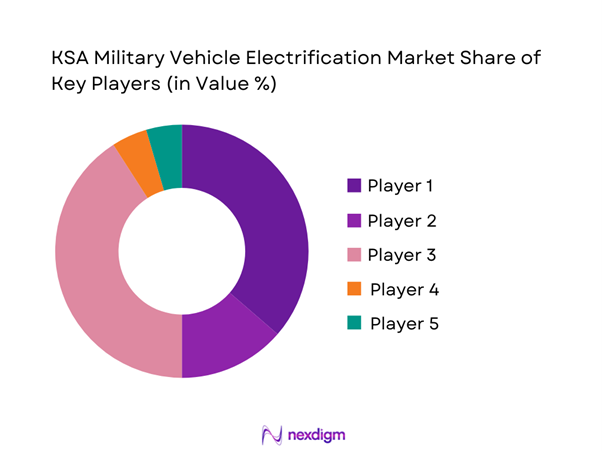
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is moderately consolidated, with strong participation from international defense vehicle manufacturers and domestic industrial groups. Market competition centers on drivetrain integration capability, compliance with military standards, and local manufacturing alignment. Long-term contracts, offset programs, and technical partnerships shape vendor positioning. Players focus on reliability, lifecycle support, and platform adaptability to secure procurement advantages.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Saudi Arabian Military Industries | 2017 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Advanced Electronics Company | 1988 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BAE Systems | 1976 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rheinmetall | 1889 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Oshkosh Defense | 1917 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Military Vehicle Electrification Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising focus on silent mobility and reduced thermal signatures
Military doctrine emphasized stealth mobility, with over 65 percent of modern operations requiring reduced acoustic and thermal detectability. Defense agencies recorded more than 40 percent of tactical missions involving night or covert movement. Electrified drivetrains reduce acoustic signatures by nearly 60 percent compared with diesel platforms. Thermal imaging countermeasures gained relevance as regional surveillance deployments expanded by 35 percent. Energy-efficient platforms lowered infrared visibility during operations exceeding 12 continuous hours. Electrification supported reduced idle time, which previously accounted for nearly 30 percent of vehicle fuel consumption. Defense mobility studies indicated hybrid systems improved operational endurance by over 25 percent. Silent watch capabilities enabled mission persistence exceeding 8 hours without engine use. Integration of electric subsystems aligned with modernization targets covering over 70 percent of land fleets. Strategic emphasis on survivability reinforced demand for low-signature vehicle architectures.
Vision 2030 defense localization and technology transfer goals
National localization strategies targeted over 50 percent domestic defense content across major platforms. Defense industrial output increased by more than 20 percent through structured localization initiatives. Vehicle electrification aligns with technology transfer frameworks covering power electronics and energy systems. Over 30 joint ventures were approved to strengthen local manufacturing capabilities. Localization policies emphasized indigenous integration of propulsion subsystems and battery management units. Government procurement frameworks prioritized domestically supported platforms for long-term sustainment. Workforce development programs trained more than 10,000 technicians in advanced mobility systems. Localization milestones included certified testing facilities and localized component assembly. Defense spending allocation favored platforms enabling domestic value creation. Electrification served as a catalyst for broader industrial capability development.
Challenges
High upfront costs of electrified military platforms
Electrified military vehicles require capital investments exceeding conventional platforms by over 35 percent. Battery systems account for nearly 40 percent of total platform integration complexity. Specialized power electronics increase procurement and validation timelines significantly. Maintenance infrastructure upgrades require additional allocation across more than 20 major bases. Certification processes extend development cycles by up to 18 months. Limited economies of scale constrain cost optimization in early adoption phases. Defense budgets face competing priorities including aviation and missile modernization. Lifecycle cost assessments remain uncertain due to evolving battery degradation models. Spare parts inventories require diversification, increasing logistics complexity. Budgetary approvals demand multi-year justification aligned with operational readiness metrics.
Limited domestic battery and power electronics supply base
Domestic battery manufacturing capacity remains below 25 percent of projected military requirements. Dependence on imported cells exposes programs to supply chain volatility. Power electronics localization remains constrained by limited semiconductor fabrication capabilities. Environmental qualification of batteries requires extensive testing exceeding 1,000 operational hours. Thermal management challenges persist under desert operating conditions above 45 degrees Celsius. Limited supplier competition restricts pricing flexibility and delivery timelines. Certification bottlenecks delay platform integration schedules. Workforce shortages exist in electrochemical and power systems engineering. Import dependency increases lead times by up to 40 percent. Strategic stockpiling is required to mitigate supply disruptions.
Opportunities
Localized assembly and powertrain manufacturing partnerships
Localization initiatives encourage joint ventures for powertrain assembly within national defense zones. Government programs support establishment of battery pack assembly lines with capacity exceeding 10,000 units annually. Technology transfer agreements enable domestic integration of electric drivetrains. Local manufacturing reduces lead times by nearly 30 percent compared to imports. Industrial clusters support supplier ecosystem development across electronics and thermal management. Incentive frameworks promote long-term manufacturing investments exceeding multi-year horizons. Skilled workforce availability improves through targeted technical training programs. Domestic assembly enhances lifecycle control and upgrade flexibility. Export potential increases through compliance with regional defense standards. Strategic partnerships strengthen supply chain resilience and national security objectives.
Retrofit and hybridization of existing vehicle fleets
Legacy fleet modernization offers cost-effective electrification across more than 60 percent of active vehicles. Retrofit programs extend platform life by over 15 operational years. Hybrid kits reduce fuel consumption by approximately 25 percent during patrol missions. Retrofit cycles require shorter certification timelines compared to new builds. Existing platforms provide standardized integration interfaces for electric subsystems. Retrofit programs align with sustainability mandates without fleet replacement. Maintenance crews adapt faster due to platform familiarity. Energy recovery systems improve operational efficiency during stop-start missions. Hybridization supports gradual transition toward full electrification. Retrofit strategies optimize capital utilization across defense budgets.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to experience steady expansion through the forecast period driven by defense modernization and localization strategies. Electrification adoption will gradually extend from support vehicles to combat platforms. Technological advancements in energy storage and hybrid systems will enhance operational viability. Government-backed programs will continue to shape procurement priorities. The long-term outlook remains positive as electrification becomes integral to military mobility strategies.
Major Players
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Advanced Electronics Company
- BAE Systems
- Rheinmetall
- Oshkosh Defense
- Leonardo
- Thales Group
- Hanwha Defense
- General Dynamics Land Systems
- Iveco Defence Vehicles
- Patria Group
- FNSS Defence Systems
- QinetiQ
- Arquus
- GM Defense
Key Target Audience
- Saudi Ministry of Defense procurement divisions
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries program offices
- Defense vehicle OEMs and system integrators
- Military logistics and fleet management units
- Defense technology investors and venture capital firms
- Government defense acquisition agencies
- Powertrain and energy system suppliers
- Defense infrastructure development authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market boundaries were defined based on vehicle electrification scope, defense platform classifications, and operational use cases. Key performance variables and technology parameters were identified. Regulatory and procurement frameworks were reviewed to establish market relevance.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segment-level assessment was conducted using fleet deployment trends and electrification adoption patterns. Demand drivers were mapped across vehicle categories. Technology penetration levels were evaluated through platform analysis.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry insights were validated through discussions with defense engineers, procurement specialists, and systems integrators. Assumptions were refined based on operational feasibility and deployment realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation of qualitative and quantitative inputs. Data consistency checks ensured alignment with defense modernization trajectories. Final insights were structured for strategic decision-making.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and electrification scope alignment, defense vehicle taxonomy and platform classification, bottom-up fleet electrification sizing methodology, powertrain cost and value attribution modeling, primary interviews with defense OEMs and Saudi procurement stakeholders, triangulation using defense budgets and vehicle program data)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and mission-driven electrification use cases
- Defense mobility and powertrain ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and localization framework
- Regulatory and defense policy environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising focus on silent mobility and reduced thermal signatures
Vision 2030 defense localization and technology transfer goals
Increasing fuel logistics vulnerability in expeditionary missions
Modernization of aging ground vehicle fleets
Integration of advanced electronic and power-hungry subsystems
Demand for lower lifecycle and maintenance costs - Challenges
High upfront costs of electrified military platforms
Limited domestic battery and power electronics supply base
Harsh climatic impact on battery performance
Interoperability with legacy fleets
Restricted access to classified performance data
Extended qualification and military testing cycles - Opportunities
Localized assembly and powertrain manufacturing partnerships
Retrofit and hybridization of existing vehicle fleets
Development of military-grade battery systems for extreme environments
Export potential to GCC and allied markets
Integration with autonomous and unmanned ground systems
Energy storage solutions for forward operating bases - Trends
Shift from full diesel to hybrid-first architectures
Adoption of silent watch and exportable power features
Co-development between global OEMs and Saudi entities
Increased emphasis on modular and scalable powertrains
Testing of solid-state and advanced lithium chemistries
Electrification alignment with digital battlefield concepts - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Main battle tanks and armored combat vehicles
Tactical wheeled vehicles
Logistics and transport vehicles
Reconnaissance and ISR platforms
Special purpose and support vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Combat operations
Logistics and mobility support
Surveillance and reconnaissance
Command and control
Training and base operations - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Hybrid electric vehicles
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
Battery electric vehicles
Fuel cell electric vehicles - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Saudi Land Forces
Saudi National Guard
Royal Saudi Land Forces Aviation
Border Guard and Internal Security Forces
Defense training and logistics units - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Wired vehicle networks
Wireless communication systems
Tactical data link integration
Vehicle-to-vehicle communication
Vehicle-to-infrastructure connectivity
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (vehicle electrification level, powertrain technology, localization capability, defense certification status, integration capability, pricing strategy, after-sales support, government alignment)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Saudi Arabian Military Industries (SAMI)
Advanced Electronics Company (AEC)
General Dynamics Land Systems
BAE Systems
Rheinmetall Defence
Oshkosh Defense
Leonardo Defence Systems
Thales Group
Hanwha Defense
Iveco Defence Vehicles
Patria Group
FNSS Defence Systems
GM Defense
QinetiQ
Arquus
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


