Market Overview
Based on a recent historical assessment, the KSA Remote Weapon Systems market was valued at USD ~ billion, supported by confirmed procurement disclosures issued by the Saudi Ministry of Defense, SIPRI arms transfer records, and officially published national defense budget allocations. Market size expansion is driven by sustained land force modernization, large-scale border security programs, and accelerated adoption of remotely operated combat solutions across armored vehicles and fixed installations. Additional drivers include force protection mandates, reduced soldier exposure requirements, and the integration of stabilized fire-control, electro-optical, and thermal targeting technologies across operational environments.
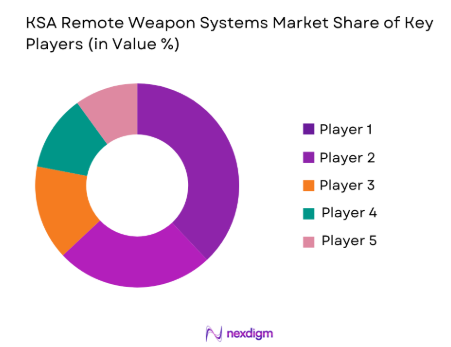
Based on a recent historical assessment, Riyadh dominates the KSA Remote Weapon Systems market due to its role as the central defense procurement, planning, and contract administration hub, hosting major military commands and domestic defense manufacturers. Jeddah contributes significantly through naval security and coastal defense deployments, while the Eastern Province supports demand linked to critical energy infrastructure protection. National dominance is reinforced by Saudi Arabia’s strategic emphasis on border security, domestic defense industrialization, and long-term capability development programs aligned with sovereign security objectives and localized manufacturing frameworks.

Market Segmentation
By Product Type
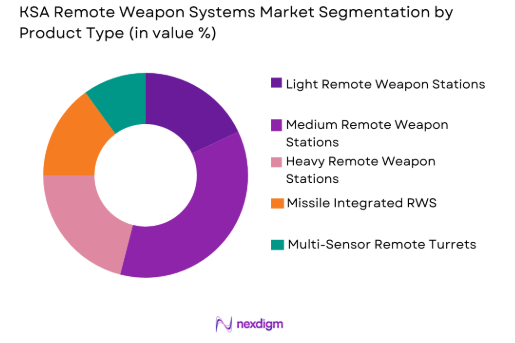
KSA Remote Weapon Systems market is segmented by product type into light remote weapon stations, medium remote weapon stations, heavy remote weapon stations, missile integrated remote weapon stations, and multi-sensor remote turrets. Recently, medium remote weapon stations have emerged as the dominant sub-segment due to their optimal balance between firepower, mobility, and system integration flexibility. These systems are widely adopted across armored personnel carriers, tactical vehicles, and border patrol platforms because they support commonly deployed calibers while maintaining manageable weight, recoil, and power requirements. Their compatibility with advanced electro-optical sensors, thermal imaging, laser rangefinders, and fire-control systems enhances engagement accuracy in desert and urban operational environments. Procurement preference is further supported by mature supplier ecosystems, lower lifecycle costs compared to heavy-caliber systems, ease of retrofit on existing fleets, and proven operational reliability across diverse mission profiles deployed within the kingdom.
By Platform Type
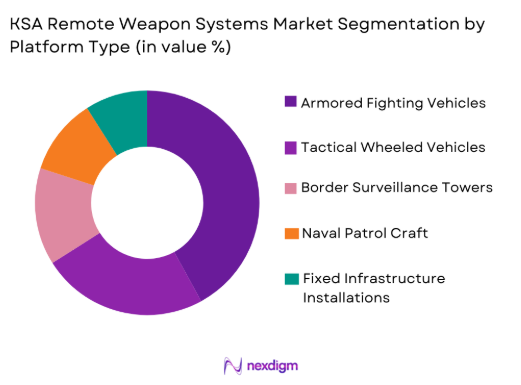
KSA Remote Weapon Systems market is segmented by platform type into armored fighting vehicles, tactical wheeled vehicles, border surveillance towers, naval patrol craft, and fixed critical infrastructure installations. Recently, armored fighting vehicles have captured the dominant position due to sustained fleet modernization programs and consistent investment in land force survivability enhancement. Remote weapon systems mounted on armored platforms provide superior crew protection, stabilized firing capability during movement, and multi-threat engagement capacity aligned with modern combat doctrines. Dominance of this sub-segment is reinforced by ongoing upgrade cycles, compatibility with legacy armored fleets, centralized procurement structures, and continuous demand driven by operational readiness requirements across land forces responsible for territorial defense and internal security missions.
Competitive Landscape
The KSA Remote Weapon Systems market demonstrates moderate consolidation, with a limited number of global defense manufacturers and domestic entities holding long-term procurement and integration contracts. Competitive positioning is influenced by localization capability, technology transfer commitments, and system integration depth rather than unit pricing alone. Domestic firms increasingly partner with international OEMs to align with national industrial participation policies, while major global suppliers retain influence through advanced sensor technology, combat-proven systems, and sustainment expertise.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Localization Capability |
| Saudi Arabian Military Industries | 2017 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Advanced Electronics Company | 1988 | Saudi Arabia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace | 1814 | Norway | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rheinmetall | 1889 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
KSA Remote Weapon Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Border and Land Security Modernization Programs
Border and land security modernization programs remain the most influential growth driver for the KSA Remote Weapon Systems market, as Saudi Arabia continues to prioritize territorial integrity, internal stability, and rapid-response capability across expansive land borders and sensitive regions. Remote weapon systems enable persistent surveillance and precision engagement without exposing personnel to direct threats, aligning strongly with national force protection doctrines. These systems are increasingly integrated with command-and-control architectures, unmanned surveillance assets, and ground sensor networks, enhancing coordinated response capabilities. Centralized procurement mechanisms and long-term modernization roadmaps ensure continuity of demand and reduce procurement volatility. The harsh desert environment further drives adoption of stabilized, remotely operated systems capable of reliable performance under extreme temperatures and dust conditions. As border security missions evolve toward technology-driven deterrence and early threat neutralization, remote weapon systems continue to be viewed as essential force multipliers across land-based formations.
Domestic Defense Industrialization and Localization Mandates
Domestic defense industrialization and localization mandates significantly accelerate market expansion by reshaping procurement criteria toward systems that support in-kingdom value creation. Saudi Arabia’s industrial participation policies encourage technology transfer, licensed production, local assembly, and domestic sustainment of remote weapon systems. Suppliers offering modular architectures that allow localized integration of mounts, sensors, wiring, and software gain a competitive advantage. Localization reduces long-term lifecycle costs, improves system availability, and minimizes dependence on external supply chains during geopolitical disruptions. Workforce development initiatives linked to defense manufacturing further strengthen domestic capability, enabling faster maintenance and upgrade cycles. As localization requirements continue to tighten across defense programs, remote weapon systems designed for scalable domestic involvement are expected to experience sustained procurement preference.
Market Challenges
Export Control and Technology Access Constraints
Export control regulations and restricted technology access remain persistent challenges for the KSA Remote Weapon Systems market, particularly for advanced electro-optical sensors, fire-control software, encrypted communications, and autonomous functions. Compliance with multiple international regulatory frameworks increases administrative complexity and lengthens procurement timelines. Delays in licensing approvals can disrupt delivery schedules and complicate program planning. Restrictions on source code access and software modification limit customization flexibility and slow system upgrades. These constraints also elevate sustainment risk, as access to spare parts and software patches may be subject to external approvals. As the market increasingly shifts toward digitally enabled and networked weapon systems, navigating export control limitations will remain a critical operational and commercial challenge for both suppliers and end users.
Integration Complexity with Legacy Platforms
Integration of modern remote weapon systems with legacy vehicle fleets presents ongoing technical and operational challenges. Many existing platforms require structural reinforcement, power system upgrades, and interface adaptation to support advanced remote turrets. Variations in vehicle architecture increase engineering complexity and integration cost. Software compatibility issues arise when legacy command systems must interface with modern digital fire-control units. Training requirements expand as operators transition from manual or semi-remote systems to fully stabilized and sensor-integrated platforms. Certification, testing, and validation processes further extend deployment timelines. These challenges collectively slow large-scale rollouts and necessitate phased integration strategies rather than rapid fleet-wide adoption.
Opportunities
Expansion of Fixed Site and Critical Infrastructure Protection
Growing emphasis on protecting energy assets, ports, transportation hubs, and government facilities creates a significant opportunity for remote weapon systems deployed in fixed-site configurations. These systems provide continuous, automated perimeter defense while reducing manpower requirements. Integration with surveillance cameras, radar, and access control systems enhances early threat detection and response coordination. Fixed installations offer longer system lifecycles and predictable maintenance profiles, making them attractive for long-term security planning. As national infrastructure protection strategies evolve toward layered and technology-centric defense, demand for remote weapon systems in static applications is expected to expand steadily.
Advanced Sensor and AI-Enabled System Upgrades
The increasing adoption of artificial intelligence, sensor fusion, and automation presents strong growth opportunities for suppliers offering upgradeable remote weapon systems. AI-enabled target detection and tracking reduce operator workload and improve engagement speed. Advanced electro-optical and thermal sensors enhance performance in low-visibility and adverse weather conditions. Modular upgrade pathways allow existing systems to be modernized without full replacement, extending asset lifespan. Alignment with network-centric warfare concepts further increases relevance of digitally integrated weapon stations. Suppliers capable of delivering scalable, future-ready upgrade solutions are well positioned to capture incremental demand from both new procurement and retrofit programs.
Future Outlook
The KSA Remote Weapon Systems market is expected to witness sustained and structured growth over the next five years, underpinned by long-term defense modernization programs and continued prioritization of force protection across land, border, and critical infrastructure domains. Procurement activity is likely to remain stable due to centralized defense planning, multi-year budget allocations, and alignment with national security objectives. Technological evolution will play a defining role, with increasing emphasis on advanced electro-optical sensors, AI-enabled target recognition, and improved system stabilization for enhanced operational accuracy. Regulatory support for domestic manufacturing, localization, and technology transfer will further strengthen supplier participation and reduce lifecycle dependency risks. Demand-side momentum will be reinforced by expanding border surveillance requirements, infrastructure protection mandates, and the gradual upgrade of legacy platforms, collectively positioning the market for resilient medium-term expansion.
Major Players
- Saudi Arabian Military Industries
- Advanced Electronics Company
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- Elbit Systems
- Rheinmetall
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- ASELSAN
- Leonardo
- Thales
- Saab
- BAE Systems
- FN Herstal
- RTX
- Hanwha Defense
- L3Harris Technologies
Key Target Audience
- Defense procurement authorities
- Armed forces modernization units
- Border security agencies
- Internal security forces
- Critical infrastructure operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Defense system integrators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables were identified through analysis of defense procurement programs, operational doctrines, and system specifications. Secondary data sources were reviewed to establish baseline assumptions. Variables were filtered for relevance. Final selection reflected demand, supply, and regulatory dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market construction involved consolidating procurement data, budget disclosures, and company financials. Data normalization ensured comparability. Segment-level assessment was conducted. Cross-validation improved reliability.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through consultation with defense experts and system integrators. Assumptions were stress-tested against operational realities. Feedback refined segmentation logic. Validation enhanced analytical robustness.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated insights were synthesized into a structured narrative. Quantitative and qualitative elements were aligned. Internal consistency checks were applied. Final output reflects verified market conditions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Border security modernization and persistent surveillance needs
Vehicle survivability upgrades prioritizing standoff engagement
Rising demand for stabilized day-night EO/IR sensor integration
Local content policies accelerating domestic assembly and MRO
Multi-domain base protection requirements across critical sites - Market Challenges
Export controls and licensing constraints for key subsystems
Complex integration with legacy vehicles and mixed fleets
Sustainment burden for sensors, actuators, and spares readiness
Cybersecurity and comms hardening for networked weapon stations
Training load for operators and maintainers across dispersed units - Market Opportunities
Localization of RWS assembly, wiring harnesses, and submodule MRO
Integration packages for border towers, critical infrastructure, and ports
Sensor and fire-control upgrades enabling higher accuracy and autonomy - Trends
Shift toward multi-sensor payloads combining EO, IR, and laser range finding
Adoption of AI-assisted detection, tracking, and cueing workflows
Greater emphasis on modular architectures and open integration standards
Demand for remote operation from protected cabins and command posts
Increased retrofit programs tied to fleet modernization cycles
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Light Remote Weapon Stations
Medium Remote Weapon Stations
Heavy Remote Weapon Stations
Anti-Tank Guided Missile Integrated RWS
Dual-Weapon and Multi-Sensor RWS Modules - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Armored Fighting Vehicles and APCs
Tactical and Utility Ground Vehicles
Border Surveillance and Fixed Site Installations
Naval Patrol Craft and Fast Interceptors
Static Perimeter Towers and Observation Posts
- By Fitment Type (In Value%)
New-build vehicle integration (OEM fit)
Retrofit and mid-life upgrade integration
Containerized and deployable mount integration
Mast and tower mounted fixed integration
Remote turret replacement integration
- By End User Segment (In Value%)
Royal Saudi Land Forces
Royal Saudi Naval Forces
Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces
Saudi Border Guard and Land Border Security
Ministry of Interior Special Security Forces - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct government-to-government procurement
Prime contractor led system integration contracts
Domestic defense manufacturer procurement
Framework agreements and long-term IDIQ contracts
Operational urgent requirements and rapid acquisition - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Electro-optical and infrared stabilized sighting suites
Fire-control computers and ballistic algorithms
Recoil mitigation mounts and vibration isolation systems
Encrypted remote operator consoles and HMI software
AI-enabled target detection and tracking modules
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Stabilization accuracy, EO/IR sensor performance, Weapon caliber compatibility, Integration lead time, Power and data interface standards, Remote console ergonomics, Cybersecurity compliance, Local content and offset readiness, Lifecycle sustainment capability)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Key Players
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
Advanced Electronics Company
Middle East Propulsion Company
Tawazun Industrial Park
Rheinmetall Air Defence
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
Elbit Systems
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
ASELSAN
FN Herstal
Leonardo
Saab
BAE Systems
Thales
RTX
- Border security units prioritizing fixed-site and mobile overwatch configurations
- Land forces focusing on armored vehicle retrofits and survivability upgrades
- Naval users adopting stabilized mounts for small craft and littoral patrol roles
- Interior security forces seeking rapid-deployable systems for facility protection
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035