Market Overview
The KSA Predictive Analytics in Healthcare Market is valued at USD ~, reflecting its position as a high-impact subset of the national healthcare analytics ecosystem. The market scale is driven by growing digitization of clinical workflows, expansion of electronic health records, and increasing demand for proactive decision-making across hospitals and payers. Historical healthcare IT spending exceeded USD ~ in the previous period and continued to rise to USD ~ as predictive models became essential for reducing avoidable admissions, optimizing resource utilization, and improving clinical outcomes. Predictive analytics is structurally important as it shifts healthcare delivery from reactive reporting toward anticipatory, data-driven care planning and financial control.
Demand within the country is concentrated in major metropolitan healthcare hubs where tertiary hospitals, national referral centers, and payer headquarters are clustered. These regions dominate adoption because they host large patient volumes, complex case mixes, and the most advanced digital infrastructure, enabling effective deployment of predictive models. Supply and technology influence is driven by global platform vendors and enterprise software providers whose solutions are localized through partnerships and regional delivery teams, ensuring compliance, scalability, and integration with national health systems without fragmenting domestic control of healthcare data.
Market Segmentation
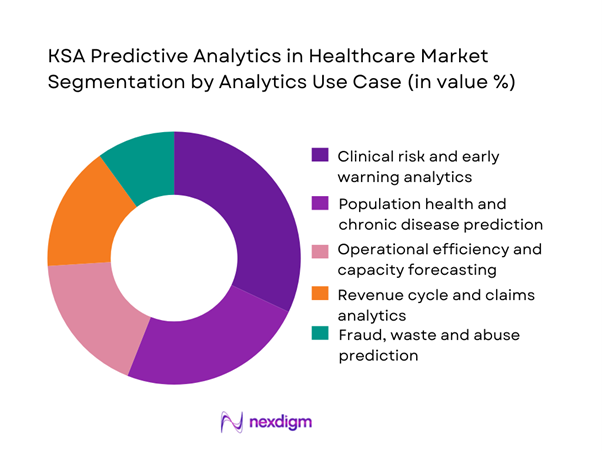
By Analytics Use Case
The KSA predictive analytics in healthcare market is segmented by analytics use case into clinical risk and early warning analytics, population health prediction, operational efficiency forecasting, revenue cycle analytics, and fraud and abuse prediction. Clinical risk and early warning analytics dominate this segmentation because hospitals face persistent pressure to manage high-acuity patients, reduce mortality risk, and prevent unexpected deterioration. Predictive alerts embedded into clinical workflows support early intervention in intensive care units and emergency departments, directly influencing patient outcomes and length of stay. National healthcare transformation initiatives have also prioritized outcome-based performance indicators, further reinforcing investment in clinical predictive models. Compared to financial or administrative use cases, clinical risk prediction delivers visible impact at the bedside, strengthening clinician acceptance and accelerating enterprise-wide rollout across hospital clusters.
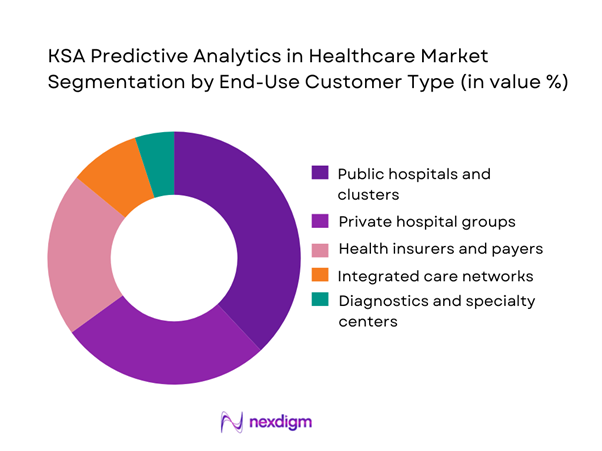
By End-Use Customer Type
The KSA predictive analytics in healthcare market is segmented by end-use customer type into public hospitals, private hospital groups, health insurers, integrated care networks, and diagnostics centers. Public hospitals and clusters hold the dominant market share due to their scale, centralized governance, and mandate to improve efficiency while managing national disease burdens. These institutions operate large datasets covering inpatient, outpatient, and emergency care, which are ideal for predictive modeling. Centralized procurement and standardized IT frameworks also allow faster scaling of analytics platforms across multiple facilities. While payers are increasing adoption for utilization management, provider-led demand remains stronger as hospitals directly experience operational bottlenecks and clinical risk, making predictive analytics a mission-critical capability rather than a supporting function.
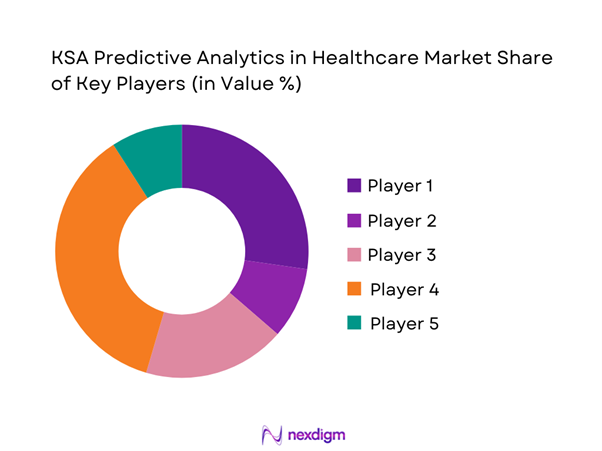
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Predictive Analytics in Healthcare market is dominated by a few major players, including Oracle Health and global brands like Microsoft, Google Cloud, and Amazon Web Services. This consolidation highlights the significant influence of these key companies.
| Company | Established Year | Headquarters | Primary Role in KSA Deployments | Typical Healthcare Predictive Use-Cases | Deployment Strength | Interoperability Readiness (FHIR / national exchange integration) | Compliance & Security Posture (PDPL / NCA-aligned controls) | Local Delivery Footprint |
| Oracle Health (Cerner) | 1979 (Cerner) / 1977 (Oracle) | US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Microsoft (Azure) | 1975 | US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Google Cloud | 2008 | US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SAS | 1976 | US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| IBM | 1911 | US | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Predictive Analytics in Healthcare Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
National Digital Health Transformation Programs
National digital health transformation initiatives in Saudi Arabia have fundamentally reshaped how healthcare data is generated, standardized, and exchanged across the ecosystem. The rollout of unified electronic health records, national health information exchanges, and standardized coding frameworks has reduced data silos between public hospitals, private providers, insurers, and regulators. Predictive analytics benefits directly from this transformation, as models rely on longitudinal, high-quality datasets spanning clinical, administrative, and utilization records. With providers increasingly required to comply with national data interoperability standards, analytics platforms can access cleaner and more structured inputs. This environment accelerates adoption of predictive tools for early risk identification, capacity planning, and care pathway optimization, as healthcare organizations shift from retrospective reporting to forward-looking decision support embedded within daily operations.
Rising Chronic Disease Burden
The growing prevalence of chronic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and respiratory diseases continues to place sustained pressure on Saudi Arabia’s healthcare system. Chronic disease management involves frequent hospital visits, repeated diagnostics, long-term medication adherence, and high-cost complications if conditions are not proactively managed. Predictive analytics plays a critical role by identifying patients at risk of deterioration, non-adherence, or avoidable hospitalization before adverse events occur. This allows providers to implement targeted interventions such as care coordination, remote monitoring, and personalized treatment plans. For healthcare organizations, predictive capabilities support better utilization of clinical resources while reducing strain on inpatient facilities. As chronic care becomes a dominant workload driver, demand for analytics that can forecast risk and guide preventive action continues to grow.
Challenges
Fragmented Clinical Data Environments
Despite ongoing digitization efforts, clinical data across Saudi Arabia’s healthcare system remains fragmented across multiple legacy systems, departmental platforms, and vendor-specific architectures. Many hospitals operate hybrid environments where modern electronic records coexist with older systems that were not designed for large-scale analytics. This fragmentation complicates data integration, normalization, and governance, which are essential prerequisites for reliable predictive modeling. Inconsistent data formats, incomplete patient histories, and limited interoperability can reduce model accuracy and delay deployment timelines. Healthcare organizations often must invest significant time and resources into data harmonization initiatives before analytics platforms deliver value. These technical and organizational complexities remain a key barrier, especially for institutions with limited in-house data engineering capabilities.
Clinical Trust and Model Validation Barriers
For predictive analytics to influence clinical decision-making, insights must be trusted by physicians, nurses, and care teams. In many cases, resistance arises when models are perceived as “black boxes” that generate recommendations without transparent clinical logic. Clinicians may hesitate to rely on predictions that do not clearly align with established medical guidelines or workflow realities. Additionally, healthcare organizations must ensure that predictive models are validated against local patient populations and continuously monitored for bias or performance drift. Achieving this level of validation requires close collaboration between data scientists and clinicians, as well as robust governance structures. These processes take time and often slow adoption, particularly in environments where clinical accountability and patient safety are paramount.
Opportunities
Proactive Population Health Management
Predictive analytics creates a significant opportunity to shift healthcare delivery from reactive treatment to proactive population health management. By analyzing patterns across large patient populations, analytics platforms can identify emerging risk clusters, predict disease progression, and prioritize interventions for vulnerable groups. This capability supports targeted preventive programs, improved chronic disease outreach, and more efficient allocation of healthcare resources. For national health systems, population-level prediction enables better planning of workforce requirements, facility utilization, and service expansion. As Saudi Arabia emphasizes long-term health outcomes and prevention-oriented care models, predictive analytics becomes a strategic enabler rather than a purely technical tool, supporting system-wide efficiency and improved patient experiences.
Claims Leakage and Fraud Prevention
Predictive analytics presents strong opportunities for detecting claims leakage, inappropriate utilization, and fraudulent billing behaviors across payer and provider networks. By analyzing historical claims data, treatment patterns, and provider behavior, predictive models can flag anomalies that deviate from expected clinical or financial norms. This allows payers and integrated health systems to intervene early, reducing financial losses while maintaining service quality. Beyond outright fraud, analytics can identify inefficiencies such as redundant testing, suboptimal referral patterns, or excessive admissions. These insights support tighter utilization management and better alignment between clinical outcomes and cost controls. As healthcare financing structures mature, the ability to predict and prevent revenue leakage becomes increasingly valuable across the ecosystem.
Future Outlook
The KSA predictive analytics in healthcare market is positioned for sustained expansion as analytics becomes embedded into core clinical and operational processes. The focus will shift from pilot deployments toward enterprise-wide platforms supporting continuous decision-making, with greater emphasis on automation, real-time insights, and outcome-driven performance management across the healthcare system.
Major Players
- Oracle Health
- Microsoft
- Google Cloud
- Amazon Web Services
- SAS
- IBM
- SAP
- Palantir
- InterSystems
- Epic Systems
- Philips
- GE HealthCare
Key Target Audience
- Public hospital clusters and health systems
- Private hospital groups
- Health insurance companies and payers
- Integrated care networks
- Digital health platform operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Large diagnostics and specialty care providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping stakeholders across providers, payers, regulators, and technology vendors. Key adoption variables such as data availability, interoperability, and compliance requirements are identified through structured desk research.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical demand patterns are analyzed using procurement activity, deployment scale, and platform adoption indicators. Revenue attribution is aligned with use cases and care settings to ensure consistency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions are validated through structured discussions with healthcare IT leaders and analytics practitioners. Feedback is used to refine segmentation logic and competitive positioning.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights from multiple sources are triangulated to produce a cohesive and validated market view. The final report integrates quantitative structuring with qualitative interpretation.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Inclusions/Exclusions, Abbreviations, Topic-Specific Taxonomy, Market Sizing Framework, Revenue Attribution Logic Across Use Cases or Care Settings, Primary Interview Program Design, Data Triangulation and Validation, Limitations and Data Gaps)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Genesis and Evolution
- Healthcare Analytics Value-Chain and Care-Continuum Mapping
- Business Cycle and Demand Seasonality
- KSA Healthcare Delivery Architecture
- Growth Drivers
National digital health transformation programs
Rising chronic disease burden
Pressure on hospital capacity utilization
Payer-driven cost containment
Expansion of health data interoperability - Challenges
Fragmented clinical data environments
Clinical trust and model validation barriers
Data privacy and cybersecurity compliance
Integration complexity with legacy systems
Shortage of advanced analytics talent - Opportunities
Proactive population health management
ICU and emergency care optimization
Claims leakage and fraud prevention
AI-enabled clinical decision support
Predictive maintenance of medical assets - Trends
- Regulatory & Policy Landscape
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder & Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competitive Intensity & Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2019–2024
- By Solution Revenues vs Services Revenues, 2019–2024
- By Buyer Spend Split, 2019–2024
- By Analytics Use Case (in Value %)
Clinical risk and early warning analytics
Population health and chronic disease prediction
Operational efficiency and capacity forecasting
Revenue cycle and claims analytics
Fraud, waste and abuse prediction - By End-Use Customer Type (in Value %)
Public hospitals and clusters
Private hospital groups
Health insurers and payers
Integrated care networks
Diagnostics and specialty centers - By Technology Platform Type (in Value %)
Statistical modeling platforms
Machine learning platforms
AI-based clinical decision engines
Data lake and analytics platforms
Embedded EHR analytics modules - By Deployment Model (in Value %)
On-premise
Private cloud
Public cloud
Hybrid cloud - By Customer Size (in Value %)
Large hospital clusters
Mid-sized hospitals
Small hospitals and clinics
National health programs
Payer enterprises - By Region (in Value %)
Central region
Western region
Eastern region
Southern region
Northern region
- Competition ecosystem overview
- Cross Comparison Parameters (NPHIES interoperability readiness, clinical model validation depth, PDPL compliance architecture, real-time analytics capability, EHR integration breadth, deployment flexibility, scalability across clusters, local delivery capability)
- SWOT analysis of major players
Pricing and commercial model benchmarking - Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Oracle Health
Microsoft
Google Cloud
Amazon Web Services
SAS
IBM
SAP
Palantir
InterSystems
Epic Systems
Philips
GE HealthCare
Siemens Healthineers
IQVIA
Snowflake
- Buyer personas and decision-making units
- Procurement and contracting workflows
- KPIs used for evaluation
- Pain points and adoption barriers
- By Value, 2025–2030
- By Solution Revenues vs Services Revenues, 2025–2030
- By Buyer Spend Split, 2025–2030


